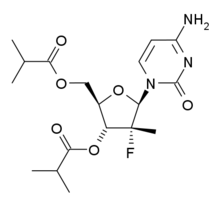
Mericitabine
Mericitabine (RG-7128) is an antiviral drug, a deoxycytidine analog (a type of nucleoside analog). It was developed as a treatment for hepatitis C, acting as a NS5B RNA polymerase inhibitor, but while it showed a good safety profile in clinical trials, it was not sufficiently effective to be used as a stand-alone agent. However mericitabine has been shown to boost the efficacy of other antiviral drugs when used alongside them, and as most modern treatment regimens for hepatitis C use a combination therapy of several antiviral drugs, clinical trials have continued to see if it can form a part of a clinically useful drug treatment program.[1][2]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Mericitabine |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C18H26FN3O6 |
| Molar mass | 399.419 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
See also
References
- Gentile I, Coppola N, Buonomo AR, Zappulo E, Borgia G (September 2014). "Investigational nucleoside and nucleotide polymerase inhibitors and their use in treating hepatitis C virus". Expert Opinion on Investigational Drugs. 23 (9): 1211–23. doi:10.1517/13543784.2014.921680. PMID 24848437.
- Wedemeyer H, Forns X, Hézode C, Lee SS, Scalori A, Voulgari A, et al. (2016). "Mericitabine and Either Boceprevir or Telaprevir in Combination with Peginterferon Alfa-2a plus Ribavirin for Patients with Chronic Hepatitis C Genotype 1 Infection and Prior Null Response: The Randomized DYNAMO 1 and DYNAMO 2 Studies". PLOS ONE. 11 (1): e0145409. Bibcode:2016PLoSO..1145409W. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0145409. PMC 4713467. PMID 26752189.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.