Taharqa
Taharqa, also spelled Taharka or Taharqo (Egyptian: 𓇿𓉔𓃭𓈎 tꜣ-h-rw-k, Neo-Assyrian: ![]()
| Taharqa | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Statue of Taharqa. His name appears on the center of his belt: 𓇿𓉔𓃭𓈎 (tꜣ-h-rw-k, "Taharqa"). The statue is 2.7 meters tall. Taharqa has a striding pose, the arms held tight, and holds the mekes staff. He wears a pleated kilt called shendjyt and on the head the double uraeus signifying the double rule over Nubia and Egypt. Kerma Museum.[2] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pharaoh | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reign | 690–664 BC (25th dynasty) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predecessor | Shabaka | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Successor | Tantamani | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Consort | Great Queen Takahatenamun, Atakhebasken, Naparaye, Tabekenamun[4] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Children | Amenirdis II, Ushankhuru, Nesishutefnut | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Father | Piye | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mother | Abar | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Died | 664 BC | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| t h r ḳ (Taharqo) in hieroglyphs |
|---|
Early life
Taharqa was the son of Piye, the Nubian king of Napata who had first conquered Egypt. Taharqa was also the cousin and successor of Shebitku.[7] The successful campaigns of Piye and Shabaka paved the way for a prosperous reign by Taharqa.
Ruling period
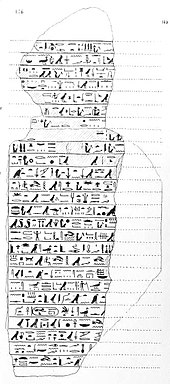
Taharqa's reign can be dated from 690 BC to 664 BC.[8] Evidence for the dates of his reign is derived from the Serapeum stele, catalog number 192. This stela records that an Apis bull born and installed (fourth month of Season of the Emergence, day 9) in year 26 of Taharqa died in Year 20 of Psamtik I (4th month of Shomu, day 20), having lived 21 years. This would give Taharqa a reign of 26 years and a fraction, in 690–664 BC.[9]
Irregular accession to power
Taharqa explicitly states in Kawa Stela V, line 15, that he succeeded his predecessor (generally assumed to be Shebitku but now established to be Shabaka instead) after the latter's death with this statement: "I received the Crown in Memphis after the Falcon flew to heaven."[10] The reference to Shebitku was an attempt by Taharqa to legitimise his accession to power.[11] However, Taharqa never mentions the identity of the royal falcon and completely omits any mention of Shabaka's intervening reign between Shebitku and Taharqa possibly because he ousted Shabaka from power.[12]

In Kawa IV, line 7-13, Taharqa states:
He (Taharqa) sailed northward to Thebes amongst the beautiful young people that His Majesty, the late King Shabataqo/Shebitku, had sent from Nubia. He was there (in Thebes) with him. He appreciated him more than any of his brothers. (There here follows a description of the [poor] state of the temple of Kawa as observed by the prince). The heart of his Majesty was in sadness about it until his Majesty became king, crowned as King of Upper and Lower Egypt (...). It was during the first year of his reign he remembered what he had seen of the temple when he was young.[13]

In Kawa V: line 15, Taharqa states “I was brought from Nubia amongst the royal brothers that his Majesty had brought. As I was with him, he liked me more than all his brothers and all his children, so that he distinguished me. I won the heart of the nobles and was loved by all. It was only after the hawk had flown to heaven that I received the crown in Memphis.”[14]
Therefore, Taharqa says that King Shebitku, who was very fond of him, brought him with him to Egypt and during that trip he had the opportunity to see the deplorable state of the temple of Amun at Kawa, an event he remembered after becoming king. But on Kawa V Taharqa says that sometime after his arrival in Egypt under a different king whom this time he chose not to name, there occurred the death of this monarch (Shabaka here) and then his own accession to the throne occurred. Taharqa's evasiveness on the identity of his predecessor suggests that he assumed power in an irregular fashion and chose to legitimise his kingship by conveniently stating the possible fact or propaganda that Shebitku favoured him "more than all his brothers and all his children."[11]
