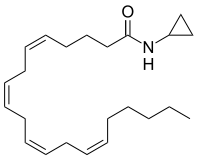
Arachidonylcyclopropylamide
Arachidonylcyclopropylamide (ACPA) is a synthetic agonist of the cannabinoid receptor 1 (CB1R). ACPA is considered to be a selective cannabinoid agonist as it binds primarily to the CB1R and has low affinity to the cannabinoid receptor 2 (CB2R) (Ki = 2.2 nM for CB1R; Ki = 700 nM for CB2R).[1]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
N-(Cyclopropyl)-5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z-eicosatetraenamide | |
| Other names
ACPA | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C23H37NO | |
| Molar mass | 343.555 g·mol−1 |
| Solubility in other solvents | soluble in ethanol, chloroform, THF and DMSO |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
References
- Hillard, CJ; et al. (1999). "Synthesis and characterization of potent and selective agonists of the neuronal cannabinoid receptor (CB1)". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 289 (3): 1427–33. PMID 10336536.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.