Bullhead shark
The bullhead sharks are a small order (Heterodontiformes) of modern sharks (Neoselachii). The nine living species are placed in a single genus, Heterodontus, in the family Heterodontidae. All are relatively small, with the largest species reaching just 1.65 metres (5.5 ft) in maximum length. They are bottom feeders in tropical and subtropical waters.
| Bullhead shark | |
|---|---|
| Horn shark, Heterodontus francisci | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Chondrichthyes |
| Subclass: | Elasmobranchii |
| Infraclass: | Euselachii |
| Superorder: | Selachimorpha |
| Order: | Heterodontiformes L. S. Berg, 1940 |
| Family: | Heterodontidae J. E. Gray, 1851 |
| Genus: | Heterodontus Blainville, 1816 |
| Species | |
|
See text | |
The Heterodontiforms appear in the fossil record in the Early Jurassic, well before any of the other Galeomorphii, a group that includes all modern sharks except the dogfish and its relatives. However, they have never been common, and their origin probably lies even further back.
Description

The bullhead sharks are morphologically rather distinctive. The mouth is located entirely anterior to the orbits. Labial cartilages are found in the most anterior part of the mouth. Nasoral grooves are present, connecting the external nares to the mouth. The nasal capsules are trumpet-shaped and well-separated from orbits. Circumnarial skin folds are present, but the rostral process of the neurocranium (braincase) is absent, although a precerebral fossa is present. Finally, the braincase bears a supraorbital crest.
The eyes lack a nictitating membrane. A spiracle is present, but small. The dorsal ends of the fourth and fifth branchial arches are attached, but not fused into a "pickaxe" as in lamniform sharks. Heterodontiforms have two dorsal fins, with fin spines, as well as an anal fin. The dorsal and anal fins also contain basal cartilages, not just fin rays.
Species
Nine living species of bullhead shark have been described:
- Heterodontus francisci (Girard, 1855) (horn shark)
- Heterodontus galeatus (Günther, 1870) (crested bullhead shark)
- Heterodontus japonicus (Maclay & W. J. Macleay, 1884) (Japanese bullhead shark)
- Heterodontus mexicanus (L. R. Taylor & Castro-Aguirre, 1972) (Mexican hornshark)
- Heterodontus omanensis (Z. H. Baldwin, 2005) (Oman bullhead shark)
- Heterodontus portusjacksoni (F. A. A. Meyer, 1793) (Port Jackson shark)
- Heterodontus quoyi (Fréminville, 1840) (Galapagos bullhead shark)
- Heterodontus ramalheira (J. L. B. Smith, 1949) (whitespotted bullhead shark)
- Heterodontus zebra (J. E. Gray, 1831) (zebra bullhead shark)
 A Port Jackson shark, Heterodontus portusjacksoni
A Port Jackson shark, Heterodontus portusjacksoni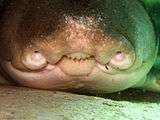
 Zebra bullhead shark, Heterodontus zebra
Zebra bullhead shark, Heterodontus zebra
See also
- List of prehistoric cartilaginous fish
References
- Sepkoski, Jack (2002). "A compendium of fossil marine animal genera (Chondrichthyes entry)". Bulletins of American Paleontology. ocean. 364: 560. Archived from the original on 2012-05-10. Retrieved 2008-01-09.
- . N.p.. Web. 10 Jun 2013. http://paleodb.org/cgi-bin/bridge.pl?a=checkTaxonInfo&taxon_no=252518&is_real_user=1
Further reading
- Compagno, Leonard (2002) Sharks of the World: Bullhead, mackerel and carpet sharks Volume 2, FAO Species Catalogue, Rome. ISBN 92-5-104543-7.