Confluence
In geography, a confluence (also: conflux) occurs where two or more flowing bodies of water join together to form a single channel.[1] A confluence can occur in several configurations: at the point where a tributary joins a larger river (main stem); or where two streams meet to become the source of a river of a new name (such as the confluence of the Monongahela and Allegheny rivers at Pittsburgh, forming the Ohio); or where two separated channels of a river (forming a river island) rejoin at the downstream end.
Scientific study of confluences
Confluences are studied in a variety of sciences. Hydrology studies the characteristic flow patterns of confluences and how they give rise to patterns of erosion, bars, and scour pools.[2] The water flows and their consequences are often studied with mathematical models.[3] Confluences are relevant to the distribution of living organisms (i.e., ecology) as well; "the general pattern [downstream of confluences] of increasing stream flow and decreasing slopes drives a corresponding shift in habitat characteristics."[4]
Another science relevant to the study of confluences is chemistry, because sometimes the mixing of the waters of two streams triggers a chemical reaction, particularly in a polluted stream. The United States Geological Survey gives an example: "chemical changes occur when a stream contaminated with acid mine drainage combines with a stream with near-neutral pH water; these reactions happen very rapidly and influence the subsequent transport of metals downstream of the mixing zone."[5]
A natural phenomenon at confluences that is obvious even to casual observers is a difference in color between the two streams; see images in this article for several examples. According to Lynch, "the color of each river is determined by many things: type and amount of vegetation in the watershed, geological properties, dissolved chemicals, sediments and biologic content – usually algae." Lynch also notes that color differences can persist for miles downstream before they finally blend completely.[6]
River confluence flow zones
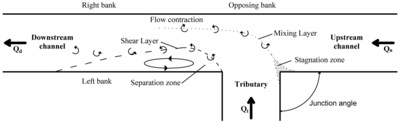
Hydrodynamic behaviour of flow in a confluence can be divided into six distinct features[7] which are commonly called confluence flow zones (CFZ). These include
- Stagnation zone
- Flow deflection zone
- Flow separation zone / recirculation zone
- Maximum velocity zone
- Flow recovery zone
- Shear layers
Confluences and mankind

Since rivers often serve as political boundaries, confluences sometimes demarcate three abutting political entities, such as nations, states, or provinces, forming a tripoint. Various examples are found in the list below.
A number of major cities, such as Chongqing, St. Louis, and Khartoum, arose at confluences; further examples appear in the list. Within a city, a confluence often forms a visually prominent point, so that confluences are sometimes chosen as the site of prominent public buildings or monuments, as in Koblenz, Lyon, and Winnipeg. Cities also often build parks at confluences, sometimes as projects of municipal improvement, as at Portland and Pittsburgh. In other cases, a confluence is an industrial site, as in Philadelphia or Mannheim. Often a confluence lies in the shared floodplain of the two rivers and nothing is built on it, for example at Manaus, described below.
One other way that confluences may be exploited by humans is as sacred places in religions. Rogers suggests that for the ancient peoples of the Iron Age in northwest Europe, watery locations were often sacred, especially sources and confluences.[8] Pre-Christian Slavic peoples chose confluences as the sites for fortified triangular temples, where they practiced human sacrifice and other sacred rites.[9] In Hinduism, the confluence of two sacred rivers often is a pilgrimage site for ritual bathing.[10] In Pittsburgh, a number of adherents to Mayanism consider their city's confluence to be sacred.[11]
Notable confluences

Africa
- At Lokoja, Nigeria, the Benue River flows into the Niger.
- At Kazungula in Zambia, the Chobe River flows into the Zambezi. The confluence defines the tripoint of Zambia (north of the rivers), Botswana (south of the rivers) and Namibia (west of the rivers). The land border between Botswana and Zimbabwe to the east also reaches the Zambezi at this confluence, so there is a second tripoint (Zambia-Botswana-Zimbabwe) only 150 meters downstream from the first. See Kazungula and Quadripoint, and Gallery below for image.
- The Sudanese capital of Khartoum is located at the confluence of the White Nile and the Blue Nile, the beginning of the Nile.
Asia
- 82 km north of Basra in Iraq at the town of Al-Qurnah is the confluence of the rivers Tigris and Euphrates, forming the Shatt al-Arab.
- At Devprayag in India, the Ganges River originates at the confluence of the Bhagirathi and the Alaknanda; see images above.
