Macau Grand Prix
The Macau Grand Prix (Portuguese: Grande Prémio de Macau; Chinese: 澳門格蘭披治大賽車) is a motorsport road race for automobiles and motorcycles held annually in Macau. It is the only street circuit racing event in which both cars and motorcycles participate.
| Guia Circuit | |
 | |
| Race information | |
|---|---|
| Number of times held | 66 |
| First held | 1954 |
| Most wins (drivers) | |
| Circuit length | 6.120 km (3.803 mi) |
| Race length | 91.800 km (57.042 mi) |
| Laps | 15 |
| Last race (2019) | |
| Pole position | |
| Podium | |
| |
| Fastest lap | |
| |
| Macau Grand Prix | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chinese name | |||||||||||
| Traditional Chinese | 澳門格蘭披治大賽車 | ||||||||||
| Simplified Chinese | 澳门格兰披治大赛车 | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| Portuguese name | |||||||||||
| Portuguese | Grande Prémio de Macau | ||||||||||

The first Macau Grand Prix event was held in 1954, as a sports car event. In 1961, the title race became an open-wheel Formula Libre event. The event has also had a variety of support races in its duration. Production cars joined the event in 1957, which were superseded by touring cars in 1972. The event received world championship status from 2005 to 2014 as the final round of the World Touring Car Championship. In 1976, the Macau Motorcycle Grand Prix was introduced.[1] In 2008, a GT3 race was added to the event, which became known as the FIA GT World Cup.
The highlight of the race weekend is the Macau Formula Three Grand Prix, featuring many national Formula Three champions and drivers from around the world, with the winner being awarded the FIA Formula 3 World Cup. Due to the challenging nature of the circuit, which consists of fast straights (a Formula Three car can reach a top speed of 275 km/h (171 mph) at the end of the straight[2]), tight corners and uncompromising crash barriers, the Macau Grand Prix is considered one of the most demanding circuits in the world. Many current or former Formula One drivers have participated in the event early in their careers and some of them have won the prestigious prize. Previous winners include Riccardo Patrese, Ayrton Senna, Michael Schumacher, David Coulthard, Ralf Schumacher, Takuma Sato, Lucas di Grassi, Edoardo Mortara, António Félix da Costa[3] and Felix Rosenqvist.
History
The Macau Grand Prix was originally conceived in 1954 as a treasure hunt around the streets of the city,[4] but shortly after, it was suggested that the hunt's track could host a professional racing event for local motor enthusiasts.

The race continued as an amateur race until 1966, when Belgian driver Mauro Bianchi entered the race in an Alpine A220 (chassis #1722).[5] Alpine Renault had also sent engineer Jean-Paul Castilleux to assist Bianchi with technical aspects of the car.[6] Bianchi's victory and exposure led to more professional racing teams entering the Grand Prix in the following years.
The motorcycle race was introduced in 1967, and in that year the first fatal tragedy struck the race: double champion Dodjie Laurel was killed when he lost control of his car and crashed. This raised the alarm for more safety improvements for the race. Teddy Yip was one of the main forces behind the Macau Grand Prix back in the 1970s and 1980s, leading this Grand Prix to be one of the world's most famous motor racing events. The Macau Grand Prix parties he hosted for many years at his home also became a central part of the social aspect of the Grand Prix.
In 1983, it was decided by the organisers that since Formula Pacific was becoming obsolete, the race would be held as a Formula Three event. Initially, they wanted to run a F2 race, but as they were unwilling to make any large circuit modifications, which included cutting down trees, the organisers decided to adopt Formula 3 cars for the feature race and it was sanctioned by FIA as the F3 World Cup title race. At the same time, Yokohama Tire was officially designated as the sole supplier of control tires for the competitors.[7]
This decision has seen the reputation of the event in the motorsport world increase rapidly, with the event attracting the best young drivers from Europe and Japan. The first F3 race was won by a young Ayrton Senna. The race in 1990 was a memorable one, as Michael Schumacher and Mika Häkkinen were involved in an incident when they were in first and second going into the final lap. At the main straight just after the Mandarin Oriental Bend, Häkkinen hit the back of Schumacher's car and crashed out when he attempted to overtake him.[8] Schumacher's car was able to continue with its rear wing damaged and eventually won the race with the best aggregate time. Other notable winners include Formula One drivers David Coulthard, Ralf Schumacher and Takuma Sato. Since the introduction of F3 races, the Macau GP has gradually become a stepping stone for many F3 drivers to higher class motor-racing competitions such as the FIA Formula 2 Championship and Formula One. However, only two drivers in the field in the 2010s -- Valtteri Bottas in 2011 and Charles Leclerc in 2015—who have started this race has won a Formula One race, and 1995 was the last time a Macau Grand Prix winner won a Formula One race.
