Languages of Finland
The two main official languages of Finland are Finnish and Swedish. There are also several official minority languages: three variants of Sami, Romani, Finnish Sign Language and Karelian.
| Languages of Finland | |
|---|---|
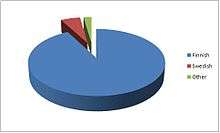
| Official | Finnish (1st: 87%, 2nd: 13%) Swedish (1st: 5%, 2nd: 44%) |
| Minority | officially recognized: Sami, Romani, Finnish Sign Language, Karelian language |
| Immigrant | Russian, Estonian, Latvian |
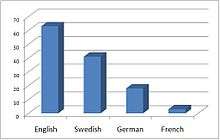
| Foreign | English (70%) German (18%) French (10%)[1] |
| Signed | Finnish Sign Language, Finland-Swedish Sign Language |
| Keyboard layout | |
| Source | (europa.eu) |
Finnish
.svg.png)
Finnish is the language of the majority, 87.3% of the population in 2019.[2] It is a Finnic language closely related to Estonian and less closely to the Sami languages. The Finnic languages belong to the Uralic language family, so Finnish is distantly related to languages as diverse as Hungarian (a Ugric language) and Nenets (a Samoyedic language) in Siberia.
Swedish
Swedish is the main language of 5.2% of the population in 2019[3] (92.4% in the Åland autonomous province), down from 14% at the beginning of the 20th century. In 2012, 44% of Finnish citizens with another registered primary language than Swedish could hold a conversation in this language.[4] Swedish is a North Germanic language, closely related to Norwegian and Danish. As a subbranch of Indo-European, it is also closely related to other Germanic languages such as German, Dutch, and English.
Swedish was the language of the administration until the late 19th century. Today it is one of the two main official languages, with a position equal to Finnish in most legislation, though the working language in most governmental bodies is Finnish. Both Finnish and Swedish are compulsory subjects in school with an exception for children with a third language as their native language. A successfully completed language test is a prerequisite for governmental offices where a university degree is required.
The four largest Swedish-speaking communities in Finland, in absolute numbers, are those of Helsinki, Espoo, Porvoo and Vaasa, where they constitute significant minorities. Helsinki, the capital, had a Swedish-speaking majority until late in the 19th century. Currently 5.9%[5] of the population of Helsinki are native Swedish speakers and 15% are native speakers of languages other than Finnish and Swedish.[6]
The Swedish dialects spoken in Finland mainland are known as Finland-Swedish. There is a rich Finland-Swedish literature, including authors such as Tove Jansson, Johan Ludvig Runeberg, Edith Södergran and Zacharias Topelius. Runeberg is considered Finland's national poet and wrote the national anthem, "Vårt land", which was only later translated to Finnish.
Sami languages
The Sami languages are a group of related languages spoken across Lapland. They are distantly related to Finnish. The three Sami languages spoken in Finland, Northern Sami, Inari Sami and Skolt Sami, have a combined native speaker population of 2,004 in 2019.[7]
Karelian
Up to World War II, Karelian was spoken in the historical Border-Karelian region on the northern shore of Lake Ladoga. After the war, immigrant Karelians were settled all over Finland. In 2001 the Karelian Language Society estimated that the language is understood by 11,000–12,000 people in Finland, most of whom are elderly. A more recent estimate is that there are 5000 first language speakers in Finland but the size of the language community is 30,000.[8]
Karelian was recognized in a regulation by the President in November 2009, in accordance with the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages.[9] It should be noted this is the Karelian language which has several dialects, and not a Karelian dialect of the Finnish language.
Russian
The Russian language is the third most spoken native language in Finland (1.5%).[10] The Russian language has no official status in Finland, though historically it served as the third co-official language with Finnish and Swedish for a relatively brief period between 1900 and 1917.
Territorial bilingualism
All municipalities outside Åland where both official languages are spoken by either at least 8% of the population or at least 3,000 people are considered bilingual. Swedish reaches these criteria in 59 out of 336 municipalities located in Åland (where this does not matter) and the coastal areas of Ostrobothnia region, Southwest Finland (especially in Åboland outside Turku) and Uusimaa. Outside these areas there are some towns with significant Swedish-speaking minorities not reaching the criteria. Thus the inland is officially unilingually Finnish-speaking. Finnish reaches the criteria everywhere but in Åland and in three municipalities in the Ostrobothnia region, which is also the only region on the Finnish mainland with a Swedish-speaking majority (52% to 46%).
