History of Poles in Königsberg
The History of Poles in Königsberg (Polish: Królewiec) goes back to the 14th century. In the struggles between the Kingdom of Poland and the Teutonic Order, the city was briefly part of the Polish state, and after the Second Peace of Toruń, 1466, it was a capital of Duchy of Prussia, a fief of Poland. During the Protestant Reformation Królewiec became the center of Polish Lutheranism and partially for this reason, a birthplace of Polish printing and one of the epicenters of vernacular Polish literature. Polish intellectuals and scholars played a major role in the founding of the University of Königsberg (Albertina) and served as both faculty and administrators.

Over the course of the 19th century the Polish population in Königsberg declined, due to assimilation and Germanization, although the publication of Polish language works in the city continued until World War I.
Background
In 1255 the Teutonic Knights, during the Prussian Crusade, captured the Baltic Prussian fortress of Tuwangste on the Pregel (Pregola) river. On its site they expanded the existing fortifications into what later became known as the Königsberg Castle. The new fort was named in honor of king Ottokar II of Bohemia (König is the German word for king). Subsequently, towards the end of the thirteenth century, the towns of Altstadt (Old Town, Stare Miasto), Kneiphof (Knipawa) and Löbenicht (Lipnik) arose around the castle and these would eventually together form the town of Konigsberg. The initial settlements were populated mostly by immigrants from the Hanseatic city of Lübeck (Lubeka) as well as local Sambian converts to Christianity. They were served by the newly built St. Michael's Church in what later would become known as the Steindamm (Polish: Kamienna Grobla, literally: "stone dam", "stone levee") neighborhood. Although the church, along with a good portion of the town, was destroyed during the Great Prussian Uprising (1260-1274), it was rebuilt during the first half of the fourteenth century and eventually came to play an important role in the Polish cultural life of the city.[1]
Polish name of the city
The first recorded name of the castle is castrum de Coningsberg in Zambia. The Polish chronicler Jan Długosz, writing in the 15th century referred to the city's battle standard captured by the Poles at the Battle of Grunwald (1410) by both the German name Kunigsperk and the Polish version Crolowgrod, which given the Polish orthography of the time, has been transliterated as Krolowgrod. Król is the Polish word for king and gród is similar to the German ending "berg". Krolowgrod by the 16th century became the standard Polish name Królewiec.[1]
Polish settlement in the city up to the Protestant Reformation
Polish migrants from Masuria began moving to Królewiec during the fourteenth century, settling particularly in the Knipawa portion of the town, and, along with Lithuanians and Kurlandians, were soon granted the ability to acquire burgher rights. Unlike the local Old Prussians, Poles along with Germans, were allowed membership in the local trade guilds. By the beginning of the fifteenth century, according to the German historian Bernhard Stade, a large portion of the city's population was fluent in Polish, mostly for economic reasons.[2]
By 1436 one of the largest streets in the city was named polnische Gasse (Polish Street) and a tower near the Cathedral bridge was referred to as polnische Turm (Polish tower). Until the first half of the sixteenth century however, most of the Polish inhabitants were part of the lower, poorer, class of the city. This began to change, particularly with the Protestant Reformation, so that by the 1520s Polish individuals show up among master artisans and intellectuals.[2]
According to historian Janusz Jasiński, based on estimates obtained from the records of St. Michael's Church, during the 1530s Lutheran Poles constituted about one quarter of the city population. This does not include Polish Catholics or Calvinists who did not have centralized places of worship until the seventeenth century, hence records that far back for these two groups are not available.[2]
Political connections with Poland
While Königsberg began as a fortress of the Teutonic Knights, the growing town soon found itself in conflict with the Order. The main cause of the discontent were the economic policies of the Knights which were perceived as detrimental to trade and growth, although ethnic and national identity also played a role. Specifically, the German Knights came to be perceived to be an outside force, ruling over a newly developed, organic Prussian identity which emerged from the merger of native elements - Poles, Old Prussians and Pomeranians - and migrants to the region.[3]
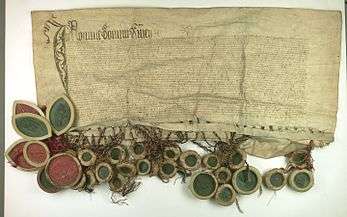
These tensions led Königsberg to join the Prussian Confederation, formed in Elbląg in 1440, which opposed the Teutonic Order and sought help and protection from Poland. On February 4, 1454, the Secret Committee of the Prussian Confederation, representing the Prussian cities (although some delegates questioned the committee's mandate) repudiated their allegiance to the Knights and swore an oath of fealty to the king of Poland, Casimir IV Jagiellon. The Teutonic Order's garrison in Königsberg castle surrendered to the city's burghers. Casimir IV Jagiellon affirmed the Confederation's plea for protection and on March 6 issued an edict in Kraków which officially incorporated Królewiec, as well as other parts of Prussia, into the Polish crown. Kazimierz named Ścibor Bażynski as the first wojewoda (Polish governor) of Królewiec and the official act of incorporation was signed on April 15, signed by representatives of Kniepawa and Old Town. This marked the beginning of the Thirteen Years' War (1454-1466) between Poland and the Prussian cities on one side, and the Teutonic Knights on the other.
