Catron County, New Mexico
Catron County is a county in the U.S. state of New Mexico. As of the 2010 census, the population was 3,725,[2] making it New Mexico's third-least populous county. Its county seat is Reserve.[3] Catron County is New Mexico's largest county by area.
Catron County | |
|---|---|
 Catron County Courthouse in Reserve. | |
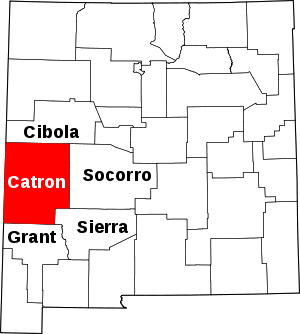 Location within the U.S. state of New Mexico | |
 New Mexico's location within the U.S. | |
| Coordinates: 33°55′N 108°25′W | |
| Country | |
| State | |
| Founded | February 25, 1921 |
| Named for | Thomas B. Catron |
| Seat | Reserve |
| Largest village | Reserve |
| Area | |
| • Total | 6,929 sq mi (17,950 km2) |
| • Land | 6,924 sq mi (17,930 km2) |
| • Water | 5.5 sq mi (14 km2) 0.08%% |
| Population | |
| • Estimate (2019) | 3,527[1] |
| • Density | 0.5/sq mi (0.2/km2) |
| Time zone | UTC−7 (Mountain) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−6 (MDT) |
| Congressional district | 2nd |
| Website | www |
History
Settlement in the Catron County region dates to some of the earliest in the Americas. During the Clovis period between 10999 BC and 8000 BC and Folsom period between 7999 BC and 5999 BC, the Ake Site was occupied near Datil.[4] Bat Cave, near Horse Springs, was occupied around 3,500 BC.
The Mimbres culture was part of the Mogollon people who lived throughout the Catron County area from AD 1000 to 1130. Their art is renowned for its beauty.
In 1598, the region was declared part of Santa Fé de Nuevo México, a province in New Spain. The province remained in Spanish control until Mexico's declaration of independence in 1821. Under the 1824 Constitution of Mexico, this became the federally administered Territory of New Mexico. European settlement of this region started with the Spanish. It intensified after the US acquired New Mexico as a result of the Mexican–American War. More settlers moved to the state after it was admitted to the Union in 1912.
Mexico ceded the region to the U.S. in the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo in 1848 after the Mexican–American War. In 1849, President Zachary Taylor proposed that New Mexico, including this region, immediately become a state to sidestep political conflict over slavery in the territories. That did not happen.
In 1880, Sergeant James C. Cooney was the first person to find silver and gold ore in the mountains of Catron County. He was reportedly killed by Chiricahua Apaches led by Victorio that year in what became known as the "Alma Massacre". His remains are buried at Cooney's Tomb. During this time Cochise was active as another well-known Chiricahua leader. Noted war chief Goyaałé (Geronimo) had several hideouts in the county. Later in 1880, Buffalo Soldiers led by Sergeant George Jordan defeated Chiricahua Apache warriors led by Victorio in the Battle of Fort Tularosa. Four years later, self-appointed sheriff Elfego Baca was the hero of the so-called Frisco shootout in San Francisco Plaza.
In the mid-1880s Butch Cassidy and his Wild Bunch gang holed up at a ranch near Alma, New Mexico. Notorious outlaw Tom Ketchum also lived in Catron County around this time.
Catron County's lands were part of Socorro County from the creation of Santa Fé de Nuevo México until 1921. At that split, Catron county was named for Thomas B. Catron, a leading figure in New Mexico statehood and its first senator. In 1927, the State Legislature attempted to abolish both Socorro and Catron in order to create a new Rio Grande County. A court suit voided this act and the two counties retained their independence.[5]
The Lightning Field, an art installation on the open earth, brought national attention to Quemado in the late 1970s.
Geography
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has a total area of 6,929 square miles (17,950 km2), of which 6,924 square miles (17,930 km2) is land and 5.5 square miles (14 km2) (0.08%) is water.[6]
Catron County is the largest county, by area, in New Mexico. At almost 7,000 square miles (18,000 km2), Catron County is larger than four states. With a population of only 3,400 people, the county is as sparsely populated as many an old West frontier area. The elk population at some 12,000 head, is much larger than the sparse human population.