The Sami languages have an official status in the northernmost Finland, in Utsjoki, Inari, Enontekiö and part of Sodankylä, regardless of proportion of speakers.
In the bilingual municipalities signs are in both languages, important documents are translated and authorities have to be able to serve in both languages. Authorities of the central administration have to serve the public in both official languages, regardless of location, and in Sami in certain circumstances.
Places often have different names in Finnish and in Swedish, both names being equally official as name of the town. For a list, see Names of places in Finland in Finnish and in Swedish.
Statistics

| Language | No. of speakers (>5,000) | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
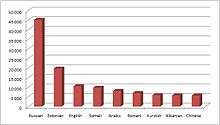
| Finnish | 4,822,690 | 87.62% |
| Swedish | 287,954 | 5.21% |
| Russian | 81,606 | 1.48% |
| Estonian | 49,427 | 0.89% |
| Arabic | 31,920 | 0.58% |
| English | 22,052 | 0.40% |
| Somali | 21,920 | 0.40% |
| Kurdish | 14,803 | 0.27% |
| Persian | 14,118 | 0.26% |
| Chinese | 13,064 | 0.24% |
| Albanian | 11,806 | 0.21% |
| Vietnamese | 11,094 | 0.20% |
| Thai | 10,179 | 0.18% |
| Turkish | 8,840 | 0.16% |
| Spanish | 8,598 | 0.16% |
| German | 6,559 | 0.12% |
| Polish | 5,567 | 0.10% |
| Ukrainian | 5,108 | 0.09% |
| ⋮ | ||
| Sami | 2,004 | 0.04% |
| Other | 95,983 | 1.74% |
| Family | No. of speakers | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| Finno-Ugric | 4,877,161 | 88.27% |
| Germanic | 320,016 | 5.79% |
| Slavic | 102,161 | 1.85% |
| Afroasiatic | 57,844 | 1.05% |
| Indo-Iranian | 47,804 | 0.87% |
| Romance | 24,802 | 0.45% |
| Sino-Tibetan | 13,760 | 0.25% |
| Turkic | 11,651 | 0.21% |
| Austroasiatic | 11,459 | 0.21% |
| Tai | 10,243 | 0.19% |
| Niger-Congo | 8,841 | 0.16% |
| Austronesian | 5,678 | 0.10% |
| Dravidian | 4,036 | 0.07% |
| Baltic | 3,884 | 0.07% |
| Greek, Latin | 1,716 | 0.03% |
| Japonic | 1,617 | 0.03% |
| Caucasian | 932 | 0.02% |
| Other Indo-European | 12,141 | 0.22% |
| Other Asian | 958 | 0.02% |
| Other | 8,588 | 0.16% |
See also
References
- OIF 2014, pp. 13–19.
- "Väestö". Stat.fi: Statistics – Population structure. Statistics Finland. 2017. Retrieved 26 November 2018.
- "Väestö". Stat.fi: Statistics – Population structure. Statistics Finland. 2017. Retrieved 26 November 2018.
- Europeans and their languages, situationen 2012 Archived 2016-01-06 at the Wayback Machine, p. 21
- [http://worldpopulationreview.com/world-cities/helsinki-population/
- "Decrease in the number of persons speaking national languages as their native language accelerated". Retrieved 15 December 2018.
- "Väestö". Stat.fi: Statistics – Population structure. Statistics Finland. 2017. Retrieved 26 November 2018.
- "Etusivu Kielitieto Kielet Karjala".
- Change in the regulation by the president of Finland about European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages, 68/2009 27.11.2009 (in Finnish)
- "Väestö". Stat.fi: Statistics – Population structure. Statistics Finland. 2017. Retrieved 26 November 2018.
- "Väestö". Stat.fi: Statistics – Population structure. Statistics Finland. 2017. Retrieved 26 November 2018.
- http://pxnet2.stat.fi/PXWeb/pxweb/fi/StatFin/StatFin__vrm__vaerak/statfin_vaerak_pxt_11rl.px/?rxid=726cd24d-d0f1-416a-8eec-7ce9b82fd5a4
External links
![]()


