1965 in spaceflight
 Launch of a Delta D rocket carrying the first commercial geosynchronous communications satellite, Intelsat I F1 | |
| Orbital launches | |
|---|---|
| First | 11 January |
| Last | 28 December |
| Total | 124 |
| Successes | 108 |
| Failures | 15 |
| Partial failures | 1 |
| Catalogued | 112 |
| National firsts | |
| Satellite | |
| Orbital launch | |
| Rockets | |
| Maiden flights | Atlas LV-3C Centaur-D Delta E Diamant-A Kosmos-2M Scout A Scout B Soyuz/Vostok 11A510 Thor LV-2D Burner-1 Thor LV-2D MG-18 Titan IIIC UR-500 (Proton) |
| Retirements | Atlas LV-3A Agena-B Atlas LV-3C Centaur-C Delta D Kosmos-1 Molniya 8K78 Molniya-L 8K78L Saturn I Scout X-4 Thor DSV-2A Ablestar Thor LV-2D MG-18 Thor SLV-2 Agena-B Titan IIIA |
| Crewed flights | |
| Orbital | 6 |
| Total travellers | 13 |
Deep Space Rendezvous
| Date (UTC) | Spacecraft | Event | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| 20 February | Ranger 8 | Lunar impact | Impacted Mare Tranquillitatis at 09:57:37, returned 7,137 images |
| 24 March | Ranger 9 | Lunar impact | Impacted Alphonsus Crater at 14:08:20, returned 5,814 images |
| 12 May | Luna 5 | Lunar impact | Failed lander, impacted at 19:10 |
| 11 June | Luna 6 | Lunar flyby | Failed lander, closest approach: 160,000 kilometres (99,000 mi) |
| 15 July | Mariner 4 | Flyby of Mars | Returned 21 images |
| 20 July | Zond 2 | Flyby of Mars | Communications system failed before flyby |
| 6 August | Zond 3 | Lunar Flyby | Returned 25 images |
| 7 October | Luna 7 | Lunar impact | Failed lander, impacted at 22:08 |
| 6 December | Luna 8 | Lunar impact | Failed lander, impacted at 21:51:30 |
EVAs
| Start date/time | Duration | End time | Spacecraft | Crew | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 18 March 08:34 |
12 minutes | 08:47 | Voskhod 2 | First EVA in history.[1] Leonov had difficulty fitting back into the spacecraft due to spacesuit stiffness in vacuum. He vented air from his spacesuit to bend back into the capsule.[2] | |
| 3 June 19:46 |
20 minutes | 20:06 | Gemini IV | First US EVA.[3] White also had difficulty returning to the Gemini spacecraft. Although very fit, the effort left White exhausted.[4] |
Orbital launch summary
By country
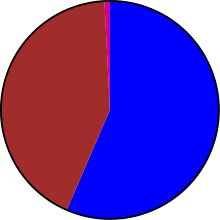 |
| |||||||
| Orbital launch attempts by country in 1965 | ||||||||
| Country | Launches | Successes | Failures | Partial failures |
Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | First orbital launch | |
| 53 | 46 | 7 | 0 | ||
| 70 | 61 | 8 | 1 |
By rocket
By orbit
| Orbital regime | Launches | Achieved | Not Achieved | Accidentally Achieved |
Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low Earth | 96 | 85 | 9 | 2 | |
| Medium Earth | 7 | 6 | 1 | 0 | |
| High Earth | 13 | 11 | 2 | 0 | Including Highly elliptical and Molniya orbits |
| Geosynchronous/transfer | 3 | 1 | 2 | 1* | * - One launch to geosynchronous orbit reached geosynchronous transfer orbit |
| Heliocentric | 5 | 4 | 1 | 0 |
gollark: Perhaps.
gollark: The lorem ipsum one is good.
gollark: `test` is only obtainable by cheating anyway.
gollark: Okay, list them, ideally with mildly witty but still somewhat dumb names.
gollark: If you have suggestions, please do tell me them.
References
Generic references:

- Bergin, Chris. "NASASpaceFlight.com".
- Clark, Stephen. "Spaceflight Now".
- Kelso, T.S. "Satellite Catalog (SATCAT)". CelesTrak.
- Krebs, Gunter. "Chronology of Space Launches".
- Kyle, Ed. "Space Launch Report".
- McDowell, Jonathan. "Jonathan's Space Report".
- Pietrobon, Steven. "Steven Pietrobon's Space Archive".
- Wade, Mark. "Encyclopedia Astronautica".
- Webb, Brian. "Southwest Space Archive".
- Zak, Anatoly. "Russian Space Web".
- "ISS Calendar". Spaceflight 101.
- "NSSDCA Master Catalog". NASA Space Science Data Coordinated Archive. NASA Goddard Space Flight Center.
- "Space Calendar". NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory.
- "Space Information Center". JAXA.
- "Хроника освоения космоса" [Chronicle of space exploration]. CosmoWorld (in Russian).
Footnotes
- Alexander Anikeev (2008). "Spacecraft "Voskhod-2" web page". Manned Astronautics: Figures and Facts website. Archived from the original on 11 February 2009. Retrieved 26 December 2008.
- Mark Wade (2008). "Leonov web page". Encyclopedia Astronautica web site. Archived from the original on 23 December 2008. Retrieved 26 December 2008.
- David R. Williams (2004). "The First U.S. Spacewalk - Gemini 4". Lunar and Planetary Science. NASA. Retrieved 28 December 2009.
- Cernan, Eugene; Don Davis (1999). The Last Man on the Moon. New York: St. Martin's Press. p. 83. ISBN 0-312-19906-6.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.