Within the boundaries of Catron County lie parts of the Gila National Forest, the Apache National Forest and the Cibola National Forest. The establishment of these national forests, in the past called "forest reserves," led to the name Reserve being given to a village on the San Francisco River, which also serves as the County Seat. There are no stop lights in the whole county, so when license tests are given in Reserve, an artificial portable stop light is set up in a parking lot.
Bordering Arizona, Catron County affords the shortest route between Albuquerque and Phoenix or Tucson. Reserve can also be reached by following U.S. Route 180 north from Silver City and New Mexico State Road 12 east for a total of 99 miles (159 km).
In Catron County there is a volcanic area that until recently contained sufficient heat to cause steam to rise after a slight rain. It is called Burning Mountain and appears to have been used by the Apache for healing purposes.[7] The county is home to the Red Hill Volcanic Field as well as the Plains of San Agustin.
Mountains
- Black Mountain
- Black Range
- Datil Mountains
- Diablo Range
- Gallo Mountains
- Mangas Mountains
- Mogollon Mountains
- Saliz Mountains
- San Francisco Mountains
- Tularosa Mountains
- Whitewater Baldy
Bodies of water
- San Francisco River
- Tularosa River
- Rio Salado
- Middle Fork Hot Springs
- Jordan Hot Springs
- Turkey Creek Hot Springs
- Zuni Salt Lake
Forests
- Apache-Sitgreaves National Forest
- Blue Range Wilderness
- Cibola National Forest
- Gila Wilderness
- Gila National Forest
- Whitewater Canyon National Forest Recreation Area
Adjacent counties
- Cibola County - north
- Socorro County - east
- Sierra County - southeast
- Grant County - south
- Greenlee County, Arizona - west
- Apache County, Arizona - west
National protected areas
Demographics
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1930 | 3,282 | — | |
| 1940 | 4,881 | 48.7% | |
| 1950 | 3,533 | −27.6% | |
| 1960 | 2,773 | −21.5% | |
| 1970 | 2,198 | −20.7% | |
| 1980 | 2,720 | 23.7% | |
| 1990 | 2,563 | −5.8% | |
| 2000 | 3,543 | 38.2% | |
| 2010 | 3,725 | 5.1% | |
| Est. 2019 | 3,527 | [8] | −5.3% |
| U.S. Decennial Census[9] 1790–1960[10] 1900–1990[11] 1990–2000[12] 2010–2016[2] | |||
2000 census
As of the 2000 census[13] of 2000, there were 3,543 people, 1,584 households, and 1,040 families living in the county. The population density was 0.51 people per square mile (0.20/km²). There were 2,548 housing units at an average density of 0.37 per square mile (0.14/km²). The racial makeup of the county was 87.75% White, 0.28% Black or African American, 2.20% Native American, 0.68% Asian, 0.06% Pacific Islander, 5.42% from other races, and 3.61% from two or more races. 19.16% of the population were Hispanic or Latino of any race.
There were 1,584 households out of which 22.30% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 55.40% were married couples living together, 7.60% had a female householder with no husband present, and 34.30% were non-families. 30.10% of all households were made up of individuals and 11.40% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.23 and the average family size was 2.75.
In the county, the population was spread out with 21.10% under the age of 18, 4.20% from 18 to 24, 19.50% from 25 to 44, 36.40% from 45 to 64, and 18.80% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 48 years. For every 100 females there were 104.70 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 101.70 males.
The median income for a household in the county was $23,892, and the median income for a family was $30,742. Males had a median income of $26,064 versus $18,315 for females. The per capita income for the county was $13,951. About 17.40% of families and 24.50% of the population were below the poverty line, including 39.60% of those under age 18 and 14.90% of those age 65 or over.
