Civic Democratic Party (Czech Republic)
The Civic Democratic Party (Czech: Občanská demokratická strana, ODS) is a liberal-conservative[9][10][11] eurosceptic political party in the Czech Republic. It holds 25 seats in the Chamber of Deputies, and is the second strongest party following the 2017 election.
Civic Democratic Party Občanská demokratická strana | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Abbreviation | ODS |
| Leader | Petr Fiala |
| Deputy Leaders | Zbyněk Stanjura Alexandr Vondra Martin Baxa Martin Kupka Miloš Vystrčil |
| Chamber of Deputies Leader | Zbyněk Stanjura |
| Senate Leader | Martin Červíček |
| MEP Leader | Jan Zahradil |
| Founder | Václav Klaus |
| Founded | 21 April 1991 |
| Preceded by | Civic Forum |
| Headquarters | Truhlářská 9, Prague |
| Newspaper | ODS News[1] |
| Think tank | CEVRO[2] Right Riverbank[3] |
| Youth wing | Young Conservatives Young Civic Democrats |
| Membership (2019) | 13,563 |
| Ideology | |
| Political position | Centre-right[16][17] to right-wing[18][19][20] |
| European affiliation | European Conservatives and Reformists Party |
| International affiliation | International Democrat Union |
| European Parliament group | European Conservatives and Reformists |
| Colours | Blue |
| Chamber of Deputies | 23 / 200 |
| Senate | 19 / 81 |
| European Parliament | 4 / 21 |
| Regional councils | 76 / 675 |
| Governors of the regions | 0 / 13 |
| Local councils | 2,845 / 61,892 |
| Prague City Assembly | 14 / 65 |
| Party flag | |
 | |
| Website | |
| http://www.ods.cz/ | |
Founded in 1991 as the pro-free market wing of the Civic Forum by Václav Klaus and modelled on the British Conservative Party,[21] the ODS won the 1992 legislative election, and has remained in government for most of the Czech Republic's independence. In every legislative (except for the 2013 election) it emerged as one of the two strongest parties. Václav Klaus served as the first Prime Minister of the Czech Republic after the partition of Czechoslovakia, from 1993 to 1997. Mirek Topolánek, who succeeded him as leader of the party in December 2002, served as Prime Minister from 2006 to 2009. In the 2010 election, the party lost 28 seats, finishing second, but as the largest party right of the centre, it formed a centre-right government with Petr Nečas as Prime Minister. In the 2013 legislative election, the party was marginalized by only securing 16 seats in the Chamber of Deputies, relegating the party to the opposition since July 2013. In the 2017 legislative election, it has partly recovered and secured 25 seats in the Chamber of Deputies, making it the second strongest party in chamber. The party is currently being led by Petr Fiala, who has been leader since the 2014 party convention.
The ODS is a member of the International Democratic Union, and co-founded together with the British Conservatives the eurosceptic European Conservatives and Reformists Party (ECR Party) and the European Conservatives and Reformists (ECR group) in the European Parliament.
History
Formation
The party was founded in 1991 as one of two successors to the Civic Forum, which was a big tent movement that consisted of two major wings. The strongest wing was the Interparliamentary Club of the Democratic Right which was transformed into the ODS when Civic Forum split.[22] ODS represented followers of Václav Klaus and was pro-free market, as opposed to the centrist Civic Movement. An agreement was reached to split the party in half at the Civic Forum Assembly on 23 February 1991. This was followed on 21 April by a formal declaration of a new party, and Klaus was elected its first President.[23] The party agreed to continue in a coalition government with the Civic Movement, but this collapsed in July 1991.
The Civic Democrats, who represented demands for a tighter Czechoslovak federation, began to organize in Slovakia.[24] Ahead of the 1992 election, the ODS ruled out an electoral alliance with the Liberal Democrats, but agreed to an alliance with Václav Benda's Christian Democratic Party (KDS) in order to boost its appeal to conservatives.[24] The ODS won the election, winning 66 seats (and the KDS another ten), and formed a centre-right coalition with the Civic Democratic Alliance (ODA) and the KDU-ČSL, with Klaus as Prime Minister.[25]
Dominant party
It was the dominant party in two coalition governments in the Czech Republic from 1992–1997, a majority administration (1992–96) and a short-lived minority government (1996–97).
On 2 June 1995, the ODS and KDS signed a merger agreement, which would come into effect on 18 March 1996, ahead of that year's election. However, at the election, whilst the ODS improved to 68 seats, its allies fell, leading to the government receiving only 99 seats: two short of a majority. Klaus continued with a minority government, relying on its acceptance by the Social Democratic Party (ČSSD).
In December 1997, allegations of the party receiving illegal donations and maintaining a secret slush fund caused the ODA and KDU-ČSL to withdraw from the coalition, and the government collapsed. Josef Tošovský was appointed caretaker, pending new elections in June 1998. Despite the scandal, Klaus was re-elected party chairman. In January 1998, some legislators opposed to Klaus, led by Jan Ruml and Ivan Pilip, left the party in the so-called 'Sarajevo Assassination' and formed the Freedom Union (US).[26]
Opposition agreement
At the elections, the ODS fell even further, to 63 seats, while the US won 19. Due to the split, the Freedom Union refused to support the ODS, preventing them from getting a majority; the US's executive also refused to support the ČSSD. As a result, on 9 July 1998, the ODS signed the Opposition Agreement, which pledged the party to provide confidence and maintain a ČSSD government under Miloš Zeman.[27] This agreement was then superseded by the more explicit 'Patent of Tolerance' in January 2000.[28]
Opposition 2002–2006
In the 2002 legislative election, the party went from being the largest seat holder to being the second largest party in the Chamber of Deputies with 58 of 200 seats, and for the first time in its history assumed the role of a true opposition party. Mirek Topolánek took over the party leadership. The former Czech president, Václav Klaus, has been the party's honorary president for his first term in the office. In the European Parliament elections in June 2004 and in Senate and regional assembly elections in November 2004, it received over 30% of the votes.
