18th Arkansas Infantry Regiment (Carroll's)
The 18th Arkansas Infantry Regiment (also known as "Carroll's regiment") was an infantry formation in the Confederate States Army during the American Civil War. The regiment was raised in April 1862 under the command of Col. D Carroll. It served east of the Mississippi in several actions before being surrendered at Port Hudson in July 1863. Re-organized, the regiment was finally merged with several other Arkansas units to form the 2nd Arkansas Consolidated Infantry Regiment. This unit was known as 18th (Carroll's) Arkansas Infantry. There was another regiment designated as the 18th Arkansas. When Lieutenant-Colonel John Sappington Marmaduke's 1st Arkansas Infantry Battalion was increased to a regiment, it was briefly designated as the 18th (Marmaduke's) Arkansas Infantry Regiment. Marmaduke's regiment was subsequently redesignated as the 3rd Confederate Infantry Regiment.[2]
| 18th Arkansas Infantry Regiment Carroll's regiment | |
|---|---|
| Active | 1862–1865 |
| Disbanded | May 26, 1865 |
| Country | |
| Allegiance | Arkansas |
| Branch | |
| Type | Infantry |
| Size | Regiment |
| Nickname(s) | "Carroll's regiment" |
| Facings | Light blue |
| Engagements | American Civil War
|
Arkansas Confederate Infantry Regiments | |
|---|---|
| Previous | Next |
| 17th Arkansas Infantry Regiment (Lemoyne's) | 18th Arkansas Infantry Regiment (Marmaduke's) |
Organization
The 18th Arkansas Infantry was organized at DeValls Bluff, Arkansas, on April 2, 1862, composed of ten volunteer companies from central Arkansas:[3]
- Company A – "Jefferson Minute-Men" – This company was organized at Byrd Springs, Jefferson county, Arkansas, on February 25, 1862, with the election of James C. Thompson, captain; George D. Hardy, first lieutenant; John E. Price, second lieutenant; and Alphonzo C. Thompson, third lieutenant. Captain Thompson remained in command of the company until the surrender at Port Hudson. At least fifteen men of Company A died in the measles epidemic of the Spring of 1862. In June, 1862, three of its members were transferred to the newly organized 12th Arkansas Battalion (Sharpshooters). Company A suffered nine casualties at the Battle of Corinth, and surrendered with 23 men at Port Hudson, Louisiana. A total of 65 men are known to have served in Company A.[4]
- Company B – "Princeton Rifles" – This company began recruiting on March 1, 1862, and completed its organization at Princeton, Dallas county, Arkansas, on March 12, with the election of Israel N. McClendon, captain; Robert G. Pattillo, first lieutenant; Robert M. Thrasher, second lieutenant; and Stephen Winstead, Jr., third lieutenant. Lieutenants Pattillo and Thrasher each subsequently served as captain of this company. At least twenty men of Company B died in the measles epidemic of the Spring of 1862. In June, 1862, five of its members were transferred to the newly organized 12th Arkansas Battalion (Sharpshooters). Company B suffered fifteen casualties at the Battle of Corinth, and surrendered with 31 men at Port Hudson, Louisiana. A total of 85 men are known to have served in Company B.[5]
- Company C – "Prairie County Avengers" – This company was organized at Des Arc, Prairie county, Arkansas, on March 8, 1862, with the election of M. C. Peel, captain; W. T. Black, first lieutenant; T. R. Lawrence, second lieutenant; and Henry F. Dickson, third lieutenant. Captain Peel remained in command of the company until the surrender at Port Hudson. At least eighteen men of Company C died in the measles epidemic of the Spring of 1862. In June, 1862, three of its members were transferred to the newly organized 12th Arkansas Battalion (Sharpshooters). Company C suffered twelve casualties at the Battle of Corinth, and surrendered with 24 men at Port Hudson, Louisiana. A total of 74 men are known to have served in Company C. A number of the men of this company had been members of the Des Arc Vigilance Committee, organized in December 1859 in response to rumors of outsiders allegedly conspiring to instigate a slave uprising.[6]