2010 census
As of the 2010 census, there were 3,725 people, 1,787 households, and 1,080 families living in the county.[14] The population density was 0.5 inhabitants per square mile (0.19/km2). There were 3,289 housing units at an average density of 0.5 per square mile (0.19/km2).[15] The racial makeup of the county was 89.8% white, 2.7% American Indian, 0.4% black or African American, 0.2% Asian, 3.8% from other races, and 3.1% from two or more races. Those of Hispanic or Latino origin made up 19.0% of the population.[14]
The largest ancestry groups were: [16]
- 29.1% American
- 18.8% English
- 17.5% German
- 10.4% Mexican
- 9.8% Irish
- 5.1% Spanish
- 3.3% Scottish
- 2.3% Scotch-Irish
- 2.1% Navajo
- 1.8% Swedish
- 1.8% Welsh
- 1.7% Danish
- 1.2% Dutch
- 1.1% Italian
- 1.1% Norwegian
Of the 1,787 households, 16.4% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 52.2% were married couples living together, 4.8% had a female householder with no husband present, 39.6% were non-families, and 34.8% of all households were made up of individuals. The average household size was 2.03 and the average family size was 2.57. The median age was 55.8 years.[14]
The median income for a household in the county was $31,914 and the median income for a family was $40,906. Males had a median income of $46,304 versus $23,325 for females. The per capita income for the county was $20,895. About 10.1% of families and 15.3% of the population were below the poverty line, including 31.5% of those under age 18 and 12.0% of those age 65 or over.[17]
Points of interest
- Ake Site - A prehistoric archaeological location near the town of Datil in the San Augustine Basin, it has been dated during the Clovis period between 10999 BC 8000 BC, and during the Folsom period between 7999BC and 5999 BC, making it among the oldest inhabited sites in the American Southwest.[4]
- Bat Cave - Formed by ancient wave, the cave was covered by an inland sea 35 miles long and 165 feet deep 15,000 years ago. In the late 1940s and early 50s, archeologists found stone artifacts of human inhabitation spanning 5,000 years.[18]
- Bearwallow Park
- Bearwallow Mountain Lookout Cabins and Shed - Built in 1940 by the Works Progress Administration, they are one of three New Deal-era buildings in the Gila National Forest.
- Black Mountain Lookout Cabin
- Catwalk National Recreation Trail - A remnant of a water system for the former mining town of Graham, as many as 29,000 visitors a year walk on the Catwalk's trail or picnic at the mouth of the canyon.
- Cooney's Tomb - Located on the outskirts of Alma and near the ghost town of Cooney, Cooney's Tomb is a large boulder beside the road. It marks the burial location of James C. Cooney, a miner in the area who was killed by Apaches in 1880.
- El Caso Lake
- El Caso Lookout Complex - Built in 1934 by the Works Progress Administration, the complex was one of three New Deal-era forest fire lookouts built in Catron County.
- Glenwood State Trout Hatchery
- Mangas Mountain Lookout Complex
- Mogollon Historic District - The site of many historic buildings, Mogollon was a successful mining town until the turn of the 20th century.
- Mogollon Baldy Lookout Cabin
- Mogollon Pueblo
- Tularosa River Site and Tularosa Ranger Station - A collection of more than 500 petroglyphs and a historic US Forest Service ranger station dating to the 1920s.
- Whitewater Canyon National Forest Recreation Area
- Zuni Salt Lake and Sanctuary - The Pueblo people of the Southwest have made annual pilgrimages to Zuñi Salt Lake to harvest salt, for both culinary and ceremonial purposes for thousands of years. Ancient roadways radiate out from the lake to the various pueblos and ancient pueblo sites.