2006: Return to government

In the 2006 legislative election the ODS was the largest seat holder in the Chamber of Deputies with 81 seats. ODS originally aimed to make a deal with Czech Social Democratic Party but talks with the Social democratic leader Jiří Paroubek were unsuccessful. Mirek Topolánek then introduced his first minority cabinet that consisted of Civic Democrats and independents. It was designated on 4 September 2006 but lost a vote of confidence on 3 October 2006.
ODS then formed a government in coalition with the Populars (KDU-ČSL) and the Green Party (SZ). Projects of the cabinet included reform of public finances. Topolánek also discussed possible emplacement of United States Missile defense in the Czech Republic which resulted in public resistance.
The party suffered heavy losses in regional and Senate elections in 2008, losing all 12 regional governorships it had previously held. However, a year later, ODS won the European Parliament election, keeping all 9 seats and gaining more votes than in previous elections.
ODS-led government during Czech Presidency of the Council of the European Union 2009. Czech presidency had to deal with problems such as Gas crisis in Ukraine, conflict in Gaza or economic crisis. There were also controversies like Entropa but some aspects such as resolution of gas crisis were positively evaluated.[29]
The Cabinet had lost a no confidence vote on 24 March 2009. The country was then governed by a newly formed caretaker Cabinet, which was nominated by ODS, ČSSD and SZ. Early elections were set for 9–10 October 2009 but were postponed to May 2010 due to unexpected developments in the Constitutional Court and House of Deputies
Civic Democratic Party won the second place after Czech Social Democratic Party and formed a centre-right Government with TOP 09 and Public Affairs. Public Affairs split from the government on 22 April 2012 but were replaced by LIDEM. The Civic Democratic Party was widely defeated in the regional election that same year, finishing third overall and winning only in the Plzeň region. The party also lost 2010 and 2012 Senate elections.

ODS nominated Přemysl Sobotka for president of the Czech Republic during the 2013 presidential election. Sobotka received only 2.46% of votes and didn't qualify for second round. ODS has held 2012 presidential primaries which Přemysl Sobotka has won. Sobotka's poor showing in the 2013 general election was seen as caused by the government's unpopularity and lack of support from the party.[30] The party's leadership supported Karel Schwarzenberg of TOP 09 in the second round of the presidential election.[31]
2013: Back in opposition

After resignation and fall of Cabinet of Prime Minister Petr Nečas ODS proposed Miroslava Němcová to the position of the Prime Minister to President Zeman saying that she will be able to form a coalition and succeed a vote of confidence in the Chamber of Deputies. However, President Zeman refused to appoint her and instead appointed Jiří Rusnok's Cabinet. After that, opposition called for a dissolution of Chamber of Deputies and early election (such vote was only recently made possible by a constitutional amendment). The motion of dissolution passed with 147 out of 200 votes (120 required), all parties except ODS, whose deputies left the chamber, voted for dissolution, including their former coalition partners Public Affairs and TOP 09. President Zeman then called on early elections on 25–26 October 2013. ODS suffered heavy losses. It gained only 16 seats and finished 5th. The party also lost elections of the European parliament and of Senate and municipal in 2014.
The 24th Congress of the Civic Democratic Party elected on 18–19 January 2014 a new leadership of ODS. The former rector of Masaryk University and minister Petr Fiala was elected as chairman and Member of the European Parliament. Jan Zahradil was elected as first-vice-chairman. In his book Citizens, Democrats and Party Members (Czech: Občané, demokraté a straníci), Fiala says the party needs to be attractive to new, young people and ODS shall have experts on economics, health care, education, etc.
In the Chamber of Deputies ODS formed an informal coalition relationship with TOP 09 and both have been opposing laws such as Control report of Value-added tax. On 26 May 2015, ODS, TOP 09 and Dawn of Direct Democracy called an unsuccessful vote of no confidence of the Cabinet of Bohuslav Sobotka.
As of December 2015 opinion polls showed ODS with 8.6% nationwide.[32] Some polling agencies and political commentators are of the opinion that ODS is on the path to become main centre-right party again.[33][34][35]
On 16 January 2016, Fiala was re-elected as Leader of the ODS. ODS participated in 2016 regional and Senate election. It received about 10% of votes and its candidate's secured seats in all regions. 6 candidates nominated by ODS qualified for the second round for Senate. 4 of them were eventually elected Fiala then said that ODS returned to the position of the major right wing party.[36][37]
ODS agreed to participate in the 2017 legislative election together with Freeholder party. Parties will present themselves during the campaign as ODS with the support of Freeholders. This agreement means that Freeholders will take 40 places on ODS candidacy list.[38] In February 2017, ODS started a campaign called "We create program." which was series of tours to Czech regions with party leaders discussing priorities with supporters and potential voters for an upcoming election.[39] On 19 April 2017, ODS introduced its tax program. The Civic Democrats want to lower taxes which they say would increase the income of Czech citizens. ODS also wants to decrease spending in social benefits and subsidies. Chief Whip Zbyněk Stanjura said that many people take advantage of social benefits even though they don't deserve it. These plans resembled those that ODS had in the 2006 legislative election manifesto.[40][41] Tours concluded with Conference "Strong program for Strong Czechia" held on 22 April where ODS presented their election manifesto and candidates.[42][43]

Following the 2017 Czech government crisis, ODS grew in polls, approaching the Czech Social Democratic Party.[44] According to a poll by TNS Kantar, ODS would become the second strongest party,surpassing ČSSD and KSČM.[45] ODS introduced its campaign for 2017 election on 29 May 2017. It is inspired by the British Conservative Party's campaign for 2017 general election.[46] In the 2017 election, ODS sought to get more than 10%.[47] According to poll by STEM/Mark in September. ODS would get 7.5% of votes.[48]
ODS received 11% in 2017 legislative election and became the second largest political party in the Czech Republic.[49] The party then won 2018 Senate election confirming its position as the main right wing party.[50]
Ideology
The ODS is liberal-conservative[51][52][53] and conservative-liberal,[54][55][56] supports economic liberalism,[57] and is Eurosceptic.[12][58] There are also multiple ideological factions in the party, including the national conservative faction,[9][59][60][61] the national liberal faction, the Christian conservative faction (former Christian Democratic Party) and so on.