- Company D – "Pine Bluff Rebels" – This company was organized at Pine Bluff, Jefferson county, Arkansas, on March 1, 1862, with the election of Read Fletcher, captain; John R. Holland, first lieutenant; William G. Butler, second lieutenant; and Joseph W. Wright, third lieutenant. Captain Fletcher remained in command of the company until the surrender at Port Hudson. At least seventeen men of Company D died in the measles epidemic of the Spring of 1862. In June, 1862, seven of its members were transferred to the newly organized 12th Arkansas Battalion (Sharpshooters). Company D suffered eight casualties at the Battle of Corinth, and surrendered with 24 men at Port Hudson, Louisiana. A total of 87 men are known to have served in Company D.[7]
- Company E – "Arkansas Rifles" – This company was organized at DeWitt, Arkansas county, Arkansas, on February 24, 1862, with the election of Felix R. Robertson, captain; Simon Rice, first lieutenant; James J. Gillcoat, second lieutenant; and Charles J. Miller, third lieutenant. Captain Robertson left the company because of illness, and was succeeded by Simon Rice (killed in action at Corinth), then Charles J. Miller, who remained in command of the company until the surrender at Port Hudson. At least sixteen men of Company E died in the measles epidemic of the Spring of 1862. In June, 1862, five of its members were transferred to the newly organized 12th Arkansas Battalion (Sharpshooters). Company E suffered nineteen casualties at the Battle of Corinth, and surrendered with 21 men at Port Hudson, Louisiana. A total of 87 men are known to have served in Company E.[8]
- Company F – "Auburn Grays" – This company was organized at Auburn, Arkansas county, Arkansas, on March 3, 1862, with the election of Joseph W. Barnett, captain; D. M. Alexander, first lieutenant; William A. Davidson, second lieutenant; and James A. Ashford, third lieutenant. Captain Barnett resigned in December, and was succeeded by John L. Brent, who remained in command of the company until the surrender at Port Hudson. At least twelve men of Company F died in the measles epidemic of the Spring of 1862. In June, 1862, five of its members were transferred to the newly organized 12th Arkansas Battalion (Sharpshooters). Company F suffered twelve casualties at the Battle of Corinth, and surrendered with 22 men at Port Hudson, Louisiana. A total of 75 men are known to have served in Company F.[9]
- Company G – "Cotton Plant Guards" – This company was organized at Cotton Plant, St Francis (now Woodruff) county, Arkansas, in February, 1862, with the election of Charles F. Lynch, captain; John A. Baker, first lieutenant; James W. Moore, second lieutenant; and Watson, J. Turner, third lieutenant. The company marched to Little Rock, where they were enlisted in Confederate service on March 2, 1862. Captain Lynch was killed in action at Corinth, and was succeeded by Lieutenant Moore, who remained in command of the company until the surrender at Port Hudson. At least twenty men of Company G died in the measles epidemic of the Spring of 1862. In June, 1862, six of its members were transferred to the newly organized 12th Arkansas Battalion (Sharpshooters). Company G suffered 23 casualties at the Battle of Corinth, and surrendered with 44 men at Port Hudson, Louisiana. A total of 126 men are known to have served in Company G, seventeen of whom had previously served in John A. Baker's Company, 30-Day Volunteers, in November to December, 1861.[10]
- Company H – "North Fork Rangers" – This company was organized in Saline county, Arkansas, in February, 1862, with the election of William Nelson Parish, captain; John B. Walker, first lieutenant; George W. Isaacs, second lieutenant; and John W. Jay, third lieutenant. The company was enrolled in Confederate service at Little Rock, Arkansas, on March 3, 1862. Captain Parish was appointed lieutenant-colonel on January 4, 1863, and Lieutenant Walker was promoted to captain, and remained in command of the company until the surrender at Port Hudson. At least twenty men of Company H died in the measles epidemic of the Spring of 1862. In June, 1862, five of its members were transferred to the newly organized 12th Arkansas Battalion (Sharpshooters). Company H suffered sixteen casualties at the Battle of Corinth, and surrendered with 27 men at Port Hudson, Louisiana. A total of 100 men are known to have served in Company H.[11]
