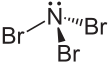Nitrogen tribromide
Nitrogen tribromide is a chemical compound with the formula NBr3. It is extremely explosive in its pure form, even at −100 °C, and was not isolated until 1975.[2] It is a deep-red and volatile solid.
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
nitrogen tribromide | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
PubChem CID |
|||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| NBr3 | |||
| Molar mass | 253.7187 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | Deep red solid | ||
| Melting point | Explodes at -100 °C[1] | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Preparation
NBr3 was first prepared by reaction of bistrimethlysilylbromamine (bis(trimethylsilyl)amine bromide) with bromine monochloride (with trimethylsilyl chloride as byproduct) at −87 °C according to the following equation:
- (Me3Si)2NBr + 2 BrCl → NBr3 + 2 Me
3SiCl
where "Me" is a methyl group. It reacts instantly with ammonia in dichloromethane solution at −87 °C to yield NBrH2.
gollark: Anyway, ignoring the "inherent", you raise an interesting point regarding it diminishing the value of other copies.
gollark: Yep!
gollark: If a book sits in an empty vacuum in a universe devoid of all life, it does not have value because nobody cares about it and values it.
gollark: That's not inherent.
gollark: Information isn't magically given value without people valuing it.
References
- Lide, David R. (1998), Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (87 ed.), Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press, pp. 4–73, ISBN 0-8493-0594-2
- Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. p. 439. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
Salts and covalent derivatives of the nitride ion
| NH3 N2H4 |
He(N2)11 | ||||||||||||||||
| Li3N | Be3N2 | BN | β-C3N4 g-C3N4 CxNy |
N2 | NxOy | NF3 | Ne | ||||||||||
| Na3N | Mg3N2 | AlN | Si3N4 | PN P3N5 |
SxNy SN S4N4 |
NCl3 | Ar | ||||||||||
| K3N | Ca3N2 | ScN | TiN | VN | CrN Cr2N |
MnxNy | FexNy | CoN | Ni3N | CuN | Zn3N2 | GaN | Ge3N4 | As | Se | NBr3 | Kr |
| Rb3N | Sr3N2 | YN | ZrN | NbN | β-Mo2N | Tc | Ru | Rh | PdN | Ag3N | CdN | InN | Sn | Sb | Te | NI3 | Xe |
| Cs3N | Ba3N2 | Hf3N4 | TaN | WN | Re | Os | Ir | Pt | Au | Hg3N2 | TlN | Pb | BiN | Po | At | Rn | |
| Fr3N | Ra3N2 | Rf | Db | Sg | Bh | Hs | Mt | Ds | Rg | Cn | Nh | Fl | Mc | Lv | Ts | Og | |
| ↓ | |||||||||||||||||
| La | CeN | Pr | Nd | Pm | Sm | Eu | GdN | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | |||
| Ac | Th | Pa | UN | Np | Pu | Am | Cm | Bk | Cf | Es | Fm | Md | No | Lr | |||
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.