.jpg)
The party's ideas are very close to those of the British Conservative Party, Swedish Moderate Party, and other liberal-conservative parties in Europe. The basic principles of the party's program are "low taxes, public finances and future without debts, support for families with children, addressable social system, reducing bureaucracy, better conditions for business, a safe state with the transatlantic links. No tricks and populism."
Many prominent politicians in the party openly oppose political correctness.[62][63][64]
.jpg)
ODS also supports the right of law abiding citizens to own and carry firearms,[65] being the main reason Czech gun laws are much more liberal than in nearly all other European countries. This makes them different to parties they are based on, as most of them, especially British Conservatives, reject the idea that anyone has a right to own and carry firearms and other weapons, making the ODS much more similar to American Republicans in this matter, although they still support gun control measures (such as background checks, licenses and registration). ODS, especially its defense expert Jana Černochová, was one of the main supporters of embedding the right to keep and bear arms for the purposes of national security into the Czech constitution, although it was Social Democrat Milan Chovanec who originally proposed it. The amendment failed in the Senate, but there is a proposal to submit it again after the 2018 elections in which the ODS gained several seats.
Symbols
Name
Václav Klaus stated that party's name represents the fact that ODS is based on the idea of the civic freedoms. It also shows that ODS is a Civic Party, which differentiates it from other parties that existed prior to 1991. The adjective Democratic represents that ODS should protect parliamentary democracy.[66]
Besides its official name, ODS also received some informal names from media. Party members are sometimes called "the Blues" or the "Blue Birds" and ODS is sometimes called the Blue Party due to party's association with the color blue.[67][68][69][70]
Logo
The first logo was introduced on 4 June 1991, created by Aleš Krejča. It was chosen from over 250 entries to a public competition.[71][72]
A new logo was introduced in 1992, including the silhouette of a bird in blue. The logo was created by Petr Šejdl. In 1994 when the bird's tail was shortened and in 1998 the font was changed as a result of the "Sarajevo betrayal" of autumn 1997, in which ODS colleagues used allegations of bribery to precipitate the resignation of Václav Klaus' government while he was on a trip to Sarajevo.[73][71] The party used this version until 2015 with modifications for individual election campaigns.[74]
The ODS introduced a new party logo in a congress in Prague in 2015. The design of the bird was updated and flies upwards rather than to the left. The logo was designed by Libor Jelínek.[75]
 Party logo, 1991–1992
Party logo, 1991–1992 Party symbol, 1994–2015
Party symbol, 1994–2015.svg.png) Current logo, since 2015
Current logo, since 2015
Organisation
Party structure
The highest body of the ODS is Congress which meets every year and elects leadership every two years. The party is led by the Executive Council and Republic Assembly in time between meetings of Congress. The executive body meets every Month and the party is led by Panel between meetings of the Executive Council. Panel consists of Party's Leader, Deputy Leaders and Chief Whips of the Parliamentary ODS.[76]
ODS is structured similarly to the subdivisions of the Czech Republic. The structure consists of local associations. Group of local associations forms area. Areas are organised as parts of Region.[77][78]
Membership
| Year | Members | Ref. | Year | Members | Ref. | Year | Members | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1991 | 18,500 | 2001 | 18,280 | [79] | 2011 | 27,648 | ||
| 1992 | 23,000 | 2002 | 20,412 | 2012 | 24,507 | |||
| 1993 | 2003 | 21,641 | [80] | 2013 | 21,578 | |||
| 1994 | 2004 | 23,138 | 2014 | 17,944 | [81] | |||
| 1995 | 21,803 | [82] | 2005 | 2015 | 14,771 | |||
| 1996 | 2006 | 2016 | 14,123 | |||||
| 1997 | 2007 | 2017 | 14,005 | [83] | ||||
| 1998 | 16,000 | 2008 | 2018 | 14,095 | ||||
| 1999 | 19,300 | 2009 | 34,000 | [84] | 2019 | 13,563 | [85] | |
| 2000 | 17,000 | [86] | 2010 | 31,011 |
ODS had 18,500 Members in 1991. The number of members grew with the party's influence and soon rose to over 23,000. It decreased during political crisis in 1998 to 16,000. The party stopped the decrease after preliminary election and membership grew once again. It peaked in 2010 when it reached 31,011. The member base started to decline rapidly after 2010. It had only 17,994 members prior the 2013 election.[87] ODS had 14,771 members in May 2015 and the member base was stabilised according to leaders of the party.[88]

The party runs a membership organisation known as Supporters of ODS. It is a looser form of involvement with the party. It is meant for people who doesn't want to be members of ODS but sympathize with its program.[89] It replaced the organisation known as Blue Team[90]
Faces of ODS is a project of party's members who share their life's story. It was described as honour for all members of the party who didn't abandon it in hard times.[91]
Young Conservatives
Young Conservatives (Czech: Mladí konzervativci, MK) is a youth wing of ODS. Young people from the age of 15 to 35 can apply for a membership in the MK. The founding congress of MK was held on 8 December 1991 as a result of previous preparations through Charter of Young Conservatives by a group of students at the University of Technology in Brno and Law Students' Association "Všehrd" from Faculty of Law at the Charles University. The Young Conservatives organize a wide range of events from meetings with local or national politicians to elections campaigns and international events.
CEVRO Liberal Conservative Academy
CEVRO Liberal Conservative Academy (Czech: CEVRO Liberálně konzervativní akademie) is a think-tank affiliated with ODS. It was established in 1999. Its goal is political education which tries to spread liberal-conservative thinking. In 2005, CEVRO established its own private university known as CEVRO Institute. CEVRO has four newspapers – CEVRO Revue, The Week in European Politics, The Week in Czech Politics and Forthnightly.[92]
Center for Civic Freedoms
Center for Civic Freedoms (Czech: Centrum pro občanské svobody) is a think-tank founded by Václav Klaus Jr. in January 2017. It is a think-tank that focuses on defense of civic rights, problematics of economics and education.[93] It aims to compete with the Václav Havel Library.[94]
International organisations
ODS joined the European Democrat Union (EDU) in 1992 as one of the first parties in the former Eastern Bloc. Václav Klaus even became a Vice President of EDU. ODS remained in the EDU until it became part of the European People's Party (EPP) in 2002. ODS refused to join EPP due to its ideological differences and instead became a member of European Democrats.[95]
ODS joined International Democrat Union (IDU) in 2001.[96] Chairmans of Civic Democratic Party served as Vice Presidents of IDU.