- Company I – "Ouachita Rifles" – This company was organized at Camden, Ouachita county, Arkansas, on March 15, 1862, with the election of Samuel H. Southerland, captain; Lee Morgan, first lieutenant; Rowland B. Smith, second lieutenant; and James E. Webb, third lieutenant. Captain Southerland was promoted to major on January 4, 1863, and was succeeded as captain by Lieutenant Webb, who remained in command of the company until the surrender at Port Hudson. At least fourteen men of Company I died in the measles epidemic of the Spring of 1862. In June, 1862, four of its members were transferred to the newly organized 12th Arkansas Battalion (Sharpshooters). Company I suffered ten casualties at the Battle of Corinth, and surrendered with 44 men at Port Hudson, Louisiana. A total of 80 men are known to have served in Company I.[12]
- Company K – "Jefferson Rifles" – This company was organized at Pine Bluff, Jefferson county, Arkansas, on February 22, 1862, with the election of David W. Carroll, captain; William F. Owen, first lieutenant; [unknown], second lieutenant; and Benjamin F. Hancock, third lieutenant. Captain Carroll was appointed colonel at the organization of the regiment on April 2, 1862. Lieutenant Owen was promoted to captain and remained in command of the company until the surrender at Port Hudson. At least thirteen men of Company K died in the measles epidemic of the Spring of 1862. In June, 1862, seven of its members were transferred to the newly organized 12th Arkansas Battalion (Sharpshooters). Company K suffered 24 casualties at the Battle of Corinth, and surrendered with 44 men at Port Hudson, Louisiana. A total of 119 men are known to have served in Company K.[13]
David W. Carroll, captain of Company A, was appointed colonel; John N. Daly, a private in Company I, was appointed lieutenant-colonel; and Robert Hamilton Crockett, a private in Company E, was appointed major.[14][15]
Service
Fort Pillow
Soon after being organized, the regiment was ordered to Mississippi, along with the rest of General Earl Van Dorn's Army of the West.[16] The unit boarded a steamer at Des Arc and moved down White River, out at its mouth, then up the Mississippi River and landed at Memphis, Tennessee. The Confederate commander at Memphis reported on April 7 that Colonel Carroll's command with 817 soldiers was present and armed with endfield rifles.[17] The unit was assigned to the Brigade of Brigadier General Albert Rust. The regiment was immediately ordered with the remainder of Rust's Brigade to Fort Pillow, approximately 50 miles (80 km) north of Memphis. The unit moved via steamer to Fort Pillow. At Fort Pillow the regiment saw their first enemy fire, during the bombardment of Fort Pillow by Union gunboats.[18]
The new regiment got off to an inauspicious, indeed, a tragic start. Measles broke out among the men almost immediately, and by the time the regiment arrived at its assigned station at Fort Pillow, near Fulton, Tennessee, it had become a full-fledged epidemic. It is possible to track the movements of the regiment in April 1862 by following the bodies. The unfortunate soldiers of the 18th Arkansas were dying in great numbers, and every camp between DeValls Bluff and Fort Pillow contained the graves of those who had died during the night. At Fort Pillow, the regiment was literally decimated by the epidemic. The extremely muddy conditions and very poor quality of the water supply at Fort Pillow undoubtedly contributed to these losses.[18] By the time the epidemic had run its course, over a fourth of the men were dead, discharged or simply stricken from the rolls. The unit remained at Fort Pillow for about two weeks.[17] The unit left Fort Pillow on April 26, moved back to Memphis and then on to Corinth, Mississippi.[17]
In early May 1862 the Confederate Army underwent an army-wide reorganization due to the passage of the Conscription Act by the Confederate Congress in April 1862.[19] All twelve-month regiments had to re-muster and enlist for two additional years or the duration of the war; a new election of officers was ordered; and men who were exempted from service by age or other reasons under the Conscription Act were allowed to take a discharge and go home. Officers who did not choose to stand for re-election were also offered a discharge. The reorganization was accomplished among all the Arkansas regiments in and around Corinth, Mississippi, following the Battle of Shiloh. Colonel Carroll was forced to resign due to illness, and was succeeded by Lieutenant-Colonel Daly.[3]