Politics
| Year | Republican | Democratic | Third parties |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | 71.5% 1,464 | 20.8% 427 | 7.7% 158 |
| 2012 | 70.4% 1,494 | 26.4% 560 | 3.3% 69 |
| 2008 | 66.2% 1,398 | 31.4% 664 | 2.4% 50 |
| 2004 | 71.6% 1,427 | 27.7% 551 | 0.8% 15 |
| 2000 | 74.4% 1,273 | 20.6% 353 | 5.0% 85 |
| 1996 | 60.6% 923 | 27.8% 423 | 11.7% 178 |
| 1992 | 49.7% 771 | 29.9% 465 | 20.4% 317 |
| 1988 | 62.3% 925 | 33.0% 490 | 4.8% 71 |
| 1984 | 68.6% 970 | 29.5% 418 | 1.9% 27 |
| 1980 | 62.7% 906 | 32.3% 466 | 5.0% 72 |
| 1976 | 53.2% 602 | 45.7% 517 | 1.2% 13 |
| 1972 | 73.5% 829 | 24.0% 271 | 2.5% 28 |
| 1968 | 62.3% 674 | 25.7% 278 | 12.0% 130 |
| 1964 | 48.3% 584 | 51.7% 624 | |
| 1960 | 53.9% 671 | 46.0% 573 | 0.1% 1 |
| 1956 | 59.9% 711 | 40.2% 477 | |
| 1952 | 61.5% 741 | 38.5% 464 | |
| 1948 | 44.4% 521 | 55.2% 648 | 0.3% 4 |
| 1944 | 54.2% 699 | 45.7% 589 | 0.1% 1 |
| 1940 | 47.7% 949 | 52.3% 1,039 | |
| 1936 | 35.1% 798 | 64.1% 1,456 | 0.8% 18 |
| 1932 | 37.9% 610 | 60.5% 972 | 1.6% 26 |
| 1928 | 64.8% 774 | 35.2% 420 | 0.1% 1 |
| 1924 | 47.3% 499 | 39.6% 418 | 13.1% 138 |
Notable people
- Elfego Baca
- Jerry D. Thompson, historian of the American Southwest, American Civil War, and Texas, was reared in Quemado in Catron County.
- Beverly Magennis, tile artist, author
References
- https://www.census.gov/quickfacts/fact/table/catroncountynewmexico/PST040216
- "State & County QuickFacts". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved September 27, 2013.
- "Find a County". National Association of Counties. Archived from the original on May 31, 2011. Retrieved June 7, 2011.
- (nd) National Register of Historic Places - Catron County, New Mexico. Retrieved June 13, 2007.
- "History of Socorro County" Archived February 11, 2012, at the Wayback Machine, Socorro Chamber of Commerce. Retrieved December 21, 2011.
- "2010 Census Gazetteer Files". United States Census Bureau. August 22, 2012. Archived from the original on January 1, 2015. Retrieved January 1, 2015.
- (nd) Chapter 4, Section IV. Native American Sacred Sites and the Department of Defense. Retrieved June 12, 2007.
- "Population and Housing Unit Estimates". Retrieved December 24, 2019.
- "U.S. Decennial Census". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved January 1, 2015.
- "Historical Census Browser". University of Virginia Library. Retrieved January 1, 2015.
- "Population of Counties by Decennial Census: 1900 to 1990". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved January 1, 2015.
- "Census 2000 PHC-T-4. Ranking Tables for Counties: 1990 and 2000" (PDF). United States Census Bureau. Retrieved January 1, 2015.
- "U.S. Census website". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved January 31, 2008.
- "DP-1 Profile of General Population and Housing Characteristics: 2010 Demographic Profile Data". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on February 13, 2020. Retrieved January 24, 2016.
- "Population, Housing Units, Area, and Density: 2010 - County". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on February 13, 2020. Retrieved January 24, 2016.
- "DP02 SELECTED SOCIAL CHARACTERISTICS IN THE UNITED STATES – 2006–2010 American Community Survey 5-Year Estimates". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on February 13, 2020. Retrieved January 24, 2016.
- "DP03 SELECTED ECONOMIC CHARACTERISTICS – 2006–2010 American Community Survey 5-Year Estimates". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on February 13, 2020. Retrieved January 24, 2016.
- Padilla, L. (2003) "Bat Caving on the Plains of San Agustin" Archived June 30, 2011, at the Wayback Machine. Retrieved November 17, 2010.
- Leip, David. "Dave Leip's Atlas of U.S. Presidential Elections". uselectionatlas.org. Retrieved April 1, 2018.