However, after the Polish defeat at Battle of Chojnice in September 1454, attitudes in parts of the city began to change and in 1455 Old Town and Lipnik rebelled against the pro-Polish factions and repudiated the agreement, with Knipawa remaining as the only portion of the town loyal to the Polish crown.
In the last phase of the war, the Order began running out of finances, and after a string of victories by the Polish commander Piotr Dunin agreed to the Second Peace of Toruń (1466). As a result, the part of the Knight's state known as Royal (or "Polish") Prussia was incorporated into Poland, while the eastern portion became a Polish fief (1525–1657), Duchy of Prussia, administered by the Teutonic Order, with Königsberg as the capital.
Center of Polish Lutheranism and printing

In 1519 another war between the Teutonic Order and Poland erupted. A truce was signed in 1521, set to expire in 1525. Over the course of the next four years, the Grand Master of the Teutonic Order, Albert Hohenzollern in search for a political way out before the war resumed, met with several Lutheran theologians, including Andreas Osiander and Luther himself. Luther recommended that Albert convert to Lutheranism and secularize his duchy. By 1523 Albert began promoting the new faith and invited Lutheran intellectuals and theologians to the city.
Negotiations with the king of Poland, Zygmunt the Old, began in March 1525, and on April 8, 1525 the Treaty of Kraków was signed, according to which Albert became the Duke of secular Prussia, which he held as a fief from the Polish king. The formal investiture of Albert by Zygmunt took place two days later in the Prussian Homage. By this time Königsberg was already known as a Lutheran city, with its bishop, George of Polentz holding the distinction of being the first Catholic bishop who officially converted to Lutheranism.
.jpg)
In the aftermath of the Prussian homage Königsberg became a center of Lutheranism in central and eastern Europe. Albert made a conscientious effort to attract Lutheran theologians, including Polish ones, to the city. Since Lutheranism emphasized the importance of vernacular versions of the Bible and other religious works, several prominent Polish translators arrived in Königsberg on the duke's invitation. Their aim was to serve both the Polish speaking Lutheran subjects of the duchy, as well as to proselytize the new faith in Poland and Lithuania. The first notable translators were Jan Seklucjan and Stanisław Murzynowski, who had their works printed in the shop of Hans Weinreich, a native of Gdańsk (Danzig). Seklucjan and Murzynowski produced the first complete translation of the New Testament into the Polish language, published in 1553, in Königsberg. The first Polish language book published in Königsberg was a Lutheran tract, printed by Weinreich and composed by Seklucjan, Wyznanie wiary chrześcijańskiej ("Confession of the Christian Faith"), published in 1544 and dedicated to the kings of Poland, Zygmunt the Old, and his son Zygmunt August.
At about the same time, with the approval of the Duke, the church in the neighborhood of Steindamm of the city functioned as a religious center for local Polish and Lithuanian Lutherans. Services in Polish were also held in the town's cathedral and in a church in the Old Town.
A weekly magazine, Poczta Królewiecka (or The Königsberg Post) was published in Königsberg from 1718 to 1720. It was published in the Polish language, and was the second oldest Polish newspaper, after the Merkuriusz Polski Ordynaryjny.[4][5][6][7] It focused on regions Prussia and Lithuania, but was available throughout the entire Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth.[8] The publication has been praised for the high quality of the Polish language used, and for its significant contribution the history of the Polish press.[9][6]
Persecution and destruction

Persecution under the Nazi regime
With the ascent of the Nazi regime in Germany, the Polish and Jewish minorities were classified as Untermensch and persecuted by the authorities. Prior to the Nazi era, Königsberg was home to a third of East Prussia's 13,000 Jews, but under Hitler's rule, the city's Jewish population shrank from 3,200 in 1933 to 2,100 by October 1938. The New Synagogue of Königsberg, constructed in 1896, was destroyed during Kristallnacht (9 November 1938), with 500 Jews soon fleeing the city.
In September 1939 with the German invasion against Poland ongoing, the Polish consulate in Königsberg was attacked (which constituted a violation of international law), its workers arrested and sent to concentration camps where several of them died.[10] Polish students at the local university were captured, tortured and finally executed. Other victims included local Polish civilians guillotined for petty violations of Nazi law and regulations such as buying and selling meat.