Iuka-Corinth Campaign
During the Iuka-Corinth Campaign, the 18th Arkansas was assigned along with the 19th, 20th and 21st Arkansas Infantry Regiment (Craven's), and the 8th Arkansas Infantry Battalion to Brigadier General William L. Cabell's brigade of Brigadier General Dabney H. Maury's Division of Major General Sterling Price's Corps the Confederate (Army of the West).[20]
The 18th Arkansas fought at the Battle of Iuka, Mississippi, September 16, 1862, and then ensured its place in history at the Second Battle of Corinth, Mississippi, October 4, 1862. From all contemporary accounts, the 18th Arkansas performed with magnificent courage at Corinth. Mustering a little over 300 men on the morning of the battle, only 43 answered the roll at the end of the day. Forming in a line of battle, the 18th Arkansas made a breath-taking charge under an enfilading fire from the entrenched Federal troops. Climbing through and over fallen timber, the 18th Arkansas relentlessly advanced right up to the enemy's breastworks, where the withering fire melted the regiment away. Colonel Daly, leading the charge, sword in hand, was mortally wounded. Captain Parish, of Company H, immediately assumed command and rallied the regiment to continue the charge. Although he, too, was shot down, he survived the battle and received a meritorious promotion to lieutenant-colonel for his gallant conduct.[3]
Port Hudson
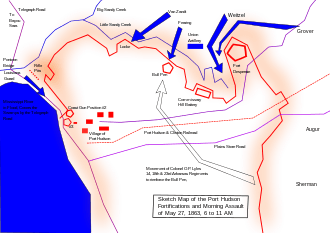
Colonel Daly died of his wounds on October 5, 1862, and was succeeded by Col. Robert Hamilton Crockett, of Arkansas County. Following the battle of Corinth, the 18th Arkansas and its sister regiments of the 2nd Brigade were ordered to Port Hudson, Louisiana. Sorely depleted after the events of April to October 1862, the 18th Arkansas underwent several field consolidations with other units while assigned to the Department of Mississippi and East Louisiana. Field consolidations were considered to be temporary, and the component regiments continued to maintain separate muster rolls. On January 7, 1863 Major General Franklin Gardner issued General Order No. 5 which consolidated several under strength Arkansas units:[21]
The troops of this post will be organized into brigades, arranged at the breastworks as follows ...
- III. Brigadier-General Beall's brigade will consist of the consolidated regiment consisting of the Fourteenth, Sixteenth, Seventeenth, Eighteenth, Twenty-third Arkansas Regiments, and First Arkansas Battalion, commanded by Col. R. H. Crockett; the consolidated regiment consisting of the Eleventh and Fifteenth Arkansas Regiments, commanded by Col. John L. Logan[21]
The order was modified in February 1863 and the 18th Arkansas was placed in a consolidated regiment with the 14th and 23rd Arkansas Infantry Regiments.[22] Logan's consolidated regiment consisted of the 11th and the Griffith's 17th Arkansas. The Johnson's 15th Arkansas was assigned to Crockett's consolidated regiment instead of the 17th.[21]
The regiment endured forty-eight day siege, and was surrendered to General Nathaniel P. Banks on July 9, 1863. Following the surrender the officers were sent as prisoners to Johnson's Island Military Prison. Two audacious lieutenants of Company K, however, James W. Hellums and George P. Atkins, escaped from their captors by jumping from the Union transport into the muddy water of the Mississippi River between Napoleon and Helena, swam ashore, and eventually reached the Confederate lines.[3]
Camden Expedition, Red River Campaign
After the fall of Port Hudson, the enlisted personnel of the 18th Arkansas returned to Arkansas and served as mounted infantry as a part of Colonel Thomas Pleasant Dockery Brigade during the Camden Expedition in the Spring of 1864.[23] As part of Dockery's Brigade, remnants of the regiment saw action at the Battles of Prairie D'Ane,[24] Marks' Mills,[25] and Jenkins Ferry.[26][27]
Final year of the war
There are few records of the 18th Arkansas after the fall of Port Hudson. They spent the remainder of the war in the Trans-Mississippi Army. The remnants of the regiment reorganized in southwest Arkansas, but were eventually consolidated with the remnants of the 23rd Arkansas and other Port Hudson units to form the 2nd Arkansas Consolidated Infantry Regiment.[3][28] The consolidated regiment was assigned along with the 1st and 3rd Arkansas Consolidated Infantry Regiments to the 2nd (McNair's) Arkansas Brigade, 1st (Churchill's) Arkansas Division, 2nd Corps, Trans-Mississippi Department, from September 1864 to May 1865.[29][30][31]
