Galidesivir
Galidesivir (BCX4430, Immucillin-A) is an antiviral drug, an adenosine analog[1] (a type of nucleoside analog).[2] It is developed by BioCryst Pharmaceuticals with funding from NIAID, originally intended as a treatment for hepatitis C, but subsequently developed as a potential treatment for deadly filovirus infections such as Ebola virus disease and Marburg virus disease.
 | |
| Legal status | |
|---|---|
| Legal status | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
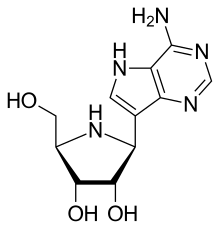
| Formula | C11H15N5O3 |
| Molar mass | 265.268 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
It also shows broad-spectrum antiviral effectiveness against a range of other RNA virus families, including bunyaviruses, arenaviruses, paramyxoviruses, coronaviruses, flaviviruses and phleboviruses.[3] BCX4430 has been demonstrated to protect against both Ebola and Marburg viruses in both rodents and monkeys, even when administered up to 48 hours after infection,[1] and development for use in humans was then being fast-tracked due to concerns about the lack of treatment options for the 2013-2016 Ebola virus epidemic in West Africa.[4]
BCX4430 later showed efficacy against Zika virus in a mouse model.[5]
Galidesivir is one of several antiviral drugs being tested for coronavirus disease 2019.[6]
On April 9th, BioCryst opened enrollment into a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial to assess the safety, clinical impact and antiviral effects of galidesivir in patients with COVID-19. The trial (NCT03891420) is being funded by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03891420
See also
References
- Warren TK, Wells J, Panchal RG, Stuthman KS, Garza NL, Van Tongeren SA, et al. (April 2014). "Protection against filovirus diseases by a novel broad-spectrum nucleoside analogue BCX4430" (PDF). Nature. 508 (7496): 402–5. Bibcode:2014Natur.508..402W. doi:10.1038/nature13027. PMID 24590073.
- Kamat SS, Burgos ES, Raushel FM (October 2013). "Potent inhibition of the C-P lyase nucleosidase PhnI by Immucillin-A triphosphate". Biochemistry. 52 (42): 7366–8. doi:10.1021/bi4013287. PMC 3838859. PMID 24111876.
- Westover JB, et al. Galidesivir limits Rift Valley fever virus infection and disease in Syrian golden hamsters. Antiviral Res. 2018 Aug;156:38-45. Westover, J. B.; Mathis, A.; Taylor, R.; Wandersee, L.; Bailey, K. W.; Sefing, E. J.; Hickerson, B. T.; Jung, K. H.; Sheridan, W. P.; Gowen, B. B. (2018). "Galidesivir limits Rift Valley fever virus infection and disease in Syrian golden hamsters". Antiviral Research. 156: 38–45. doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2018.05.013. PMC 6035881. PMID 29864447.
- Rodgers P (8 April 2014). "BioWar Lab Helping To Develop Treatment For Ebola". Forbes Magazine.
- Julander JG, Siddharthan V, Evans J, Taylor R, Tolbert K, Apuli C, et al. (January 2017). "Efficacy of the broad-spectrum antiviral compound BCX4430 against Zika virus in cell culture and in a mouse model". Antiviral Research. 137: 14–22. doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2016.11.003. PMC 5215849. PMID 27838352.
- Praveen Duddu. Coronavirus outbreak: Vaccines/drugs in the pipeline for Covid-19. clinicaltrialsarena.com 19 February 2020.