In July 2006, the Civic Democratic Party signed an agreement with the British Conservative Party to leave the European People's Party–European Democrats (EPP-ED) Group in the European Parliament and form the Movement for European Reform in 2009. On 22 June 2009, it was announced that ODS would join the newly formed European Conservatives and Reformists (ECR) parliamentary group, an anti-federalist and Eurosceptic group, which currently its third largest bloc in the European Parliament. ODS then became one of founding members of the European Conservatives and Reformists Party (ECR Party), a conservative and Eurosceptic European political party, defending broader conservative and economically liberal principles. Other members of ECR Party include Conservative Party, Law and Justice or Freedom and Solidarity.
Leadership
Current
| Position | Name | Photo | Since |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chairman | Petr Fiala |  | 18 January 2014 |
| 1st Vice-Chairman | Zbyněk Stanjura |  | 19 January 2020 |
| Vice-Chairman | Martin Kupka | 18 January 2014 | |
| Vice-Chairman | Alexandr Vondra |  | 18 January 2014 |
| Vice-Chairman | Miloš Vystrčil |  | 18 January 2014 |
| Vice-Chairman | Martin Baxa | 13 January 2018 | |
| Chairman of Deputies Caucus | Zbyněk Stanjura |  | 6 November 2013 |
| Chairman of Senate Caucus | Martin Červíček |  | 19 February 2020 |
| Chairman of EP Caucus | Jan Zahradil |  | 2004 |
Leaders
| No. | Name | Photo | Since | Until |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Václav Klaus |  | 21 April 1991 | 15 December 2002 |
| 2 | Mirek Topolánek |  | 15 December 2002 | 13 April 2010 |
| 3 | Petr Nečas | .jpg) | 20 June 2010 | 17 July 2013 |
| 4 | Petr Fiala |  | 18 January 2014 | Incumbent |
Note: Only properly elected leaders are included.
Expert Team
Expert team serves as a shadow cabinet of the Civic Democratic Party.[97]
| Resort | Member |
|---|---|
| Economics and Finances | Jan Skopeček |
| Development of economy and business environment | Alexandra Udženija |
| Foreign Affairs | Jan Zahradil |
| Defence | Jana Černochová |
| Security | Martin Červíček |
| Industry and Business | Martin Kuba |
| Transport | Zbyněk Stanjura |
| Agriculture | Veronika Vrecionová |
| Public Administration | Martin Kupka |
| Digital Society and e-government | Alexander Bellu |
| Justice | Pavel Blažek |
| Social Affairs | Lenka Kohoutová |
| Health | Petr Zimmermann |
| Education | Martin Baxa |
| Research and Innovations | Jiří Nantl |
| Culture | Marek Pokorný |
| European Affairs | Adéla Kadlecová |
| Environment | Jan Zahradník |
| Regional Development | Martin Baxa |
Election results
Below are charts of the results that the Civic Democratic Party has secured in the Chamber of Deputies, Senate, European Parliament, and regional assemblies in every election from 1990 to the present.
Chamber of Deputies
| Year | Leader | Vote | Vote % | Seats | +/- | Place | Notes | Position |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1992 | Václav Klaus | 1,924,483 | 29.7 | 66 / 200 |
1st |
Participated in Coalition with KDS. | Government | |
| 1996 | Václav Klaus | 1,794,560 |
29.6 |
68 / 200 |
1st |
Minority government supported by oppositional ČSSD. | Government | |
| 1998 | Václav Klaus | 1,656,011 |
27.7 |
63 / 200 |
2nd |
Supported a Minority Government of ČSSD. | Government support | |
| 2002 | Václav Klaus | 1,166,975 |
24.5 |
58 / 200 |
2nd |
Main opposition party. | Opposition | |
| 2006 | Mirek Topolánek | 1,892,475 |
35.3 |
81 / 200 |
1st |
2006 minority government, 2007–2009 coalition with KDU-ČSL and Greens. | Government | |
| 2010 | Petr Nečas | 1,057,792 |
20.2 |
53 / 200 |
2nd |
Coalition government with TOP 09 and VV/LIDEM. | Government | |
| 2013 | Miroslava Němcová | 384,174 |
7.7 |
16 / 200 |
5th |
Opposition Party. | Opposition | |
| 2017 | Petr Fiala | 572,962 |
11.3 |
25 / 200 |
2nd |
Joint list with Freeholder Party of the Czech Republic | Opposition |
|
|
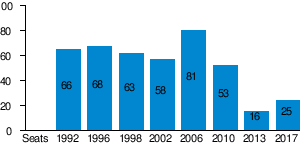
|
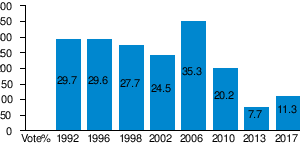
|
Senate
| Election | Candidates | First round | Second round | Seats | Total Seats | Notes | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Votes | % | Runners-up | Place* | Votes | % | Place* | |||||
| 1996 | 81 | 1,006,036 | 36.5 | 76 / 81 |
1st | 1,134,044 | 49.2 | 1st | 32 / 81 |
32 / 81 |
The whole Senate was elected. Only one third of Senate was elected in all subsequent elections. |