On 22 January 1865, Major General Churchill was ordered to move his division to Minden, Louisiana, and occupy winter quarters.[32] Union commanders in the Department of the Gulf reported on March 20, 1865 that General McNair's brigade was located at Minden, Louisiana, with the rest of Churchill's Division.[33] In early April 1865, the division concentrated near Shreaveport Louisiana, and then moved to Marshall Texas by mid April 1865.[34]
Campaign Credit
The 18th Arkansas was involved in the following engagements:[3]
- Battle of Rowlett's Station, Kentucky, December 17, 1861
- Battle of Shiloh, Tennessee, April 6–7, 1862
- Iuka-Corinth Campaign, September – October, 1862
- Battle of Iuka, Mississippi, September 16, 1862
- Second Battle of Corinth, October 3–4, 1862
- Siege of Port Hudson, May 22–July 9, 1863
- Camden Expedition, March 23–May 2, 1864.[35]
- Battle of Mount Elba, March 30, 1863
- Battle of Prairie D'Ane, April 9–13, 1864[24]
- Battle of Marks' Mills, April 25, 1864[25]
- Battle of Jenkins Ferry, April 30, 1864[27]
Final Consolidation and Surrender
The 2nd Arkansas Consolidated Infantry was surrendered with the Department of the Trans-Mississippi, General Kirby Smith commanding, May 26, 1865.[29][30] When the Trans-Mississippi Department surrendered, all of the Arkansas infantry regiments were encamped in and around Marshall, Texas (war-ravaged Arkansas no longer able to subsist the army). The regiments were ordered to report to Shreveport, Louisiana, to be paroled. Virtually none of them did so. Some soldiers went to Shreveport on their own to be paroled, but the regiments simply disbanded without formally surrendering. For the most part, the men simply went home.[36]
See also
- List of Arkansas Civil War Confederate units
- Lists of American Civil War Regiments by State
- Confederate Units by State
- Arkansas in the American Civil War
- Arkansas Militia in the Civil War
References
- Boney, James L. "Battle at Mt. Elba", Cleveland County, Arkansas, ArGenWeb Project, Accessed 26 March 2012, http://www.argenweb.net/cleveland/battle-at-mt.-elba.htm
- Howerton, Bryan R. "Re: Understanding the 3rd Confederate", Arkansas in the Civil War Message Board, Posted 29 July 2009, Accessed 14 February 2012, http://history-sites.com/cgi-bin/bbs53x/arcwmb/webbbs_config.pl?noframes;read=20597
- Howerton, Bryan, "18th (Carroll's) Arkansas Infantry Regiment, CSA", Edward G. Gerdes Civil War Page, Accessed 30 January 2011, http://www.couchgenweb.com/civilwar/18thhis.html
- Howerton, Bryan, "18th (Carroll's) Arkansas Infantry Regiment, Company A", Edward G. Gerdes Civil War Page, Accessed 30 January 2011, http://www.couchgenweb.com/civilwar/18thcoa.html
- Howerton, Bryan, "18th (Carroll's) Arkansas Infantry Regiment, Company B", Edward G. Gerdes Civil War Page, Accessed 30 January 2011, http://www.couchgenweb.com/civilwar/18thcob.html
- Howerton, Bryan, "18th (Carroll's) Arkansas Infantry Regiment, Company C", Edward G. Gerdes Civil War Page, Accessed 30 January 2011, http://www.couchgenweb.com/civilwar/18thcoc.html
- Howerton, Bryan, "18th (Carroll's) Arkansas Infantry Regiment, Company D", Edward G. Gerdes Civil War Page, Accessed 30 January 2011, http://www.couchgenweb.com/civilwar/18thcod.html
- Howerton, Bryan, "18th (Carroll's) Arkansas Infantry Regiment, Company E", Edward G. Gerdes Civil War Page, Accessed 30 January 2011, http://www.couchgenweb.com/civilwar/18thcoe.html
- Howerton, Bryan, "18th (Carroll's) Arkansas Infantry Regiment, Company F", Edward G. Gerdes Civil War Page, Accessed 30 January 2011, http://www.couchgenweb.com/civilwar/18thcof.html
- Howerton, Bryan, "18th (Carroll's) Arkansas Infantry Regiment, Company G", Edward G. Gerdes Civil War Page, Accessed 30 January 2011, http://www.couchgenweb.com/civilwar/18thcog.html
- Howerton, Bryan, "18th (Carroll's) Arkansas Infantry Regiment, Company H", Edward G. Gerdes Civil War Page, Accessed 30 January 2011, http://www.couchgenweb.com/civilwar/18thcoh.html