- Near Allahabad, India, the Yamuna flows into the Ganges. In Hinduism, this is a pilgrimage site for ritual bathing;[12] during a Kumbh Mela event tens of millions of people visit the site. In Hindu belief the site is held to be a triple confluence (Triveni Sangam), the third river being the metaphysical (not physically present) Sarasvati.[13]
- Karad, in Maharashtra, India, is the site of the Pritisangam (meaning: Lovely Confluence), a T-shaped confluence of Krishna River and Koyna River, where Koyna River mergers into Krishna River forming a T-shape and then the merged rivers flow to the east as Krishna River.[14]
- Kuala Lumpur, the capital of Malaysia, is where the Gombak River (previously known as Sungai Lumpur, which means "muddy river") flows into the Klang River at the site of the Jamek Mosque. Recently, the Kolam Biru (Blue Pool), a pool with elaborate fountains, has been installed at the apex of the confluence.[15]
- The Nam Khan River flows into the Mekong at Luang Prabang in Laos.
- The Jialing flows into the Yangtze at Chongqing in China. The confluence forms a focal point in the city, marked by Chaotianmen Square, built in 1998.
- In the Far East, the Amur forms the international boundary between China and Russia. The Ussuri, which also demarcates the border, flows into the Amur at a point midway between Fuyuan in China and Khabarovsk in Russia. The apex of the confluence is located in a rural area, part of China, where a commemorative park, Dongji Square, has been built; it features an enormous sculpture representing the Chinese character for "East".[16] The Amur-Ussuri border region was the location of the Sino-Soviet border conflict of 1969; the borderline near the confluence was settled peacefully by treaty in 2008.
- In Georgia, in the town of Pasanauri on the southern slopes of the Caucasus Mountains, the Tetri Aragvi ("White Aragvi") is joined by the Shavi Aragvi ("Black Aragvi"). Together, these two rivers continue as the Aragvi River. The conflux is known for its dramatic visual contrast of the two rivers.
Australia
- The two largest rivers in Australia, the Murray and its tributary the Darling, converge at Wentworth, New South Wales.
Europe
Seine
- The Seine divides in the historical center of Paris, flowing around two river islands, the Île Saint-Louis and the Île de la Cité. At the downstream confluence, where the river becomes a single channel again, the Île de la Cité is crossed by the famous Pont Neuf, adjacent to an equestrian statue of King Henri IV and the historically more recent Vert Galant park. The site has repeatedly been portrayed by artists including Monet, Renoir, and Pissarro.
- Further upstream, the Marne empties into the Seine at Charenton-le-Pont, just southeast of the Paris city limits. The site is dominated by the Huatian Chinagora, a four-star hotel under Chinese management.
Rhine
- The Rhine carries much river traffic, and major inland ports are found at its confluence with the Ruhr at Duisburg, and with the Neckar at Mannheim; see Mannheim Harbour.
- The Main flows into the Rhine just south of Mainz.
- The Mosel flows into the Rhine further north at Koblenz. The name "Koblenz" itself has its origin in the Latin name "Confluentes". In German, this confluence is known as the "Deutsches Eck" ("German corner") and is the site of an imposing monument to German unification featuring an equestrian statue of Kaiser Wilhelm I.
- Upstream in Switzerland, a small town also named Koblenz (for the same reason) is where the Aare joins the Rhine.
Danube basin
- Passau, Germany, sometimes called the Dreiflüssestadt (City of Three Rivers), is the site of a triple confluence, described thus in a guidebook: "from the north the little Ilz sluices brackish water down from the peat-rich Bavarian Forest, meeting the cloudy brown of the Danube as it flows from the west and the pale snow-melt jade of the Inn from the south [i.e., the Alps] to create a murky tricolour."[17]
- The Thaya flows into the Morava in a rural location near Hohenau an der March in Austria, forming the tripoint of Austria, Czechia, and Slovakia.
- The Morava flows into the Danube at Devín, on the border between Slovakia and Austria.
- The Sava flows into the Danube at Belgrade, the capital of Serbia.
- In karst topography, which arises in soluble rock, rivers sometimes flow underground and form subterranean confluences, as at Planina Cave in Slovenia, where the Pivka and Rak merge to form the Unica.[18]
Other
- Lyon, France lies where the Saône flows into the Rhone. A major new museum of science and anthropology, the Musée des Confluences, opened on the site in 2014.