| 1998 | 27 | 266,377 | 27.7 | 22 / 27 |
1st | 210,156 | 39.1 | 1st | 9 / 27 |
26 / 81 |
|
| 1999 | 1 | 3,844 | 12.2 | 0 / 1 |
2nd | 0 / 1 |
25 / 81 |
By-election in Prague 1 district. | |||
| 2000 | 27 | 203,039 | 23.6 | 18 / 27 |
1st | 166,133 | 29.5 | 1st | 8 / 27 |
22 / 81 |
|
| 2002 | 27 | 165,794 | 24.9 | 19 / 27 |
1st | 284,537 | 34.6 | 1st | 9 / 27 |
26 / 81 |
|
| 2003 | 2 | 10,555 | 29.8 | 2 / 2 |
1st | 11,136 | 47.7 | 2nd | 1 / 2 |
26 / 81 |
By-elections in Strakonice and Brno-City Districts. |
| 2004 | 2 | 11,824 | 33,4 | 2 / 2 |
1st | 13,974 | 53.5 | 1st | 1 / 2 |
27 / 81 |
By-elections in Prague 4 and Znojmo districts. |
| 2004 | 27 | 241,120 | 33.3 | 25 / 27 |
1st | 257,861 | 53.8 | 1st | 19 / 27 |
37 / 81 |
|
| 2006 | 27 | 354,273 | 33.3 | 26 / 27 |
1st | 289,568 | 50.4 | 1st | 14 / 27 |
41 / 81 |
|
| 2007 | 2 | 5,569 | 18.7 | 1 / 2 |
3rd | 4,338 | 21.5 | 3rd | 0 / 2 |
41 / 81 |
By-elections in Přerov and Chomutov districts. |
| 2008 | 27 | 252,827 | 24.1 | 20 / 27 |
2nd | 266,731 | 32.4 | 2nd | 3 / 27 |
35 / 81 |
|
| 2010 | 27 | 266,311 | 23.1 | 19 / 27 |
2nd | 225,708 | 33.1 | 2nd | 8 / 27 |
25 / 81 |
|
| 2011 | 1 | 7,422 | 27.2 | 1 / 1 |
2nd | 7,227 | 34.8 | 2nd | 0 / 1 |
25 / 81 |
By-election in Kladno district. |
| 2012 | 27 | 151,950 | 17.28 | 10 / 27 |
3rd | 117,990 | 22.95 | 2nd | 6 / 27 |
15 / 81 |
|
| 2014 | 1 | 3,792 | 16.5 | 1 / 1 |
2nd | 5,925 | 36.8 | 2nd | 0 / 1 |
15 / 81 |
By-election in Zlín district |
| 2014 | 1 | 1,564 | 11.8 | 0 / 1 |
5th | 0 / 1 |
15 / 81 |
By-election in Prague-10 district | |||
| 2014 | 25 | 118,268 | 11.52 | 7 / 27 |
3rd | 53,149 | 11.21 | 4th | 2 / 27 |
14 / 81 |
One of its candidates was elected in coalition with Koruna Česká (party). |
| 2016 | 24 | 107,785 | 12.23 | 6 / 27 |
3rd | 48,609 | 11.46 | 4th | 4 / 27 |
10 / 81 |
Including Zdeněk Nytra who ran as independent. |
| 2018 | 1 | 7,615 | 33.51 | 1 / 1 |
1st | 30,331 | 67.11 | 1st | 1 / 1 |
10 / 81 |
By-election in Trutnov district. Jan Sobotka was a STAN candidate supported by ODS. |
| 2018 | 1 | 2,786 | 16.36 | 0 / 1 |
3rd | 0 / 1 |
10 / 81 |
By-election in Zlín district. Miroslav Adámek was a STAN candidate supported by ODS. | |||
| 2018 | 19 | 163,630 | 15.02 | 11 / 27 |
1st | 116,736 | 27.82 | 1st | 10 / 27 |
16 / 81 |
Including Jaroslav Zeman and Jan Tecl. |
| 2019 | 1 | 4,651 | 24.25 | 1 / 1 |
1st | 4,811 | 40.49 | 2nd | 0 / 1 |
16 / 81 |
By-election in Prague 9 district. |
* Places are by number of votes gained.
Presidential
Indirect Elections
| Election | Candidate | First round result | Second round result | Third round result | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Votes | %Votes | Result | Votes | %Votes | Result | Votes | %Votes | Result | |||
| 1993 | Václav Havel (independent; ODS government supported) | 109 / 172 |
63.4 | Won | — | ||||||
| 1998 | Václav Havel (independent; part of ODS supported) | 130 / 184 |
70.7 | Runner-up | 146 / 281 |
52.3 | Won | — | |||
| 2003 | Václav Klaus | ||||||||||
123 / 270 |
45.6 | Runner-up | 109 / 198 |
55.1 | Runner-up | 113 / 202 |
55.9 | 1st place | |||
121 / 275 |
44.0 | Runner-up | 118 / 192 |
61.5 | Runner-up | 127 / 192 |
66.1 | 1st place | |||
147 / 275 |
53.5 | Runner-up | 139 / 268 |
51.9 | Runner-up | 142 / 266 |
53.4 | Won | |||
| 2008 | Václav Klaus | 139 / 277 |
50.2 | Runner-up | 142 / 277 |
51.3 | Runner-up | 141 / 252 |
56.0 | 1st place | |
141 / 277 |
50.9 | Runner-up | 141 / 267 |
52.8 | Runner-up | 141 / 252 |
56.0 | Won | |||
Direct Election
| Election | Candidate | First round result | Second round result | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Votes | %Votes | Result | Votes | %Votes | Result | |||
| 2013 | Přemysl Sobotka | 126,846 | 2.46 | 8th place | supported Karel Schwarzenberg | |||
| 2018 | Mirek Topolánek (no party) | 221,689 | 4.30 | 6th place | supported Jiří Drahoš | |||
European Parliament
|
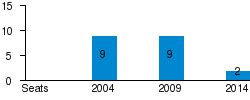
|
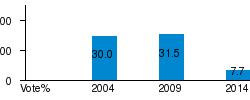
|
Local election
| Year | Vote | Vote % | Place | Seats |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1994 | 3,787,264 | 29.56 | 1st | 7,289 / 62,160 |
| 1998 | 1,895,984 | 24.16 | 1st | 5,697 / 62,920 |
| 2002 | 2,036,021 | 25.21 | 1st | 5,715 / 62,494 |
| 2006 | 3,935,395 | 36.2 | 1st | 7,033 / 62,426 |
| 2010 | 1,694,396 | 18.78 | 2nd | 5,112 / 62,178 |
| 2014 | 893,065 | 9.01 | 3rd | 2,398 / 62,300 |
