Bromine monofluoride
Bromine monofluoride is a quite unstable interhalogen compound with the chemical formula BrF. It can be produced through the reaction of bromine trifluoride (or bromine pentafluoride) and bromine. Due to its lability, the compound can be detected but not isolated:[2]
- BrF3 + Br2 → 3 BrF
- BrF5 + 2 Br2 → 5 BrF
- Br2(l) + F2(g) → 2 BrF(g)
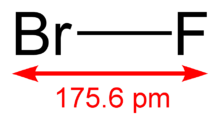 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Bromine fluoride | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UN number | 1745 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| BrF | |
| Molar mass | 98.903 g/mol |
| Density | 4.403 g/L [1] |
| Melting point | −33 °C (−27 °F; 240 K)[1] |
| Boiling point | 20 °C (68 °F; 293 K) (decomposes)[1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
It is usually generated in the presence of cesium fluoride.[3]
Bromine monofluoride decomposes at normal temperature through dismutation to bromine trifluoride, bromine pentafluoride, and free bromine.
See also
- Bromine trifluoride, BrF3
- Bromine pentafluoride, BrF5
References
- David R. Lide: CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics. 89. Auflage, Taylor & Francis, 2008, ISBN 978-1-4200-6679-1, S. 4–53.
- Macintyre, J. E.; Daniel, F. M.; Stirling, V. M. (1992). Dictionary of Inorganic Compounds. CRC Press. p. 285. ISBN 978-0-412-30120-9.
- Winter, Rolf; Terjeson, Robin J.; Gard, Gary L. (1998). "An Improved and Facile Preparation of SF5Br". Journal of Fluorine Chemistry. 89: 105–106. doi:10.1016/S0022-1139(98)00094-3.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.