- Near Toulouse, France lies where the Ariège (river) flows into the Garonne. Both take their source in the Pyrenees.
- The Lusatian Neisse flows into the Oder at a rural location in Poland opposite the German village of Ratzdorf. The two rivers form the Oder-Neisse line, the postwar boundary of Germany and Poland.
- The Triangle of Three Emperors, a former political tripoint, lies in present-day Poland. The empires that abutted (in the decades before World War I) were the Austrian, German, and Russian.
- Rovaniemi, the capital of Finnish Lapland and one of the largest towns above the Arctic Circle, is at the confluence of rivers Ounasjoki and Kemijoki.
- Kryvyi Rih, Ukraine is located (and named after) on the confluence of the Saksahan and Inhulets River.
- The Oka flows into the Volga at Nizhny Novgorod in Russia. The Alexander Nevsky Cathedral overlooks the site.
- The English city of Southampton is built at the confluence of the tidal estuaries of the River Test and River Itchen which combine to form Southampton Water estuary.[19]
North America

Mississippi basin
- The Greater Twin Cities area of Minneapolis and St. Paul, Minnesota features two important Mississippi confluences. Near historical Fort Snelling and town of Mendota—about 9 miles downstream on the Mississippi from Minneapolis—the Minnesota River flows into the Mississippi at Pike Island. The area around this confluence is a location of spiritual, cultural, and historical significance to the Dakota people and is also the site of the earliest European settlements in the Twin Cities area. About 30 miles further downstream from the Minnesota-Mississippi confluence—and 25 miles downstream from St. Paul—the Mississippi joins with the St. Croix River near Hastings, Minnesota, and Prescott, Wisconsin.
- Vicksburg, Mississippi lies atop bluffs overlooking the confluence of the Mississippi River with its tributary the Yazoo. Both rivers, as well as the bluffs, played an important role in the Vicksburg Campaign, a pivotal event of the American Civil War.
- The Missouri River flows into the Mississippi River at Jones-Confluence Point State Park, just north of St. Louis, Missouri. Slightly further upstream, the Illinois River flows into the Mississippi.
- The Madison, Jefferson and Gallatin Rivers in Three Forks, Montana form the confluence of the Missouri River.
- At Keokuk, Iowa, the Des Moines River flows into the Mississippi. This forms the political tripoint between the U.S. states of Iowa, Missouri, and Illinois.
- Just south of Cairo, Illinois, the Ohio River flows into the Mississippi, forming the tripoint between the states of Illinois, Missouri, and Kentucky.
- The Ohio River is formed by the confluence of the Monongahela and Allegheny rivers, located in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. The site is of great historical significance; in the 1970s it was upgraded by the creation of Point State Park, highlighted by a large fountain.
Atlantic watersheds
- At Harpers Ferry, West Virginia, the Shenandoah River flows into the Potomac River, at the tripoint of the U.S. states of Virginia, West Virginia, and Maryland.
- At Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, the Schuylkill River flows into the Delaware River, next to the former Philadelphia Naval Shipyard; the site remains industrial.
- At Cohoes, New York, a few miles north of Albany, the Mohawk River flows into the Hudson in three channels separated by islands. The confluence is historically important: upstream traffic on or along the Hudson often took a left turn at the Mohawk, which offers a uniquely level passageway through the Appalachian Mountains that assisted commerce and the settlement of the West.
- At Ottawa, the capital of Canada, the Rideau River flows—unusually, as a waterfall—into the Ottawa River; see Rideau Falls. On the island separating the two portions of the falls is a park with military monuments, among them the Ottawa Memorial.
- The Hochelaga Archipelago, including the island and city of Montreal, is located where the Ottawa River flows into the St. Lawrence River in Quebec, Canada.
- Winnipeg, Canada, is at the confluence of the Red River, and the Assiniboine River. The area is referred to as The Forks by locals, and has been an important trade location for over 6000 years.
Pacific watersheds
- The Green River flows into the Colorado River at the heart of Canyonlands National Park in Utah's Canyon Country.
- The Snake River flows into the Columbia River at the Tri-Cities of Washington.
- In Portland, Oregon, the Willamette River flows into the Columbia at Kelley Point Park, built on land acquired from the Port of Portland in 1984.
- Lytton, British Columbia, Canada, is located at the confluence of the muddy Fraser River and the clearer Thompson River.

South America
- Manaus, Brazil is on the Rio Negro near its confluence with the Amazon (see Meeting of Waters). It is the chief port and a hub for the region's extensive river system.