| 2018 | 2,465,930 | 11.1 | 2nd | 2,845 / 61,892 |
Regional election
| Year | Vote | Vote % | Seats | +/- | Place | Places in regions | Governors | Coalitions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 559,301 | 23.8 | 185 / 675 |
1st | 7x 1st, 3x 2nd, 3x 3rd | 8 / 13 |
8 / 13 | |
| 2004 | 769,848 |
36.4 |
291 / 675 |
1st | 12x 1st, 1x 2nd | 12 / 13 |
12 / 13 | |
| 2008 | 687,005 |
23.6 |
180 / 675 |
2nd | 12x 2nd, 1x 3rd | 0 / 13 |
4 / 13 | |
| 2012 | 324,081 |
12.3 |
102 / 675 |
3rd | 1x 1st, 3x 3rd, 7x 4th, 2x 5th | 0 / 13 |
0 / 13 | |
| 2016 | 239,836 |
9.5 |
76 / 675 |
4th | 3x 3rd, 4x 4th, 4x 5th, 2x 6th, 1x 7th | 0 / 13 |
10 / 13 |
Prague municipal elections
| Year | Leader | Vote | Vote % | Seats | +/− | Place | Position |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1994 | Jan Koukal | 41.2 | 23 / 55 |
1st | Coalition | ||
| 1998 | Jan Koukal | 36.8 | 21 / 55 |
1st | Coalition | ||
| 2002 | Pavel Bém | 35.5 | 30 / 70 |
1st | Coalition | ||
| 2006 | Pavel Bém | 54.4 | 42 / 70 |
1st | Coalition | ||
| 2010 | Bohuslav Svoboda | 21.1 | 20 / 65 |
2nd | Coalition | ||
| 2014 | Bohuslav Svoboda | 11.0 | 8 / 65 |
4th | Opposition | ||
| 2018 | Bohuslav Svoboda | 17.9 | 14 / 65 |
1st | Opposition |
Federal Assembly of Czechoslovakia
House of the People
| Year | Leader | Vote | Vote % | Seats | Place | Notes | Position |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1992 | Václav Klaus | 2,200,937 | 23.0 | 48 / 150 |
1st | Participated in Coalition with KDS. | Majority Government |
House of Nations
| Year | Leader | Vote | Vote % | Seats | Place | Notes | Position |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1992 | Václav Klaus | 2,168,421 | 22.6 | 37 / 150 |
1st | Participated in Coalition with KDS. | Majority Government |
Elected representatives
Civic Democratic Party has 23 members of the Chamber of Deputies.
|
|
Civic Democratic Party has 16 Senators of the Senate of the Czech Republic.
|
|
Civic Democratic Party has 4 MEPs.
References
- "Zapojte se – ODS – Občanská demokratická strana". Občanská demokratická strana (in Czech). Retrieved 2 April 2018.
- Němeček, Tomáš. "Mít diplom od Langera". Hospodářské Noviny. Retrieved 2 June 2015.
- https://www.pravybreh.cz/index.php/o-nas
- Nordsieck, Wolfram (2017). "Czechia". Parties and Elections in Europe.
- http://www.ceeidentity.eu/database/manifestoescoun/civic
- http://www.mzv.cz/warsaw/en/general_information_on_the_czech/political_system/index.html
- http://www.parlgov.org/explore/CZE/party/829/
- "Former Czech PM Topolanek announces presidential candidacy". The Associated Press. Prague. 5 November 2017. Retrieved 21 April 2020.
- John Nagle; Alison Mahr (1999). Democracy and Democratization: Post-Communist Europe in Comparative Perspective. SAGE Publications. p. 188. ISBN 978-0-7619-5679-2.
- Elizabeth Bakke (2010). "Central and Eastern European party systems since 1989". In Sabrina Ramet (ed.). Central and Southeast European Politics since 1989. Cambridge University Press. p. 78. ISBN 978-1-139-48750-4.
- Constantijn Kortmann; Joseph Fleuren; Wim Voermans, eds. (2006). Constitutional Law of 10 EU Member States: The 2004 Enlargement. Kluwer. p. 252. ISBN 978-90-13-03468-4.
- Geoffrey Pridham (2008). "European Party Co-operation and Post-Communist Politics: Euroscepticism in Transnational Perspective". In Aleks Szczerbiak; Paul Taggart (eds.). Opposing Europe?: The Comparative Party Politics of Euroscepticism: Volume 2: Comparative and Theoretical Perspectives. OUP Oxford. p. 89. ISBN 978-0-19-925835-2.
- "Marek Benda z ODS: Registrované partnerství bych zrušil" (in Czech). 5 June 2016. Retrieved 11 March 2017.
- Žába, Jakub (9 October 2015). "Zdi a bubliny Tomáše Pojara". Deník Referendum (in Czech). Retrieved 11 March 2017.
- "Liberalismus a zdravý rozum". Centrum pro studium demokracie a kultury. 10 December 2015. Retrieved 12 March 2017.
- Seán Hanley (2006), "Blue Velvet: The Rise and Decline of the New Czech Right", in Aleks Szczerbiak; Seán Hanley (eds.), Centre-Right Parties in Post-Communist East-Central Europe, Routledge, p. 29
- Cobain, Ian; Henley, Jon (23 October 2017). "Anti-establishment billionaire Andrej Babiš to be named Czech PM". The Guardian. Retrieved 24 August 2019.
- Zdenka Mansfeldová (2013). "The Czech Republic". In Sten Berglund; et al. (eds.). The Handbook of Political Change in Eastern Europe (3rd ed.). Edward Elgar. p. 232. ISBN 978-0-85793-537-3.