- Howerton, Bryan, "18th (Carroll's) Arkansas Infantry Regiment, Company I", Edward G. Gerdes Civil War Page, Accessed 30 January 2011, http://www.couchgenweb.com/civilwar/18thcoi.html
- Howerton, Bryan, "18th (Carroll's) Arkansas Infantry Regiment, Company K", Edward G. Gerdes Civil War Page, Accessed 30 January 2011, http://www.couchgenweb.com/civilwar/18thcok.html
- Hempstead, Fay, "A Pictorial History of Arkansas" St. Louis and New York, N. D. Thompson publishing company, 1890, Call number: 9197481, Page 418, Accessed 24 August 2011, https://archive.org/stream/pictorialhistory00hemp#page/418/mode/2up
- Howerton, Bryan, "18th (Carroll's) Arkansas Infantry Regiment, Field and Staff Officers", Edward G. Gerdes Civil War Page, Accessed 30 January 2011, http://www.couchgenweb.com/civilwar/18thfas.html
- United States. War Dept. The War of the Rebellion: A Compilation of the Official Records of the Union And Confederate Armies. Series 1, Volume 10, In Two Parts. Part 2, Correspondence, etc., Book, 1884; digital images, (http://texashistory.unt.edu/ark:/67531/metapth154614/m1/462/?q=Arkansas Corinth Battery : accessed June 15, 2012), University of North Texas Libraries, The Portal to Texas History, http://texashistory.unt.edu; crediting UNT Libraries, Denton, Texas.
- Odom, Danny "Re: 17th Arkansas Regiment, No. 2", Arkansas in the Civil War Message Board, Posted 9 June 2012, Accessed 11 June 2012, http://history-sites.com/cgi-bin/bbs53x/arcwmb/webbbs_config.pl?noframes;read=26502
- Elihu C. Beckham, "A GOOD STORY, Where I was And What I saw During the Late War By Elihu C. Bechkam, Sergeant Co. "K", 21st Ark.", The Izard County Historian, October 1977, Volume 8, Number 4. Accessed 6 June 2012, http://www.couchgenweb.com/civilwar/goodstor.html
- UPTON, EMORY, Bvt. Maj. Gen., United States Army; "THE MILITARY POLICY OF THE UNITED STATES" WASHINGTON GOVERNMENT PRINTING OFFICE 1912, Page 471, Congressional edition, Volume 6164, Google Books, Accessed 4 November 2011, https://books.google.com/books?id=2-tGAQAAIAAJ&pg=PA471&lpg=PA471&dq=Confederate+conscription+law+reorganization+regiment&source=bl&ots=7ptDBF0n2D&sig=-K_6PQoHglmh_SOzuobv_JyNWUw&hl=en#v=onepage&q=Confederate%20conscription%20law%20reorganization%20regiment&f=false
- Cozzens, Peter, The Darkest Days of the War: The Battles of Iuka and Corinth, Chapel Hill, University of North Carolina Press, 1997, ISBN 0-8078-2320-1.
- Howerton, Bryan R. "Re: Port Hudson / Vicksburg Exchanges", Arkansas in the Civil War Message Board, Posted 2 April 2012, Accessed 2 April 2012, http://history-sites.com/cgi-bin/bbs53x/arcwmb/webbbs_config.pl?noframes;read=26043
- Howerton, Bryan R. "Re: Camp Price, MS", Arkansas in the Civil War Message Board, Posted 16 December 2004, Accessed 22 May 2012,
- Odom, Danny, "Question for Danny", Arkansas in the Civil War Message Board, Posted 15 March 2012, Accessed 26 March 2012, http://history-sites.com/cgi-bin/bbs53x/arcwmb/webbbs_config.pl?noframes;read=25887
- "Confederate Memorial, Old Washington, Hempstead County, Arkansas", Civil War Buff, The Civil War in Arkansas, Accessed 26 March 2012, http://www.civilwarbuff.org/Places/Hempstead/ConfederateMarker.htm
- Taylor, Doyle. "Killed in the Battle of Mark's Mill" Arkansas Civil War Page, Accessed 26 March 2012, http://www.couchgenweb.com/civilwar/MarksMill.html
- National Park Service, Civil War Soldiers and Sailors System, Confederate Arkansas Troops, 18th Regiment, Arkansas Infantry, Accessed 2 February 2016, http://www.nps.gov/civilwar/search-battle-units-detail.htm?battleUnitCode=CAR0018RI01
- "Order of Battle " Red River Campaign, Camden Expedition, Jenkins Ferry, Civil War Landscapes Association, Accessed 26 March 2012, http://civilwarlandscapes.org/cwla/states/ar/jf/intro/oobf.htm Archived 2010-12-14 at the Wayback Machine
- National Park Service, Civil War Soldiers and Sailors System, Confederate Arkansas Troops, 25th Regiment, Arkansas Infantry, Accessed 2 February 2016, http://www.nps.gov/civilwar/search-battle-units-detail.htm?battleUnitCode=CAR0025RI
- Howerton, Bryan, "1st, 2nd & 3rd Consolidated Arkansas Infantry Regiments", Arkansas in the Civil War Message Board, Posted 26 July 2011, http://history-sites.com/cgi-bin/bbs53x/arcwmb/webbbs_config.pl?noframes;read=24472
- Sikakis, Stewart, Compendium of the Confederate Armies, Florida and Arkansas, Facts on File, Inc., 1992, ISBN 978-0-8160-2288-5, page 69.
