ADAM (protein)
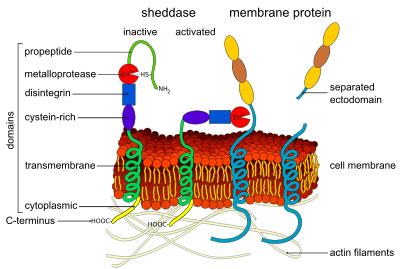
ADAMs (short for a disintegrin and metalloproteinase) are a family of single-pass transmembrane and secreted metalloendopeptidases.[1][2] All ADAMs are characterized by a particular domain organization featuring a pro-domain, a metalloprotease, a disintegrin, a cysteine-rich, an epidermal-growth factor like and a transmembrane domain, as well as a C-terminal cytoplasmic tail.[3] Nonetheless, not all human ADAMs have a functional protease domain, which indicates that their biological function mainly depends on protein–protein interactions.[4] Those ADAMs which are active proteases are classified as sheddases because they cut off or shed extracellular portions of transmembrane proteins.[4] For example, ADAM10 can cut off part of the HER2 receptor, thereby activating it.[5] ADAM genes are found in animals, choanoflagellates, fungi and some groups of green algae. Most green algae and all land plants likely lost ADAM proteins.[6]
| Disintegrin and metalloproteinase domain-containing proteins | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | ADAM | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF08516 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR027053 | ||||||||
| Membranome | 538 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
ADAMs are categorized under the EC 3.4.24.46 enzyme group, and in the MEROPS peptidase family M12B.[3] The terms adamalysin and MDC family (metalloproteinase-like, disintegrin-like, cysteine rich) have been used to refer to this family historically.[7]
ADAM family members
| Protein | Description |
|---|---|
| ADAM1 | ADAM1 (fertilin α) is a subunit of an integral sperm membrane heterodimeric glycoprotein called fertilin, which plays an important role in sperm-egg interactions. |
| ADAM2 | ADAM2 (fertilin β) is a subunit of an integral sperm membrane heterodimeric glycoprotein called fertilin, which plays an important role in sperm-egg interactions.[8] |
| ADAM7 | ADAM7 is a transmembrane protein important for the maturation of sperm cells in mammals. ADAM7 is also denoted as: ADAM_7, ADAM-7, EAPI, GP-83, and GP83.[9] |
| ADAM8 | The ADAM8 protein encoded by this gene may be involved in cell adhesion during neurodegeneration.[10] |
| ADAM9 | The ADAM9 protein encoded by this gene interacts with SH3 domain-containing proteins, binds mitotic arrest deficient 2 beta protein, and is also involved in TPA-induced ectodomain shedding of membrane-anchored heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor.[11] |
| ADAM10 | ADAM10 (EC#: 3.4.24.81) is a sheddase, and has a broad specificity for peptide hydrolysis reactions.[12] |
| ADAM11 | The ADAM11 gene represents a candidate tumor suppressor gene for human breast cancer based on its location within a minimal region of chromosome 17q21 previously defined by tumor deletion mapping.[13] |
| ADAM12 | ADAM12, a metalloprotease that binds insulin growth factor binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3), appears to be an effective early Down syndrome marker.[14] |
| ADAM15 | Through its disintegrin-like domain, this protein specifically interacts with the integrin beta chain, beta 3. It also interacts with Src family protein–tyrosine kinases in a phosphorylation-dependent manner, suggesting that this protein may function in cell-cell adhesion as well as in cellular signaling.[15] |
| ADAM17 | ADAM17 is understood to be involved in the processing of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) at the surface of the cell, and from within the intracellular membranes of the trans-Golgi network. ADAM17 also has a role in the shedding of L-selectin, a cellular adhesion molecule.[16] |
| ADAM18 | The protein encoded by this gene is a sperm surface protein.[17] Synonymous with ADAM27. |
| ADAM19 | This member is a type I transmembrane protein and serves as a marker for dendritic cell differentiation. It has also been demonstrated to be an active metalloproteinase, which may be involved in normal physiological and pathological processes such as cells migration, cell adhesion, cell-cell and cell-matrix interactions, and signal transduction.[18] |
| ADAM20 | Exclusively expressed in the testes. |
| ADAM21 | Note: Synonymous with ADAM31. |
| ADAM22 | This gene is highly expressed in the brain and may function as an integrin ligand in the brain.[19] |
| ADAM23 | This gene is highly expressed in the brain and may function as an integrin ligand in the brain.[20] |
| ADAM28 | The protein encoded by this gene is a lymphocyte-expressed ADAM protein.[21] |
| ADAM29 | |
| ADAM30 | |
| ADAM33 | This protein is a type I transmembrane protein implicated in asthma and bronchial hyperresponsiveness.[22] |
Medicine
Therapeutic ADAM inhibitors might potentiate anti-cancer therapy.[23]
See also
- ADAMTS (A disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs) family
- Ectodomain shedding
References
- Brocker, C; Vasiliou, V; Nebert, DW (October 2009). "Evolutionary divergence and functions of the ADAM and ADAMTS gene families". Human Genomics. 4 (1): 43–55. doi:10.1186/1479-7364-4-1-43. PMC 3500187. PMID 19951893.