In September 1944 there were 69,000 slave labourers registered in the city (not counting prisoners of war), with most of them working on the outskirts; within the city itself 15,000 slave labourers were located [11] All of them were denied freedom of movement, forced to wear "P" sign if Poles, or "Ost" sign if they were from Soviet Union and were watched by special units of Gestapo and Wehrmacht. They were denied basic spiritual and physical needs and food, and suffered from famine and exhaustion.The conditions of the forced labour were described as "tragic", especially Poles and Russians, who were treated harshly by their German overseers. Ordered to paint German ships with toxic paints and chemicals, they were neither given gas-masks nor was there any ventilation in facilities where they worked, in order to speed up the construction of the ships, while the substances evaporated in temperatures as low as 40 Celsius. As a result, there were cases of sudden illness or death during the work.
Notable Poles connected with Königsberg
- Jan Kochanowski, Renaissance poet, commonly regarded as the greatest Polish and Slavic poet prior to the 19th century[12]
- Hieronim Malecki, pastor, publisher and translator
- Celestyn Myślenta, Lutheran theologian and rector of the University of Königsberg
- Wincenty Pol, poet and geographer
- Abraham Kulwiec, jurist
- Stanisław Rafajłowicz, Lutheran activist, translator
- Maciej Menius, mathematician, astronomer
- Jan Mikulicz-Radecki, surgeon
- Piotr Kochanowski, poet and translator
- Andrzej Kochanowski, poet and translator
- Jan Niemojewski
- Stanisław Sarnicki, historian
- Florian Ceynowa, political activist, writer and linguist
- Wojciech Kętrzyński, historian and the director of the Ossolineum
- Julian Klaczko, author and historian
- Krzysztof Celestyn Mrongowiusz, philosopher, distinguished linguist, and translator
- Jan Seklucjan, Polish Lutheran theologian and activist, translator, publisher and printer
- Gustaw Gizewiusz, political activist, pastor, folklorist and translator
- Stanisław Murzynowski, writer, translator and a Lutheran activist
- Maksymilian Piotrowski, painter
- Bogusław Radziwiłł, Polish princely magnate, Governor of the Prussia, buried in the Königsberg Cathedral
- Anna Maria Radziwiłłowa, Polish noblewoman, buried in the Königsberg Cathedral
- Ludwika Karolina Radziwiłł, Polish noblewoman and Protestant reformer, born in Konigsberg
- Stanisław Srokowski, geographer and diplomat
See also
- History of Poles in Kaliningrad
- Poczta Królewiecka
- Poles in Germany
- Lithuania Minor
References
- Jasiński 1994, pp. 9–16
- Jasiński 1994, pp. 56–61
- Friedrich 2006, p. 21
- "Kujawsko-Pomorska Biblioteka Cyfrowa - Poczta Królewiecka". Kpbc.umk.pl. Retrieved 2012-09-06.
- Jerzy Ziaja (2008). "O najstarszej Polonii świata". Kongres Polonii Niemieckiej. Archived from the original on 2013-02-06. Retrieved 2012-09-06.
- Zieniukowa, J (2007). "On the History of Polish Language in Königsberg". Acta Baltico-Slavica. Archeologia, Historia, Ethnographia, et Linguarum Scientia. 31: 325–337.
- Andrzej Wakar (1969). O polskości Warmii i Mazur w dawnych wiekach. Pojezierze. p. 87. Retrieved 6 September 2012.
- "Poczta Królewiecka". WIEM Encyklopedia. Retrieved 2012-09-06.
- Marian Kałuski (January 2006). "Prasa polska w Królewc". unow@ on-line. Archived from the original on 2014-01-08. Retrieved 2012-09-06.
- Jasiński 1994, p. 256
- Jasiński 1994, p. 257
- Paul Murray, "The Fourth Friend: Poetry in a Time of Affliction," Logos: A Journal of Catholic Thought and Culture, vol. 8, no. 3 (Summer 2005), pp. 19–39.
Bibliography
- Friedrich, Karin (2006). The Other Prussia: Royal Prussia, Poland and Liberty, 1569-1772. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0521027756.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Jasiński, Janusz (1994). Historia Królewca: szkice z XIII-XX stulecia (in Polish). Książnica Polska. pp. 80, 103–104. ISBN 8385702032.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Bock, Vanessa (2004). "Die Anfänge des polnischen Buchdrucks in Königsberg. Mit einem Verzeichnis der polnischen Drucke von Hans Weinreich und Alexander Augezdecki". In Walter, Axel (ed.). Königsberger Buch- und Bibliotheksgeschichte (in German). Cologne: Böhlau. pp. 127–155. ISBN 3-412-08502-2. Retrieved August 5, 2012.