Moreover, in lines 13 – 14 of Kawa stela V, His Majesty (who can be none other but Shebitku), is mentioned twice, and at first sight the falcon or hawk that flew to heaven, mentioned in the very next line 15, seems to be identical with His Majesty referred to directly before (i.e. Shebitku).[15] However, in the critical line 15 which recorded Taharqa's accession to power, a new stage of the narrative begins, separated from the previous one by a period of many years, and the king or hawk/falcon that flew to heaven is conspicuously left unnamed in order to distinguish him from His Majesty, Shebitku. Moreover, the purpose of Kawa V, was to describe several separate events that occurred at distinct stages of Taharqa's life, instead of telling a continuous story about it.[15] Therefore, the Kawa V text began with the 6th year of Taharqa and referred to the High Nile flood of that year before abruptly jumping back to Taharqa's youth at the end of line 13.[15] In the beginning of line 15, Taharqa's coronation is mentioned (with the identity of the hawk/falcon—now known to be Shabaka—left unnamed but if it was Shebitku, Taharqa's favourite king, Taharqa would clearly have identified him) and there is a description given of the extent of the lands and foreign countries under Egypt's control but then (in the middle of line 16) the narrative switches abruptly back again to Taharqa's youth: "My mother was in Ta-Sety …. Now I was far from her as a twenty year old recruit, as I went with His Majesty to the North Land".[15] However, immediately afterwards (around the middle of line 17) the text jumps forward again to the time of Taharqa's accession: "Then she came sailing downstream to see me after a long period of years. She found me after I had appeared on the throne of Horus...".[15] Hence, the Kawa V narrative switches from one event to another, and has little to no chronological coherence or value.
Reign
_%2C_Kerma_Museum%2CSudan_(2).jpg)
Although Taharqa's reign was filled with conflict with the Assyrians, it was also a prosperous renaissance period in Egypt and Kush.[16][17] During this period of peace and prosperity, the empire flourished under Taharqa, due in part to a particularly large Nile river flood and abundant crops and wine.[18][17] Taharqa's inscriptions indicate that he gave large amounts of gold to the temple of amun at Kawa.[19] The Nile valley empire was as large as it had been since the New Kingdom.[20] Taharqa and the 25th dynasty revived Egyptian culture.[21] Religion, arts, and architecture were restored to their glorious Old, Middle, and New Kingdom forms.
Taharqa restored existing temples and built new ones. Particularly impressive were his additions to the Temple at Karnak, new temple at Kawa, and temples at Jebel Barkal.[22][23][24][25][26]
It was during the 25th dynasty that the Nile valley saw the first widespread construction of pyramids (many in modern Sudan) since the Middle Kingdom.[27][28][29] Taharqa built the largest pyramid (52 square meters at base) in the Nubian region at Nuri (near El-Kurru) with the most elaborate Kushite rock-cut tomb.[30] Taharqa was buried with "over 1070 shabtis of varying sizes and made of granite, green ankerite, and alabaster."[31]
War between Taharqa and Assyria
Taharqa began cultivating alliances with elements in Phoenicia and Philistia who were prepared to take a more independent position against Assyria.[32] Taharqa's army undertook successful military campaigns, as attested by the "list of conquered Asiatic principalities" from the Mut temple at Karnak and "conquered peoples and countries (Libyans, Shasu nomads, Phoenicians?, Khor in Palestine)" from Sanam temple inscriptions.[17] Imperial ambitions of the Mesopotamian based Assyrian Empire made war with the 25th dynasty inevitable. In 701 BC, Taharqa and his army aided Judah and King Hezekiah in withstanding a siege by King Sennacherib of the Assyrians (2 Kings 19:9; Isaiah 37:9)[33]. There are various theories (Taharqa's army[34], disease, divine intervention, Hezekiah's surrender, Herodotus' mice theory) as to why the Assyrians failed to take Jerusalem and withdrew to Assyria.[35] However, Sennacherib's annals record Judah was forced into tribute after the siege.[36] Many historians claim that Sennacherib was the overlord of Khor (except Gaza) following the seige in 701 BC. However, this is contradicted by Khor's frequent utilization of an Egyptian system of weights for trade[37], the 20 year cessation in Assyria's pattern (before 701 and after Sennacherib's death) of repeatedly invading Khor[38], and Taharqa flouting Assyria's ban on Lebanese cedar exports to Egypt, while Taharqa was building his temple to amun at Kawa.[39] Sennacherib was murdered by his own sons in revenge for the destruction of the rebellious Mesopotamian city of Babylon, a city sacred to all Mesopotamians, the Assyrians included.