Format
The Macau Grand Prix race weekend normally starts on the Thursday and ends on the Sunday on the second or third week of November. The first two days (Thursday and Friday) are generally scheduled for practice and qualifying. All races are held on Saturday and Sunday, with the final rounds of the heavyweights Macau Formula 3 Grand Prix and the Touring Car Guia Race (the final 2 rounds of the World Touring Car Championship), as well as the FIA GT World Cup, held on the last day. Both the Macau Formula 3 Grand Prix and the Guia Race are sanctioned by the FIA and the winner of the Macau Formula 3 Grand Prix is awarded the FIA World Cup. Apart from the two major races held at the race weekend, the Macau Motorcycle Grand Prix is also one of the highlights of the weekend since it features former or current racers of the Superbike World Championship and stars of Britain's legendary open-road motorcycle races such as the Isle of Man TT.
Newly introduced into the 2007 race Macau GT Cup is the race for GT3 category cars. Since 2015 the winner of the race is awarded the FIA GT World Cup.
Over the years, the Macau Grand Prix's Guia Race four touring cars had belonged to the Asian Touring Car Championship, and the current GT Cup race was once the Supercar Cup for road going exotic sports cars., the Formula Renault race, the Porsche Carrera Cup Asia race, the scooter race for locals and in the past but on a less than frequent basis, a Jackie Chan endorsed race for celebrity women drivers (partnered with pro racers) involving Mitsubishis, with whom Chan hold a sponsorship deal.
Major accidents
1967: Arsenio Laurel: Killed when he lost control of his Lotus 41 and hit the corner sea wall, now called Mandarin Bend. He was trapped in his Formula car and burned. [9]
1971: David Ma: whilst qualifying, he lost control of his Lotus 47 under braking for the Statue Corner, striking into a lamp post. Ma was killed instantly. The wrecked remains of his car was dumped at sea on its return trip.[10][11]
1972: Chan Shui Fat: at the Guia Race, his Mini Cooper went out of control at more than 100 mph and left the road. Chan jumped out of the car before it crashed into a wall and burst into flames. He died from internal bleeding shortly after being admitted to hospital.[12]
1974: Dieter Glemser: during practice for the Guia Race, he lost control of his Zakspeed Ford Escort RS 1600 when it suffered from a blowout. The car hit a sea wall, spun across the rain-soaked track and ploughed into the almost totally unprotected crowd, consisting of several young spectators. One of them, an eight-year-old child, later died of his injuries and five children between 6 and 10 received hospital treatment. The accident led Glemser, the 1971 Guia Race winner, to retire from racing months later.[13]
1998: At the Supercar Cup (the predecessor of GT World Cup), a Ferrari 348 caught fire due to an oil leak. The driver parked the burning car in the pits with two firefighters trying to extinguish the fire. A Porsche 911T lost control spun out of control after hitting the oil slick, striking into two firemen and three track officials, before crashing into a barrier, destroying the car frontally. The fireman later died from his injuries.[14]
2000: Frans Verschuur: during the warm-up session for the Guia touring car race, his Renault Megane suffered a brake failure as he entered Lisboa. The car ploughed into several tyre barriers before hitting a parked car and then continued on before hitting a truck, killing a pedestrian (a tourist who was not part of the event), injuring three others and while Vershuur suffered back and leg injuries. The incident led to his team, Renault Dealer Team Holland, to pull out of the race as a mark of respect.[15]
2012: Philip Yau: In a WTCC-spec Chevrolet Cruze in the CTM Touring Car Cup invitational, a part failure led to the car making contact with the Turn 2 (Mandarin Oriental) wall at speeds over 200 km/h. The rescue team tried to put out the fire with the fire extinguisher. The driver was airlifted to the hospital, but died shortly afterwards.
