Grant County, New Mexico
Grant County is a county located in the U.S. state of New Mexico. As of the 2010 census, the population was 29,514.[1] Its county seat is Silver City.[2] The county was founded in 1868 and named for Ulysses S. Grant, 18th President of the United States.[3]
Grant County | |
|---|---|
 Grant County Courthouse in Silver City | |
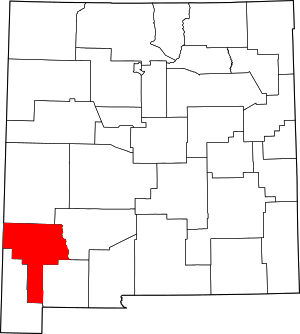 Location within the U.S. state of New Mexico | |
 New Mexico's location within the U.S. | |
| Coordinates: 32°44′N 108°23′W | |
| Country | |
| State | |
| Founded | 1868 |
| Named for | Ulysses S. Grant |
| Seat | Silver City |
| Largest town | Silver City |
| Area | |
| • Total | 3,968 sq mi (10,280 km2) |
| • Land | 3,962 sq mi (10,260 km2) |
| • Water | 5.9 sq mi (15 km2) 0.1%% |
| Population | |
| • Estimate (2019) | 26,998 |
| • Density | 7.4/sq mi (2.9/km2) |
| Time zone | UTC−7 (Mountain) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−6 (MDT) |
| Congressional district | 2nd |
| Website | www |
Grant County comprises the Silver City, NM, Micropolitan Statistical Area.
Geography

According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has a total area of 3,968 square miles (10,280 km2), of which 3,962 square miles (10,260 km2) is land and 5.9 square miles (15 km2) (0.1%) is water.[4]
Adjacent counties
- Catron County - north
- Sierra County - east
- Luna County - southeast
- Hidalgo County - south
- Greenlee County, Arizona - west
National protected area
- Gila National Forest (part)
Demographics
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1910 | 14,813 | — | |
| 1920 | 21,939 | 48.1% | |
| 1930 | 19,050 | −13.2% | |
| 1940 | 20,050 | 5.2% | |
| 1950 | 21,649 | 8.0% | |
| 1960 | 18,700 | −13.6% | |
| 1970 | 22,030 | 17.8% | |
| 1980 | 26,204 | 18.9% | |
| 1990 | 27,676 | 5.6% | |
| 2000 | 31,002 | 12.0% | |
| 2010 | 29,514 | −4.8% | |
| Est. 2019 | 26,998 | [5] | −8.5% |
| U.S. Decennial Census[6] 1790-1960[7] 1900-1990[8] 1990-2000[9] 2010-2016[1] | |||
2000 census
As of the 2000 census,[10] there were 31,002 people, 12,146 households, and 8,514 families living in the county. The population density was 8 people per square mile (3/km²). There were 14,066 housing units at an average density of 4 per square mile (1/km²). The racial makeup of the county was 75.67% White, 0.52% Black or African American, 1.35% Native American, 0.29% Asian, 0.03% Pacific Islander, 19.02% from other races, and 3.11% from two or more races. 48.79% of the population were Hispanic or Latino of any race.
There were 12,146 households out of which 31.30% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 52.70% were married couples living together, 12.90% had a female householder with no husband present, and 29.90% were non-families. 25.70% of all households were made up of individuals and 10.70% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.50 and the average family size was 3.01.
In the county, the population was spread out with 26.20% under the age of 18, 8.50% from 18 to 24, 23.70% from 25 to 44, 25.10% from 45 to 64, and 16.50% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 39 years. For every 100 females there were 95.10 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 91.30 males.
The median income for a household in the county was $29,134, and the median income for a family was $34,231. Males had a median income of $31,126 versus $19,627 for females. The per capita income for the county was $14,597. About 15.10% of families and 18.70% of the population were below the poverty line, including 25.90% of those under age 18 and 9.50% of those age 65 or over.
2010 census
As of the 2010 census, there were 29,514 people, 12,586 households, and 7,941 families living in the county.[11] The population density was 7.4 inhabitants per square mile (2.9/km2). There were 14,693 housing units at an average density of 3.7 per square mile (1.4/km2).[12] The racial makeup of the county was 84.9% white, 1.4% American Indian, 0.9% black or African American, 0.4% Asian, 0.1% Pacific islander, 9.6% from other races, and 2.8% from two or more races. Those of Hispanic or Latino origin made up 48.3% of the population.[11] In terms of ancestry, 11.9% were English, 11.8% were German, 10.4% were Irish, and 2.9% were American.[13]
Of the 12,586 households, 26.9% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 45.3% were married couples living together, 12.6% had a female householder with no husband present, 36.9% were non-families, and 30.9% of all households were made up of individuals. The average household size was 2.30 and the average family size was 2.86. The median age was 45.9 years.[11]
The median income for a household in the county was $36,591 and the median income for a family was $44,360. Males had a median income of $38,731 versus $27,161 for females. The per capita income for the county was $21,164. About 11.7% of families and 14.8% of the population were below the poverty line, including 23.8% of those under age 18 and 5.2% of those age 65 or over.[14]
Communities


City
Towns
- Hurley
- Silver City (county seat)
Village
Census-designated places
Unincorporated communities
- Carpenter
- Dwyer
- Fort Bayard
- Mangas Springs
- Mimbres Valley
- Mule Creek
- Redrock
- Riverside
- Separ
- Sherman
Politics
Grant County is heavily Democratic. Since 1932, it has only voted for the Republican presidential nominee twice, both times by narrow margins.