In 679 BC, Sennacherib's successor, King Esarhaddon, campaigned into Khor and took a town loyal to Egypt. After destroying Sidon and forcing Tyre into tribute in 677-676 BC, Esarhaddon invaded Egypt proper in 674 BC. Taharqa and his army defeated the Assyrians outright in 674 BC, according to Babylonian records.[40] This invasion, which only a few Assyrian sources discuss, ended in what some scholars have assumed was possibly one of Assyria's worst defeats.[41] Taharqa's Egypt still held sway in Khor during this period as evidenced by Esarhaddon's 671 BC annal mentioning that Tyre's King Ba'lu had "put his trust upon his friend Taharqa", Ashkelon's alliance with Egypt, and Esarhaddon's inscription asking "if the Kushite-Egyptian forces 'plan and strive to wage war in any way' and if the Egyptian forces will defeat Esarhaddon at Ashkelon."[42] However, Taharqa was defeated in Egypt in 671 BC when Esarhaddon conquered Northern Egypt, captured Memphis, imposed tribute, and then withdrew.[16] Although the Pharaoh Taharqa had escaped to the south, Esarhaddon captured the Pharaoh's family, including his son and wife, and most of the royal court, which were sent to Assyria as hostages. In 669 BC, Taharqa reoccupied Memphis, as well as the Delta, and recommenced intrigues with the king of Tyre.[16] Taharqa intrigued in the affairs of Lower Egypt, and fanned numerous revolts.[43] Esarhaddon again led his army to Egypt and on his death in 668 BC, the command passed to Ashurbanipal. Ashurbanipal and the Assyrians again defeated Taharqa and advanced as far south as Thebes, but direct Assyrian control was not established."[16] The rebellion was stopped and Ashurbanipal appointed as his vassal ruler in Egypt Necho I, who had been king of the city Sais, and Necho's son Psamtik I, who had been educated at the Assyrian capital of Nineveh during Esarhaddon's reign.[44]
Death

Taharqa died in city of Thebes[45] in 664 BC. He was followed by his appointed successor Tantamani, a son of Shabaka, himself succeeded by a son of Taharqa, Atlanersa. Taharqa was buried at Nuri, in North Sudan.[46] Egypt was still seen as vulnerable and Tantamani invaded Egypt in hopes of restoring his family to the throne. This led to a renewed conflict with Ashurbanipal and the sack of the city by the Assyrians in 663 BCE.
Biblical references

Mainstream scholars agree that Taharqa is the Biblical "Tirhakah", king of Ethiopia (Kush), who waged war against Sennacherib during the reign of King Hezekiah of Judah (2 Kings 19:9; Isaiah 37:9).[47][48]
The events in the biblical account are believed to have taken place in 701 BC, whereas Taharqa came to the throne some ten years later. If the title of king in the biblical text refers to his future royal title, he still may have been too young to be a military commander.[49]
Depictions
Taharqa, under the name "Tearco the Aethiopian", was described by the Ancient Greek historian Strabo. Strabo mentioned Taharqa in a list of other notable conquerers (Cyrus the Great, Xerxes, Sesotris) and mentioned that these princes had undertaken "expeditions to lands far remote."[50] Strabo mentions Taharqa as having "Advanced as far as Europe",[51] and (citing Megasthenes), even as far as the Pillars of Hercules in Spain:[52]
"However, Sesostris, the Aegyptian, he adds, and Tearco the Aethiopian advanced as far as Europe; and Nabocodrosor, who enjoyed greater repute among the Chaldaeans than Heracles, led an army even as far as the Pillars. Thus far, he says, also Tearco went"
The two snakes in the crown of pharaoh Taharqa show that he was the king of both the lands of Egypt and Nubia.
Aubin mentions that the biblical account in Genesis 10:6-7 (Table of Nations) lists Taharqa's predecessors, Shebitku and Shabako.[54]
Monuments of Taharqua

Taharqa has left monuments throughout Egypt and Nubia. In Memphis he rebuilt or restored the Temple of Amon.[56].
Taharqa in Karnak
Taharqa is known for various monuments in Karnak.