- Wolfsberg TG, Straight PD, Gerena RL, et al. (1995). "ADAM, a widely distributed and developmentally regulated gene family encoding membrane proteins with a disintegrin and metalloprotease domain". Dev. Biol. 169 (1): 378–383. doi:10.1006/dbio.1995.1152. PMID 7750654.
- "ADAM, cysteine-rich (IPR006586)". InterPro. Retrieved 18 February 2016.
- Edwards DR, Handsley MM, Pennington CJ (October 2008). "The ADAM metalloproteinases". Mol. Aspects Med. 29 (5): 258–89. doi:10.1016/j.mam.2008.08.001. PMC 7112278. PMID 18762209.
- Liu, P.C.; et al. (2006). "Identification of ADAM10 as a major source of HER2 ectodomain sheddase activity in HER2 overexpressing breast cancer cells". Cancer Biology and Therapy. 5 (6): 657–664. doi:10.4161/cbt.5.6.2708. PMID 16627989.
- Souza J, Lisboa A, Santos T, Andrade M, Neves V, Teles-Souza J, Jesus H, Bezerra T, Falcão V, Oliveira R, Del-Bem L (2020). "The evolution of ADAM gene family in eukaryotes". Genomics. doi:10.1016/j.ygeno.2020.05.010.
- Blobel, CP (22 August 1997). "Metalloprotease-disintegrins: links to cell adhesion and cleavage of TNF alpha and Notch". Cell. 90 (4): 589–92. doi:10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80519-x. PMID 9288739.
- "Entrez Gene: ADAM2 ADAM metallopeptidase domain 2 (fertilin beta)".
- "Entrez Gene: ADAM metallopeptidase domain 7".
- "Entrez Gene: ADAM8 ADAM metallopeptidase domain 8".
- "Entrez Gene: ADAM9 ADAM metallopeptidase domain 9 (meltrin gamma)".
- "Entry of ADAM10 endopeptidase (EC-Number 3.4.24.81 )".
- "Entrez Gene: ADAM11 ADAM metallopeptidase domain 11".
- Danforth's Obstetrics and Gynecology, 10th Edition; Copyright 2008 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; Chapter 7: Prenatal Diagnosis, Page 113
- "Entrez Gene: ADAM15 ADAM metallopeptidase domain 15 (metargidin)".
- Li Y, Brazzell J, Herrera A, Walcheck B (October 2006). "ADAM17 deficiency by mature neutrophils has differential effects on L-selectin shedding". Blood. 108 (7): 2275–9. doi:10.1182/blood-2006-02-005827. PMC 1895557. PMID 16735599.
- "Entrez Gene: ADAM18 ADAM metallopeptidase domain 18".
- "Entrez Gene: ADAM19 ADAM metallopeptidase domain 19 (meltrin beta)".
- "Entrez Gene: ADAM22 ADAM metallopeptidase domain 22".
- "Entrez Gene: ADAM23 ADAM metallopeptidase domain 23".
- "Entrez Gene: ADAM28 ADAM metallopeptidase domain 28".
- "Entrez Gene: ADAM33 ADAM metallopeptidase domain 33".
- Guo, Zhen; Jin, Xunbo; Jia, Haiyan (2013). "Inhibition of ADAM-17 more effectively down-regulates the Notch pathway than that of γ-secretase in renal carcinoma". Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research. 32 (1): 26. doi:10.1186/1756-9966-32-26. PMC 3662624. PMID 23659326.
External links
- ADAM+Proteins at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- http://www.healthvalue.net/sheddase.html