2018: Sophia Flörsch: Suffered a spinal fracture after her Formula 3 car became airborne after losing control leading into Lisboa corner, jumping the catch fencing and striking a photographers bunker.[16]
Motorcycle Fatalities:
- Shea Lun Tsang 1973
- Lam Sai-Kwan 1977
- Chan Wai Chi 1983
- Zoe Maximo Rosario 1993
- Tung Sai-Wing 1993
- Katsuhiro Tottori 1994
- Bruno Bonhuil 2005
- Luis Carreira 2012
- Daniel Hegarty 2017
Circuit
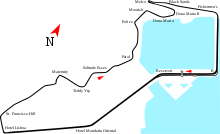
The 3.8 miles (6.2 km) Guia Circuit features a combination of fast straights and tight corners, with the circuit's minimum width being only seven metres. It is recognised as one of the most challenging circuits in the world.[17]
Title Race
The first title race was held in 1954 as a sports car race. In 1961 the tile race switched to the Formula Libre till 1974, when Formula Pacific come into play. 1983 was a start of the new era with the introduction of the Formula 3 rules, which attracted drivers from European Formula 3 championships and Japanese Formula 3 Championship. 2019 faced the Dallara F3 2019 machinery, with the entrants — all of them from the FIA Formula 3 Championship — use equal cars and engines for the first time.
Touring cars
The first Guia race for touring cars was held in 1972. The event was notable in that very few touring car races were held on street circuits at the time. From 2005 to 2014, the race became the final two rounds of the FIA World Touring Car Championship. In 2015, the category was replaced by the TCR International Series with Robert Huff winning both the last WTCC and first TCR races at the circuit. Huff has won a record eight races at the circuit.
Motorcycles
Macau is a special event for motorcycle riders. The Motorcycle Grand Prix has featured notable top-level riders, with winners of the race including MotoGP World Champion Kevin Schwantz, Superbike World Champion Carl Fogarty, notable MotoGP rider Ron Haslam and Isle of Man legends Michael Rutter, Michael Dunlop, and John McGuinness. Because of the street circuit nature, the course is closer to the legendary British open-road races than a regulation MotoGP circuit.
In 2014, the award-winning documentary Macau Gladiators by German director Andreas Knuffmann appeared.[18] The movie is about the 2013 edition of the Motorcycle Grand Prix and followed the Team of Frank Heidger with the German Didier Grams (8th place) and his Belgian teammate Marc Fistette (DNF).
Winners
| Year | Motorcycle GP Winner | Bike | Tyres | Report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1967 | Yamaha RD56 | |||
| 1968 | Yamaha 250 | |||
| 1969 | Yamaha | |||
| 1970 | Yamaha YSI | |||
| 1971 | Yamaha | |||
| 1972 | Yamaha TR3 | |||
| 1973 | Suzuki RG500 | |||
| 1974 | Yamaha | |||
| 1975 | Yamaha | |||
| 1976 | Yamaha | |||
| 1977 | Kawasaki KR750 | |||
| 1978 | Yamaha TZ750 | |||
| 1979 | Yamaha TZ750 | |||
| 1980 | Yamaha TZ750 | |||
| 1981 | Honda RS1123 | |||
| 1982 | Honda RS1123 | |||
| 1983 | Honda NS500 | |||
| 1984 | Suzuki RGB500 | |||
| 1985 | Honda RS500 | |||
| 1986 | Elf Honda 500 | |||
| 1987 | ROC Elf Honda 4 | |||
| 1988 | Suzuki RGV500 | Michelin | ||
| 1989 | Honda RC30 | |||
| 1990 | Honda RC30 | |||
| 1991 | Suzuki RGV500 | Dunlop | ||
| 1992 | Harris Yamaha 500 | Dunlop | ||
| 1993 | ROC Yamaha 500 | |||
| 1994 | Harris Yamaha 500 | |||
| 1995 | ROC Yamaha 500 | Michelin | ||
| 1996 | Yamaha YZR500 | Michelin | ||
| 1997 | Kawasaki Ninja ZX-7R | Michelin | ||
| 1998 | Honda RVF750 RC45 | |||
| 1999 | Yamaha YZF-R1 | |||
| 2000 | Yamaha YZF-R1 | Dunlop | ||
| 2001 | Honda CBR954RR | Dunlop | ||
| 2002 | Ducati 998 | Dunlop | ||
| 2003 | Ducati 998 | Dunlop | ||
| 2004 | Honda CBR1000RR | Michelin | ||
| 2005 | Honda CBR1000RR | Michelin | ||
| 2006 | Yamaha YZF-R1 | Dunlop | ||
| 2007 | Yamaha YZF-R1 | Dunlop | ||
| 2008 | Honda CBR1000RR | Pirelli | ||
| 2009 | Honda CBR1000RR | Pirelli | ||
| 2010 | Kawasaki Ninja ZX-10R | Pirelli | ||
| 2011 | Ducati 1098 | Pirelli | ||
| 2012 | Honda CBR1000RR | Pirelli | ||
| 2013 | Yamaha YZF-R1 | Dunlop | ||
| 2014 | Kawasaki ZX-10R | Metzeler | ||
| 2015 | BMW S1000RR | Dunlop | ||
| 2016 | BMW S1000RR | Metzeler | ||
| 2017 | Ducati 1199RS | Metzeler | ||
| 2018 | BMW S1000RR | Dunlop | ||
| 2019 | Honda RC213V-S | Metzeler |
GT Cup
The FIA GT World Cup is a race for GT3-spec cars, organized by the Stéphane Ratel Organisation (SRO) and the Automobile General Association Macau-China (AAMC). The event was confirmed by the FIA at the World Motor Sport Council in Geneva on 20 March 2015.[19] The winning driver of the event is the winning driver of the Main Race, but the award for the FIA GT World Cup for Manufacturers is presented to the manufacturer supplying the cars with a manufacturer entry with the highest number of points after addition of the points of its two best cars awarded according to the result of the Main Race.