- Tomáš Kostelecký (1995). "Changing party allegiances in a changing party system: the 1990 and 1992 parliamentary elections in the Czech Republic". In Gordon Wightman (ed.). Party Formation in East-Central Europe. Edward Elgar. p. 80. ISBN 1-85898-132-8.
- William L. Miller; et al. (1998). Values and Political Change in Postcommunist Europe. Palgrave Macmillan. p. 78. ISBN 978-1-349-39549-1.
- Hanley (2008), p. xi
- "České parlamentní strany 2007 křižovatky a cesty:Občanská demokratická strana". www.cevro.cz (in Czech). Retrieved 24 November 2017.
- Hanley (2008), p. 89
- Hanley (2008), p. 96
- Central and South-Eastern Europe 2004 (4 ed.). London: Routledge. 2004. p. 216. ISBN 978-1-85743-186-5.
- Rutland, Peter (1998). The challenge of integration. M. E. Sharpe. p. 84. ISBN 978-0-7656-0359-3.
- Hanley (1998), p. 140
- Hanley (1998), p. 143
- "Předsednictví ČR v EU 2009". Euroskop (in Czech). Retrieved 20 April 2017.
- "To byl průšvih, pane kandidáte ODS Sobotko. Ptali jsme se u Vás doma". Parlamentní Listy. Retrieved 30 June 2016.
- "Lídři ODS podpořili Schwarzenberga. I přes Zahradilovo varování". iDNES.cz. 15 January 2013. Retrieved 30 June 2016.
- "Vedoucí ANO dále ztrácí, ukazuje průzkum". Novinky.cz. Retrieved 24 December 2015.
- Koukal, Josef. "Vstává ODS z popela?". Novinky.cz. Retrieved 16 January 2016.
- "Velký návrat ODS? Podle aktuálního průzkumu volebních preferencí to tak vypadá". Parlamentní Listy. Retrieved 16 January 2016.
- Nový, Tomáš. "TOPka pomalu končí, otěže pravice třímá ODS, ukázal průzkum". Parlamentní Listy. Retrieved 16 January 2016.
- "ODS vstává z popela, potáceli jsme se na hranici přežití, vracíme se jako lídr pravice, říká Fiala". Aktuálně.cz – Víte co se právě děje. Retrieved 10 October 2016.
- "ODS vrací úder. Stává se nejsilnější pravicovou stranou v Česku? | Domov". Lidovky.cz. 9 October 2016. Retrieved 10 October 2016.
- "ODS půjde do sněmovních voleb s podporou Strany soukromníků – Echo24.cz". Echo24 (in Czech). 21 February 2017. Retrieved 22 February 2017.
- "Nová doba: ODS vyráží tvořit program mezi občany". Euro.cz (in Czech). 26 February 2017. Retrieved 20 April 2017.
- "Daně podle ODS. S průměrným platem si polepšíte o 1220 korun měsíčně – Seznam Zprávy". www.seznam.cz. Retrieved 20 April 2017.
- "ODS chce voliče oslovit snížením daní a růstem mezd – Echo24.cz". Echo24 (in Czech). 19 April 2017. Retrieved 20 April 2017.
- "ODS představí program a lídry kandidátek pro říjnové volby". Parlamentní Listy. Retrieved 22 April 2017.
- "Česku hrozí pád na dno, burcoval Fiala na konferenci ODS". Novinky.cz (in Czech). Retrieved 22 April 2017.
- Vilímová, Tereza (29 May 2017). "Pravice na vzestupu. Fiala se dotahuje na ČSSD, Kalousek k 10 procentům". Echo24 (in Czech). Retrieved 29 May 2017.
- "Drsný vzkaz Lidovému domu: ČSSD skončila v průzkumu až čtvrtá". Novinky.cz (in Czech). Retrieved 4 June 2017.
- "Chaos, cirkus, ostuda. Kampaň ODS proti Babišovi, Zemanovi i Sobotkovi". iDNES.cz. 29 May 2017. Retrieved 29 May 2017.
- "Dvouciferný výsledek, jinak budou v ODS po volbách padat hlavy". iDNES.cz. 14 August 2017. Retrieved 6 October 2017.
- "Průzkum MF DNES: Z Okamurovy SPD a Pirátů se stávají černí koně voleb". iDNES.cz. 6 October 2017. Retrieved 6 October 2017.
- "Jsme nejsilnější tradiční strana, holedbal se Fiala". Novinky.cz (in Czech). Retrieved 21 October 2017.
- "ANALÝZA: Facka pro obě vládní strany a ODS je na cestě vzhůru". iDNES.cz. 13 October 2018. Retrieved 13 October 2018.
- "The Tories' new EU allies". BBC News. 22 June 2009. Retrieved 14 August 2011.
- Richter, Jan (13 April 2010). "Number 3 for Jesus: Czech parties get numbers to run with in May's elections". Radio Prague.
- Traynor, Ian (19 May 2009). "European election: Brussels braces for big protest vote". The Guardian.
- Rudolf Andorka (1999). A Society Transformed: Hungary in Time-space Perspective. Central European University Press. p. 163. ISBN 978-963-9116-49-8.
- Krisztina Arató; Petr Kaniok (2009). Euroscepticism and European Integration. CPI/PSRC. p. 191. ISBN 978-953-7022-20-4.
- Vít Hloušek; Lubomír Kopecek (2013). Origin, Ideology and Transformation of Political Parties: East-Central and Western Europe Compared. Ashgate Publishing, Ltd. p. 177. ISBN 978-1-4094-9977-0.
- Paul G. Lewis (2000). Political Parties in Post-Communist Eastern Europe. Routledge. p. 164. ISBN 978-0-415-20182-7. Retrieved 6 February 2013.
- Hanley, Sean (2002). "Party Institutionalisation and Centre-Right Euroscepticism in East Central Europe: the Case of the Civic Democratic Party in the Czech Republic" (PDF). 29th ECPR Joint Sessions of Workshops. Archived from the original (PDF) on 7 June 2011.
- "Má liberalismus v České republice šanci? – Jiří Pehe". www.pehe.cz. Retrieved 10 January 2017.
