Jebel Barkal
Jebel Barkal or Gebel Barkal (Arabic: جبل بركل) is a very small mountain located some 400 km north of Khartoum, in Karima town in Northern State in Sudan, on a large bend of the Nile River, in the region called Nubia. The mountain is 98 m tall, has a flat top, and apparently was used as a landmark by the traders in the important route between central Africa, Arabia, and Egypt, as the point where it was easier to cross the great river. In 2003, the mountain, together with the historical city of Napata (which sits at its feet), were named World Heritage Sites by UNESCO. The Jebel Barkal area houses the Jebel Barkal Museum. The Jebel Barkal pyramids are one example of Nubian pyramids.
جبل بركل | |
 Jebel Barkal is a small mountain, 98 meters tall | |
 Shown within Northeast Africa  Jebel Barkal (Sudan)  Jebel Barkal (Africa) | |
| Alternative name | Gebel Barkal |
|---|---|
| Location | Karima, Northern State, Sudan |
| Region | Nubia |
| Coordinates | 18°32′12″N 31°49′42″E |
| Type | Sanctuary |
| Official name | Gebel Barkal and the Sites of the Napatan Region |
| Type | Cultural |
| Criteria | i, ii, iii, iv, vi |
| Designated | 2003 (27th session) |
| Reference no. | 1073 |
| Region | Arab States |
History
Around 1450 BCE, the Egyptian Pharaoh Thutmose III extended his empire to that region and considered Jebel Barkal its southern limit. There, he campaigned near the city of Napata that, about 300 years later, became the capital of the independent kingdom of Kush. The 25th Dynasty Nubian king Piye later greatly enlarged the New Kingdom Temple of Amun in this city and erected his Year 20 Victory stela within it.
Temples
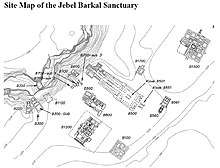
The ruins around Jebel Barkal include at least 13 temples and 3 palaces, that were for the first time described by European explorers in the 1820s. In 1862 five inscriptions from the Third Intermediate Period were recovered by an Egyptian officer and transported to the Cairo Museum, but not until 1916 were scientific archeological excavations performed by a joint expedition of Harvard University and the Museum of Fine Arts of Boston under the direction of George Reisner.[1] From the 1970s, explorations continued by a team from the University of Rome La Sapienza, under the direction of Sergio Donadoni, that was joined by another team from the Boston Museum, in the 1980s, under the direction of Timothy Kendall. The larger temples, such as the Temple of Amun, are even today considered sacred to the local population. The carved wall painted chambers of the Temple of Mut are well preserved. Temple B700 built by Atlanersa and decorated by Senkamanisken is now largely destroyed. It received the sacred bark of Amun from the nearby B500 on certain cultic occasions, and may have served during the coronation of the kings of the early Napatan period, in the mid 7th century BC.
Pyramids
Jebel Barkal served as a royal cemetery during the Meroitic Kingdom.[2] The earliest burials date back to the 3rd century BC.
- Bar. 1 King from the middle of the 1st century BCE
- Bar. 2 King Teriqas (ca. 29-25 BCE)
- Bar. 4 Queen Amanirenas ? (1st century BCE)
- Bar. 6 Queen Nawidemak (1st century BCE)
- Bar. 7 King Sabrakamani? (3rd century BCE)
- Bar. 9 King or Queen of the early 2nd century CE
- Bar. 11 King Aktisanes or Aryamani (3rd century BCE)
- Bar. 14 King Aktisanes or Aryamani (3rd century BCE)
- Bar. 15 King Kash (3rd century BCE)
Local remains
 Pyramids at Jebel Barkal in 1821
Pyramids at Jebel Barkal in 1821 Pyramids of Jebel Barkal today
Pyramids of Jebel Barkal today Pyramids in the southern group
Pyramids in the southern group The last standing pillars of Napata's temple of Amun at the foot of Jebel Barkal
The last standing pillars of Napata's temple of Amun at the foot of Jebel Barkal stone statue
stone statue Taharqa before the god Amun in Gebel Barkal (Sudan), in temple B300
Taharqa before the god Amun in Gebel Barkal (Sudan), in temple B300 Lion-headed God Appademak with Pharaoh Taharqa (right) in the Jebel Barkal Temple of Mut.
Lion-headed God Appademak with Pharaoh Taharqa (right) in the Jebel Barkal Temple of Mut. Taharqa, followed by the sistrum shaking queen Takahatenamun in the Jebel Barkal Temple of Mut.
Taharqa, followed by the sistrum shaking queen Takahatenamun in the Jebel Barkal Temple of Mut.
Artifacts in Museums
 Colossal statue of King Aspelta from the Temple of Amun, Jebel Barkal. Boston Museum of Fine Arts.[3]
Colossal statue of King Aspelta from the Temple of Amun, Jebel Barkal. Boston Museum of Fine Arts.[3].jpg) The Stele of Piye was discovered in Jebel Barkal. Cairo Museum
The Stele of Piye was discovered in Jebel Barkal. Cairo Museum The Stele of Tantamani. Cairo Museum
The Stele of Tantamani. Cairo Museum
References
- A. Reisner, "Historical Inscriptions from Gebel Barkal", Sudan Notes and Records, 4 (1921), pp. 59-75
- László Török, The kingdom of Kush: handbook of the Napatan-Meroitic Civilization
- "Statue of King Aspelta". collections.mfa.org.
Sources
- Kendall, Timothy. A Visitor's Guide to The Jebel Barkal Temples (PDF).
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Jebel Barkal. |