 Taharqa column
Taharqa column- Kiosk of Taharqa in Kanark
 Chapel of Taharqa and Shepenwepet in Karnak
Chapel of Taharqa and Shepenwepet in Karnak
Shrine of Taharqa in Kawa
A small temple of Tahaqa was once located at Kawa in Nubia (modern Sudan). It is located today in the Ashmolean Museum.[57]
 The Shrine of Taharqa, Ashmolean Museum
The Shrine of Taharqa, Ashmolean Museum Shrine and Sphinx of Taharqa. Taharqa appears between the legs of the Ram-Spinx
Shrine and Sphinx of Taharqa. Taharqa appears between the legs of the Ram-Spinx The Ram-Spinx and Taharqa
The Ram-Spinx and Taharqa Relief of Taharqa on the shrine
Relief of Taharqa on the shrine Taharqa cartouche on the Shrine
Taharqa cartouche on the Shrine
._He_makes_an_offering_to_the_ram-headed_god_Amun-Re._Kawa_shrine.jpg)

Taharqua in Jebel Barkal
Taharqa is depicted in various reliefs in Jebel Barkal, particularly in the Temple of Mut.
 Taharqa before the god Amun in Gebel Barkal (Sudan), in Temple of Mut, Jebel Barkal
Taharqa before the god Amun in Gebel Barkal (Sudan), in Temple of Mut, Jebel Barkal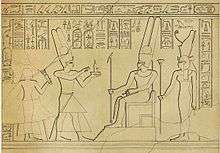 Taharqa followed by his mother Queen Abar. Gebel Barkal - room C.
Taharqa followed by his mother Queen Abar. Gebel Barkal - room C. Taharqa with Queen Takahatamun at Gebel Barkal.
Taharqa with Queen Takahatamun at Gebel Barkal. Lion-headed God Appademak with Pharaoh Taharqa (right) in the Jebel Barkal Temple of Mut.
Lion-headed God Appademak with Pharaoh Taharqa (right) in the Jebel Barkal Temple of Mut.
Museum artifacts
 Statue of Pharaoh Taharqa in the National Museum of Sudan
Statue of Pharaoh Taharqa in the National Museum of Sudan.jpg) Taharqa, ca. 690-64 BCE, Ny Carlsberg Glyptotek, Copenhagen.
Taharqa, ca. 690-64 BCE, Ny Carlsberg Glyptotek, Copenhagen. Taharqa under a sphinx, British Museum
Taharqa under a sphinx, British Museum Taharqa appears as the tallest statue in the back (2.7 meters), Kerma Museum.[61]
Taharqa appears as the tallest statue in the back (2.7 meters), Kerma Museum.[61] Granite sphinx of Taharqa from Kawa in Sudan
Granite sphinx of Taharqa from Kawa in Sudan Serpentine weight of 10 daric. Inscribed for Taharqa in the midst of Sais. 25th Dynasty. From Egypt, probably from Nesaft. The Petrie Museum of Egyptian Archaeology, London
Serpentine weight of 10 daric. Inscribed for Taharqa in the midst of Sais. 25th Dynasty. From Egypt, probably from Nesaft. The Petrie Museum of Egyptian Archaeology, London Taharqa as a sphinx
Taharqa as a sphinx Taharqa offering wine jars to Falcon-god Hemen
Taharqa offering wine jars to Falcon-god Hemen Taharqa close-up
Taharqa close-up Shabti of King Taharqa
Shabti of King Taharqa
See also
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Taharqa. |
References
- Elshazly, Hesham. "Kerma and the royal cache". Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - Elshazly, Hesham. "Kerma and the royal cache". Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - Clayton, Peter A. Chronicle of the Pharaohs: The Reign-by-Reign Record of the Rulers and Dynasties of Ancient Egypt. Thames & Hudson. p.190. 2006. ISBN 0-500-28628-0
- Aidan Dodson & Dyan Hilton, The Complete Royal Families of Ancient Egypt, (London: Thames & Hudson, 2004) ISBN 0-500-05128-3, pp.234-6
- Burrell, Kevin (2020). Cushites in the Hebrew Bible: Negotiating Ethnic Identity in the Past and Present. BRILL. p. 79. ISBN 978-90-04-41876-9.
- "Pharaoh Taharqa ruled from 690 to 664 BCE and in all likelihood was the last black pharaoh to rule over all of Egypt" in Dijk, Lutz van (2006). A History of Africa. Tafelberg. p. 53. ISBN 978-0-624-04257-0.
- Toby Wilkinson, The Thames and Hudson Dictionary of Ancient Egypt, Thames & Hudson, 2005. p.237
- Kitchen 1996, p. 380-391.
