Thallium(I) oxide
Thallium(I) oxide is the inorganic compound of thallium and oxygen with the formula Tl2O in which thallium is in its +1 oxidation state. It is black and produces a basic yellow solution of thallium(I) hydroxide (TlOH) when dissolved in water. It is formed by heating solid TlOH or Tl2CO3 in the absence of air. Thallium oxide is used to make special high refractive index glass. Thallium oxide is a component of several high temperature superconductors. Thallium(I) oxide reacts with acids to make thallium(I) salts.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Thallous oxide | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.013.838 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Tl2O | |
| Molar mass | 424.77 g/mol |
| Appearance | black orthorhombic crystals hygroscopic |
| Density | 10.45 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 596 °C (1,105 °F; 869 K) |
| Boiling point | 1,080 °C (1,980 °F; 1,350 K) (decomposes) |
| soluble | |
| Solubility | soluble in alcohol and acid |
| Structure | |
| Rhombohedral, hR18[1] | |
| R-3m, No. 166 | |
| Related compounds | |
Other cations |
Thallium(III) oxide |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
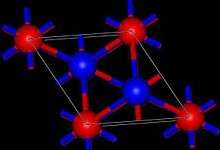
Tl2O adopts the anti-cadmium iodide structure in the solid state.[1] In this way, the Tl(I) centers are pyramidal and the oxide centers are octahedral.
Thallium(I) oxide, like all thallium compounds, is highly toxic.
References
- Sabrowsky H. (1971). "Zur Darstellung und Kristallstruktur von Tl2O". Zeitschrift für anorganische und allgemeine Chemie. 381 (3): 266. doi:10.1002/zaac.19713810305.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.