- United States. War Dept. The War of the Rebellion: A Compilation of the Official Records of the Union And Confederate Armies. Series 1, Volume 41, In Four Parts. Part 4, Correspondence, etc., Book, 1893; (http://texashistory.unt.edu/ark:/67531/metapth145061/ : accessed January 13, 2016), University of North Texas Libraries, The Portal to Texas History, http://texashistory.unt.edu; crediting UNT Libraries Government Documents Department, Denton, Texas.
- United States. War Dept. The War of the Rebellion: A Compilation of the Official Records of the Union And Confederate Armies. Series 1, Volume 48, In Two Parts. Part 1, Reports, Correspondence, etc., Book, 1896; (http://texashistory.unt.edu/ark:/67531/metapth139842/ : accessed January 08, 2016), University of North Texas Libraries, The Portal to Texas History, http://texashistory.unt.edu; crediting UNT Libraries Government Documents Department, Denton, Texas.
- United States. War Dept. The War of the Rebellion: A Compilation of the Official Records of the Union And Confederate Armies. Series 1, Volume 48, In Two Parts. Part 1, Reports, Correspondence, etc., Book, 1896; (http://texashistory.unt.edu/ark:/67531/metapth139842/m1/1233/?q=Hardy : accessed January 07, 2016), University of North Texas Libraries, The Portal to Texas History, http://texashistory.unt.edu; crediting UNT Libraries Government Documents Department, Denton, Texas.
- Price, Jeffery R. "A Courage And Desperation Rarely Equaled: The 36th Arkansas Infantry Regiment (Confederate States Army), 26 June 1862--25 May 1865". MA thesis, U.S. Army Command and General Staff College, Fort Leavenworth, Kansas, 2003, Page 36
- Steele's Retreat From Camden and The Battle of Jenkins' Ferry, Edwin C. Bearss, 1967: p.166-169, See Also Odom, Danny, "Question for Danny", Arkansas in the Civil War Message Board, Posted 15 March 2012, Accessed 26 March 2012, http://history-sites.com/cgi-bin/bbs53x/arcwmb/webbbs_config.pl?noframes;read=25887
- Howerton, Bryan, "Re: 17th/1st/35th/22nd Arkansas Infantry Regiment.", Arkansas in the Civil War Message Board, Posted 26 October 2011, Accessed 26 October 2011, http://history-sites.com/cgi-bin/bbs53x/arcwmb/webbbs_config.pl?noframes;read=24907
Bibliography
- Reynolds, Robert Edward. Into the Mouth of the Cannon: A Historical Biography of the 18th Arkansas Infantry and the Civil War in the Western Theater from 1861 to 1863. (Bloomington, IN: AuthorHouse, 2006).
- Sikakis, Stewart, Compendium of the Confederate Armies, Florida and Arkansas, Facts on File, Inc., 1992, ISBN 978-0-8160-2288-5
- United States. War Dept. The War of the Rebellion: A Compilation of the Official Records of the Union And Confederate Armies. Series 1, Volume 10, In Two Parts. Part 2, Correspondence, etc., Book, 1884
External links
- Edward G. Gerdes Civil War Home Page
- The Encyclopedia of Arkansas History and Culture
- The War of the Rebellion: a Compilation of the Official Records of the Union and Confederate Armies
- The Arkansas History Commission, State Archives, Civil War in Arkansas