- Kitchen 1996, p. 161.
- Kitchen 1996, p. 167.
- Payraudeau 2014, p. 115-127.
- Payraudeau 2014, p. 122-3.
- [52 – JWIS III 132-135; FHN I, number 21, 135-144.]
- [53 – JWIS III 135-138; FHN I, number 22, 145-158.]
- Broekman, G.P.F. (2015). The order of succession between Shabaka and Shabataka. A different view on the chronology of the Twenty-fifth Dynasty. GM 245. p. 29.
- Welsby, Derek A. (1996). The Kingdom of Kush. London, UK: British Museum Press. p. 158. ISBN 071410986X.
- Török, László (1998). The Kingdom of Kush: Handbook of the Napatan-Meroitic Civilization. Leiden: BRILL. p. 132-133,170-184. ISBN 90-04-10448-8.
- Welsby, Derek A. (1996). The Kingdom of Kush. London, UK: British Museum Press. p. 158. ISBN 071410986X.
- Welsby, Derek A. (1996). The Kingdom of Kush. London, UK: British Museum Press. p. 169. ISBN 071410986X.
- Török, László. The Kingdom of Kush: Handbook of the Napatan-Meroitic Civilization. Leiden: Brill, 1997. Google Scholar. Web. 20 Oct. 2011.
- Diop, Cheikh Anta (1974). The African Origin of Civilization. Chicago, Illinois: Lawrence Hill Books. pp. 219–221. ISBN 1-55652-072-7.
- Diop, Cheikh Anta (1974). The African Origin of Civilization. Chicago, Illinois: Lawrence Hill Books. pp. 219–221. ISBN 1-55652-072-7.
- Bonnet, Charles (2006). The Nubian Pharaohs. New York: The American University in Cairo Press. pp. 142–154. ISBN 978-977-416-010-3.
- Mokhtar, G. (1990). General History of Africa. California, USA: University of California Press. pp. 161–163. ISBN 0-520-06697-9.
- Emberling, Geoff (2011). Nubia: Ancient Kingdoms of Africa. New York: Institute for the Study of the Ancient World. pp. 9–11. ISBN 978-0-615-48102-9.
- Silverman, David (1997). Ancient Egypt. New York: Oxford University Press. pp. 36–37. ISBN 0-19-521270-3.
- Mokhtar, G. (1990). General History of Africa. California, USA: University of California Press. pp. 161–163. ISBN 0-520-06697-9.
- Emberling, Geoff (2011). Nubia: Ancient Kingdoms of Africa. New York: Institute for the Study of the Ancient World. pp. 9–11.
- Silverman, David (1997). Ancient Egypt. New York: Oxford University Press. pp. 36–37. ISBN 0-19-521270-3.
- Welsby, Derek A. (1996). The Kingdom of Kush. London, UK: British Museum Press. pp. 103, 107–108. ISBN 071410986X.
- Welsby, Derek A. (1996). The Kingdom of Kush. London, UK: British Museum Press. p. 87. ISBN 071410986X.
- Coogan, Michael David; Coogan, Michael D. (2001). The Oxford History of the Biblical World. Oxford: Oxford University Press. p. 53. ISBN 0-19-513937-2.
- Aubin, Henry T. (2002). The Rescue of Jerusalem. New York, NY: Soho Press, Inc. pp. x, 141–144. ISBN 1-56947-275-0.
- Aubin, Henry T. (2002). The Rescue of Jerusalem. New York, NY: Soho Press, Inc. pp. x, 127, 129–130, 139–152. ISBN 1-56947-275-0.
- Aubin, Henry T. (2002). The Rescue of Jerusalem. New York, NY: Soho Press, Inc. pp. x, 119. ISBN 1-56947-275-0.
- Roux, Georges (1992). Ancient Iraq (Third ed.). London: Penguin. ISBN 0-14-012523-X.
- Aubin, Henry T. (2002). The Rescue of Jerusalem. New York, NY: Soho Press, Inc. pp. x, 155–156. ISBN 1-56947-275-0.
- Aubin, Henry T. (2002). The Rescue of Jerusalem. New York, NY: Soho Press, Inc. pp. x, 152–153. ISBN 1-56947-275-0.
- Aubin, Henry T. (2002). The Rescue of Jerusalem. New York, NY: Soho Press, Inc. pp. x, 155. ISBN 1-56947-275-0.