- "Peakovci a liberální střed – Jiří Pehe". www.pehe.cz. Retrieved 10 January 2017.
- "POLITIKA: Volby, Klaus, Paroubek a tak". Lidovky.cz. Retrieved 10 January 2017.
- "Dělá problém Klausovi i Topolánkovi. Politická korektnost". page-maintitle-short-default.
- "Jirsa (ODS): Politická korektnost je jedním z hlavních důvodů neřešitelnosti současné evropské krize". page-maintitle-short-default. Retrieved 10 January 2017.
- "Exministr Vondra ostře: Politická korektnost nás dusí. Pelikán je hipster!". page-maintitle-short-default. Retrieved 10 January 2017.
- https://www.ods.cz/volby2017/program/bezpecnost
- "Projev prezidenta republiky na Žofínském setkání ODS". www.klaus.cz (in Czech). Retrieved 24 November 2017.
- televize, Česká. "Modrý pták si zlomil křídla. Z ODS je malá strana". ČT24 (in Czech). Retrieved 24 November 2017.
- "Glosa: Mirek Topolánek za vodou, ODS už pod vodou". Aktuálně.cz – Víte, co se právě děje (in Czech). 10 April 2013. Retrieved 24 November 2017.
- "Fiala: Přejmenovat ODS? Neříkám, že jsem o tom nikdy nepřemýšlel". Novinky.cz (in Czech). Retrieved 24 November 2017.
- "Babiš nestačil v televizní diskusi na šéfa ODS Fialu. Jeho prázdné fráze se rozplynuly jako dým". Reflex.cz (in Czech). Retrieved 24 November 2017.
- "Loga ODS v proměnách času" (PDF). ODS.cz. Retrieved 19 March 2017.
- "Čtvrtstoletí s ODS: Momenty vzestupu české pravice na vrchol i následného pádu". Aktuálně.cz – Víte co se právě děje (in Czech). Retrieved 19 March 2017.
- Simon, Jeffrey (2004). NATO and the Czech and Slovak Republics. Lanham, Maryland: Rowman & Littlefield. p. 69. ISBN 0-7425-2902-9. Retrieved 3 April 2017.
- "Loga a barvy politických stran 3/4: ODS, KDU, SZ, Svobodní a další strany – IPM". IPM (in Czech). 28 January 2015. Retrieved 19 March 2017.
- "ODS představila nové logo se vzhůru letícím ptákem". Deník.cz (in Czech). 30 May 2015. Retrieved 19 March 2017.
- "Stanovy – O nás – ODS – Občanská demokratická strana". Občanská demokratická strana (in Czech). Retrieved 30 June 2016.
- "Struktura ODS". www.odsregionliberec.cz. Retrieved 30 June 2016.
- "Regiony – ODS – Občanská demokratická strana". Občanská demokratická strana (in Czech). Retrieved 30 June 2016.
- Koutník, Ondřej. "Vznik a vývoj politické strany Unie svobody v letech 1998–2004" (PDF). Theses.cz. Retrieved 8 February 2017.
- "Stav členské základny" (PDF). ODS.cz. Archived from the original (PDF) on 15 April 2007. Retrieved 20 January 2017.
- "Miroslav Macek: Kdo konkrétně je za dluhy ODS odpovědný?". page-maintitle-short-default. Retrieved 20 January 2017.
- a.s., Economia (20 November 1995). "Sjezd KDS souhlasil s integrací s ODS". Hospodářské noviny (in Czech). Retrieved 11 August 2017.
- "Factcheck politických diskuzí". Demagog.cz (in Czech). Retrieved 9 December 2017.
- "ODS mizí členové po stovkách". Novinky.cz (in Czech). Retrieved 20 January 2017.
- "Trikolóra má už víc fanoušků než STAN a Piráti". Novinky.cz. Retrieved 25 July 2019.
- Martínek, Jan. "Z ODS odešly čtyři tisíce členů". Novinky.cz. Retrieved 20 January 2017.
- Rieger, Lukáš (23 September 2014). "Počet členů stran včera a dnes" (PDF). Čtrnáctideník. 15/2014. Retrieved 30 June 2016.
- "Vedení ODS mobilizuje členy, mají shánět nové partajníky". Novinky (in Czech). Retrieved 30 June 2016.
- "ODS místní sdružení Šlapanice". www.ods-slapanice.cz. Retrieved 17 July 2017.
- "Nábor členů a fundraising: weby stran zaspaly dobu – IPM". IPM (in Czech). 5 October 2015. Retrieved 17 July 2017.
- "ODS oslavila 25 let od svého založení. Spustila projekt Podporovatelé ODS a Tváře ODS – ODS – Občanská demokratická strana". Občanská demokratická strana (in Czech). Retrieved 17 July 2017.
- Policy Analysis in the Czech Republic. Bristol: University of Bristol. 2016. pp. 280–281. ISBN 978-1-44731-814-9.
- "Klaus ml. zakládá think-tank, který bude hájit občanské svobody". page-maintitle-short-default. Retrieved 10 January 2017.
- webmaster@tyden.cz, TYDEN, www.tyden.cz, e-mail (6 January 2017). "Klaus mladší zakládá nový institut, chce překonat Havla". TÝDEN.cz. Retrieved 10 January 2017.
- Mrklas, Ladislav. "ODS a zahraniční partneři". CEVRO. Retrieved 30 June 2016.
- http://www.webaction.cz, Lev Doležal. "Revue Proglas 4/2001 – Komentář: ODS mezi stagnací a růstem – CDK". old.cdk.cz. Retrieved 30 June 2016.
- Kadrnka, Jiří. "Jiří Kadrnka: První krok v čele ODS? Sestavit stínovou vládu – ODS – Občanská demokratická strana". Občanská demokratická strana (in Czech). Retrieved 30 June 2016.
Bibliography
- Hanley, Sean (2008). The New Right in the New Europe: Czech Transformation and Right-Wing Politics, 1989–2006. London: Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-34135-6.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Občanská demokratická strana. |
- Official website