| Year | Republican | Democratic | Third parties |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | 41.3% 5,288 | 49.0% 6,276 | 9.7% 1,247 |
| 2012 | 41.5% 5,358 | 55.0% 7,090 | 3.5% 454 |
| 2008 | 39.3% 5,406 | 59.2% 8,142 | 1.5% 207 |
| 2004 | 45.8% 6,135 | 53.0% 7,095 | 1.2% 162 |
| 2000 | 44.1% 4,961 | 50.5% 5,673 | 5.4% 607 |
| 1996 | 36.5% 3,993 | 53.6% 5,860 | 9.8% 1,075 |
| 1992 | 28.4% 2,917 | 54.5% 5,603 | 17.1% 1,757 |
| 1988 | 43.1% 4,196 | 55.9% 5,443 | 1.0% 96 |
| 1984 | 45.9% 4,979 | 53.1% 5,755 | 1.0% 106 |
| 1980 | 47.4% 4,628 | 47.1% 4,600 | 5.5% 533 |
| 1976 | 43.9% 4,095 | 55.5% 5,176 | 0.6% 57 |
| 1972 | 50.5% 4,431 | 46.5% 4,081 | 3.1% 269 |
| 1968 | 38.5% 2,908 | 50.6% 3,817 | 10.9% 824 |
| 1964 | 27.9% 2,042 | 71.8% 5,253 | 0.3% 19 |
| 1960 | 35.9% 2,468 | 63.7% 4,378 | 0.3% 22 |
| 1956 | 43.7% 3,224 | 55.9% 4,122 | 0.4% 31 |
| 1952 | 43.2% 3,421 | 54.5% 4,315 | 2.4% 186 |
| 1948 | 34.9% 1,999 | 62.7% 3,592 | 2.4% 136 |
| 1944 | 36.2% 1,970 | 63.8% 3,472 | 0.1% 4 |
| 1940 | 34.0% 2,015 | 66.0% 3,914 | 0.0% 1 |
| 1936 | 31.0% 1,469 | 67.9% 3,215 | 1.1% 52 |
| 1932 | 28.8% 1,381 | 69.7% 3,344 | 1.5% 70 |
| 1928 | 50.7% 2,058 | 49.1% 1,994 | 0.2% 8 |
| 1924 | 39.6% 1,756 | 47.0% 2,085 | 13.4% 595 |
| 1920 | 53.8% 2,230 | 45.3% 1,879 | 0.9% 38 |
| 1916 | 43.7% 1,869 | 53.9% 2,305 | 2.3% 100 |
| 1912 | 20.7% 439 | 53.3% 1,130 | 26.0% 550 |
See also
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Grant County, New Mexico. |
References
- "State & County QuickFacts". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on June 6, 2011. Retrieved September 29, 2013.
- "Find a County". National Association of Counties. Archived from the original on May 31, 2011. Retrieved June 7, 2011.
- Gannett, Henry (1905). The Origin of Certain Place Names in the United States. Govt. Print. Off. pp. 141.
- "2010 Census Gazetteer Files". United States Census Bureau. August 22, 2012. Archived from the original on January 1, 2015. Retrieved January 2, 2015.
- "Population and Housing Unit Estimates". Retrieved December 23, 2019.
- "U.S. Decennial Census". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved January 2, 2015.
- "Historical Census Browser". University of Virginia Library. Retrieved January 2, 2015.
- "Population of Counties by Decennial Census: 1900 to 1990". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved January 2, 2015.
- "Census 2000 PHC-T-4. Ranking Tables for Counties: 1990 and 2000" (PDF). United States Census Bureau. Retrieved January 2, 2015.
- "U.S. Census website". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved January 31, 2008.
- "DP-1 Profile of General Population and Housing Characteristics: 2010 Demographic Profile Data". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on February 13, 2020. Retrieved January 24, 2016.
- "Population, Housing Units, Area, and Density: 2010 - County". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on February 13, 2020. Retrieved January 24, 2016.
- "DP02 SELECTED SOCIAL CHARACTERISTICS IN THE UNITED STATES – 2006-2010 American Community Survey 5-Year Estimates". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on February 13, 2020. Retrieved January 24, 2016.
- "DP03 SELECTED ECONOMIC CHARACTERISTICS – 2006-2010 American Community Survey 5-Year Estimates". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on February 13, 2020. Retrieved January 24, 2016.
- Leip, David. "Dave Leip's Atlas of U.S. Presidential Elections". uselectionatlas.org. Retrieved April 1, 2018.
Further reading
- Caballero, Raymond. McCarthyism vs. Clinton Jencks. Norman: University of Oklahoma Press, 2019.