- Aubin, Henry T. (2002). The Rescue of Jerusalem. New York, NY: Soho Press, Inc. pp. x, 158–161. ISBN 1-56947-275-0.
- Ephʿal 2005, p. 99.
- Aubin, Henry T. (2002). The Rescue of Jerusalem. New York, NY: Soho Press, Inc. pp. x, 159–161. ISBN 1-56947-275-0.
- Budge, E. A. Wallis (2014-07-17). Egyptian Literature (Routledge Revivals): Vol. II: Annals of Nubian Kings. Routledge. ISBN 978-1-135-07813-3.
- Mark 2009.
- Historical Prism inscription of Ashurbanipal I by Arthur Carl Piepkorn page 36. Published by University of Chicago Press
- Why did Taharqa build his tomb at Nuri? Conference of Nubian Studies
- http://www.jewishencyclopedia.com/articles/14403-tirhakah
- Aubin, Henry T. (2002). The Rescue of Jerusalem. New York, NY: Soho Press, Inc. pp. x, 127, 129–130, 139–152. ISBN 1-56947-275-0.
- Stiebing Jr, William H. (2016). Ancient Near Eastern History and Culture. Routledge. p. 279. ISBN 9781315511160. Retrieved 23 December 2018.
- Aubin, Henry T. (2002). The Rescue of Jerusalem. New York, NY: Soho Press, Inc. pp. x, 162. ISBN 1-56947-275-0.
- Strabo (2006). Geography. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press. p. 7. ISBN 0-674-99266-0.
- Snowden, Before Color Prejudice: The Ancient View of Blacks. Cambridge: Harvard University Press, 1983, p.52
- "LacusCurtius Strabo Geography Book XV Chapter 1 (§§ 1-25)". penelope.uchicago.edu.
- Aubin, Henry T. (2002). The Rescue of Jerusalem. New York, NY: Soho Press, Inc. pp. x, 178. ISBN 1-56947-275-0.
- "L'An 6 de Taharqa" (PDF). Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - Cf. D. Meeks, Hommage à Serge Sauneron
, 1979, Une fondation Memphite de Taharqa (Stèle du Caire JE 36861), p. 221-259. - "Taharqa Shrine". Ashmolean Museum.
- Museum notice
- Museum notice
- Museum notice
- Elshazly, Hesham. "Kerma and the royal cache". Cite journal requires
|journal=(help)
Sources
- Mark, Joshua J. (2009). "Ashurbanipal". Ancient History Encyclopedia. Retrieved 28 November 2019.
- Ephʿal, Israel (2005). "Esarhaddon, Egypt, and Shubria: Politics and Propaganda". Journal of Cuneiform Studies. University of Chicago Press. 57 (1): 99–111.
- Mark, Joshua J. (2014). "Esarhaddon". Ancient History Encyclopedia. Retrieved 23 November 2019.
- Radner, Karen (2003). "The Trials of Esarhaddon: The Conspiracy of 670 BC". ISIMU: Revista sobre Oriente Próximo y Egipto en la antigüedad. Universidad Autónoma de Madrid. 6: 165–183.
- Radner, Karen (2012). "After Eltekeh: Royal Hostages from Egypt at the Assyrian Court". Stories of long ago. Festschrift für Michael D. Roaf. Ugarit-Verlag: 471–479.
- Radner, Karen (2015). Ancient Assyria: A Very Short Introduction. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-871590-0.
- Grayson, A. K. (1970). "Assyria: Sennacherib and Esarhaddon (704–669 BC)". The Cambridge Ancient History Volume 3 Part 2: The Assyrian and Babylonian Empires and Other States of the Near East, from the Eighth to the Sixth Centuries BC. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-3111033587.
- Luckenbill, Daniel David (1927). Ancient Records of Assyria and Babylonia Volume 2: Historical Records of Assyria From Sargon to the End. University of Chicago Press.
Further reading
- Kitchen, Kenneth Anderson (1996). The Third Intermediate Period in Egypt (1100–650 BC) (3rd ed.). Aris & Phillips Ltd. p. 608. ISBN 9780856682988.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Payraudeau, Frédéric (2014). Retour sur la succession Shabaqo-Shabataqo (in French). pp. 115–127.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Morkot, Robert (2000). The Black Pharaohs: Egypt's Nubian Rulers. The Rubicon Press. p. 342. ISBN 0-948695-23-4.