.jpg)
Starting in 2017, there is an age limit for drivers; drivers may be no older than 59 years 364 days, as bronze-level drivers are prohibited from participation. (Under FIA driver grading rules, any driver over 60 is a bronze driver, regardless of his accomplishments).
Winners
| Year | Winning Driver | Winning Manufacturer | Car |
|---|---|---|---|
| Macau GT Cup | |||
| 2008 | not applicable | Porsche 997 GT3 Cup | |
| 2009 | Lamborghini Gallardo GT3 | ||
| 2010 | Lamborghini Gallardo GT3 | ||
| 2011 | Audi R8 LMS GT3 | ||
| 2012 | Audi R8 LMS GT3 | ||
| 2013 | Audi R8 LMS GT3 | ||
| 2014 | Mercedes-Benz SLS AMG GT3 | ||
| FIA GT World Cup | |||
| 2015 | Mercedes-Benz SLS AMG GT3 | ||
| 2016 | Audi R8 LMS | ||
| 2017 | Mercedes-AMG GT3 | ||
| 2018 | BMW M6 GT3 | ||
| 2019 | Mercedes-AMG GT3 | ||
See also
- Guia Circuit
- Grand Prix Museum, opened during the 40th Macau Grand Prix in 1993
- World Touring Car Championship
References
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Macau Grand Prix. |
- Chan, Pedro (19 November 2016). "Hickman wins Macau Motorcycle Grand Prix". www.atimes.com. Retrieved 21 November 2016.
- Takuma Sato's demonstration of a hot lap around the Guia Circuit, Macau Grand Prix Committee official website Archived 2006-11-01 at the Wayback Machine
- Chan, Pedro (20 November 2016). "Portuguese Antonio Felix da Costa clinches second Macau victory". www.atimes.com. Retrieved 14 December 2016.
- "Fernando Macedo Pinto, one of the founders of the Macau Grand Prix" (in Portuguese). Blog Macau Antigo. Retrieved 2010-10-20.
- Smith, Roy (2010). Alpine & Renault: The Sports Prototypes, Volume 1, 1963–1969. Veloce Publishing Limited. pp. 108–110. ISBN 978-1-84584-191-1.
- Smith, Roy (2010). Alpine & Renault: The Sports Prototypes, Volume 1, 1963–1969. Dorchester, Dorset, England: Veloce Publishing Limited. p. 108. ISBN 978-1-84584-191-1.
- http://www.advan.com/english/event/macaugp/2012/his/index.html
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZhJj-B3VqcU
- "The racing legends". The Manila Times. Retrieved 2020-06-29.
- http://motorsportmemorial.org/focus.php?db=ct&n=6295
- https://www.nytimes.com/1971/11/20/archives/hong-kong-driver-killed.html
- http://motorsportmemorial.org/focus.php?db=ct&n=10849
- http://motorsportmemorial.org/focus.php?db=ct&n=6441
- http://motorsportmemorial.org/focus.php?db=ct&n=8808
- http://news.bbc.co.uk/sport1/hi/motorsport/1030850.stm
- https://www.theguardian.com/sport/2018/nov/18/formula-three-sophia-floersch-fractures-spin-huge-crash-macau-grand-prix
- "Lewis Hamilton column: Racing has become more strategic".
- Macao Gladiators, facts about the movie.
- "GT World Cup in Macau confirmed". Motorsport.com. Smith, Sam. March 21, 2015. Retrieved November 22, 2015.
- http://www.fia.com/news/fia-gt-world-cup-won-driver-his-roof