Emilian-Romagnol language
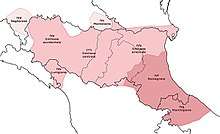
Emilian-Romagnol (emiliân-rumagnōl or langua emiglièna-rumagnôla), also known as Emiliano-Romagnolo, is a Gallo-Italic language. Its two dialect groups, Emilian and Romagnol, were traditionally considered two separate but closely related languages spoken in the eponymous northern Italian region of Emilia-Romagna and in San Marino, as well as bordering parts of Lombardy, Umbria, Marche, Liguria, Piedmont, Veneto and Tuscany.[5]
| Emilian-Romagnol | |
|---|---|
| Native to | Italy, San Marino |
| Region | Primarily Emilia-Romagna, Marche, San Marino |
Native speakers | Unknown (4.4 million population): |
Indo-European
| |
| Dialects |
|
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | (code eml deprecated in 2009)[2] Individual codes: egl – Emilianrgn – Romagnol |
| Glottolog | emil1241 Emiliano[3]roma1328 Romagnol[4] |
| Linguasphere | 51-AAA-ok |
 | |
References
- "La lingua italiana, i dialetti e le lingue straniere Anno 2006" (PDF). istat.it. Retrieved 21 February 2018.
- "639 Identifier Documentation: eml". SIL International.
- Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin, eds. (2017). "Emiliano". Glottolog 3.0. Jena, Germany: Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History.
- Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin, eds. (2017). "Romagnol". Glottolog 3.0. Jena, Germany: Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History.
- "Lingua romagnola". TuttoSu. Retrieved 21 February 2018.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.