- The Iguazú flows into the Paraná at the "Triple Frontier" (Spanish: La Triple Frontera, Portuguese: Tríplice Fronteira), the tripoint for Paraguay, Argentina, and Brazil.
- In Ciudad Guayana, Venezuela there is a confluence between Orinoco River and Caroní River.[20]
Confluences of two waterways
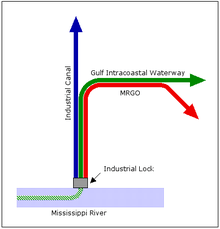
This simplified diagram shows how a section of the Industrial Canal in New Orleans also serves as the channel for the Gulf Intracoastal Waterway and the Mississippi River-Gulf Outlet Canal. At the bottom, a portion of the Intracoastal is also shown to be "confluent" with the Mississippi River.
Occasionally "confluence" is used to describe the meeting of tidal or other non-riverine bodies of water, such as two canals[21] or a canal and a lake.[22] A one-mile (1.6 km) portion of the Industrial Canal in New Orleans accommodates the Gulf Intracoastal Waterway and the Mississippi River-Gulf Outlet Canal; therefore those three waterways are confluent there.
The term confluence also applies to the merger of the flow of two glaciers.[23]
See also
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Confluences. |
- River mouth – end of a river
- Aber and Inver as place-name elements
Notes
- "Conflux – Definition of conflux by Merriam-Webster". merriam-webster.com.
- A widely cited work is James L. Best (1986) The morphology of river channel confluences. Progress in Physical Geography 10:157–174. For work citing Best, see .
- A recent contribution with review of earlier work is Laurent Schindfessel, Stéphan Creëlle and Tom De Mulder (2015) "Flow patterns in an open channel confluence with increasingly dominant tributary inflow," Water 7: 4724–4751; available on line.
- Quoted from Beechie et al. (2012), who cite earlier work. Tim Beechie, John S. Richardson, Angela M. Gurnell, and Junjiro Negishi (2012) "Watershed processes, human impacts, and process-based restoration." In Philip Roni and Tim Beechie (eds.) (2012) Stream and Watershed Restoration: A Guide to Restoring Riverine Processes and Habitats, John Wiley & Sons. Excerpts available on line at Google Books.
- U.S. Geological Survey, "How do contaminants mix at the confluence of two streams?", on line at .
- David Lynch (2014) "The Confluence of Rivers"; Earth Science Picture of the Day, at .
- Best, James L. (1987). "Flow Dynamics at River Channel Confluences: Implications for Sediment Transport and Bed Morphology". Recent Developments in Fluvial Sedimentology. pp. 27–35. doi:10.2110/pec.87.39.0027. ISBN 978-0-918985-67-5.
- Rogers, Adam (2011) Late Roman Towns in Britain: Rethinking Change and Decline. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, p. 42. Excerpts available on line at Google Books.
- Gasparini, Evel (n.d.) "Slavic religion", in Encyclopedia Britannica, on line edition:
- Source: Letizia (2017), who writes, "as rivers are considered holy entities, at the meeting of two streams the 'sacredness' of the first river add to that of the second one. The confluence seems to have a sort of 'additive fame' ... because it gives pilgrims the chance to bathe in two rivers at the same time."
- Ann Rodgers, "So how did the Point get on a Mayan calendar?", Pittsburgh Post-Gazette, June 22, 2008. On line at .
- See reporting in the New York Times () and The Atlantic ().
- The incorporation of invisible rivers into confluences elsewhere in the subcontinent is documented by Letizia (2017).
- "Karad Tourism | Top Tourist Places to Visit in Karad Area | Travel Guide". www.gruhkhoj.com. Retrieved 2019-10-14.
- See New Straits Times, August 28, 2017, 'Najib launches River of Life, Blue Pool projects", at .
- See Bruno Maçães, "Signs and Symbols on the Sino-Russian Border", published in The Diplomat. On line at .
- See Andrea Schulte-Peevers, Kerry Christiani, Marc Di Duca, Catherine Le Nevez, Tom Masters, Ryan Ver Berkmoes, and Benedict Walker (2016) Lonely Planet Germany, Lonely Planet Publishing. Excerpts posted on line at Google Books:
- Kogovšek, Janja; Petrič, Metka; Zupan Hajna, Nadja; Pipan, Tanja. "Planinska jama" [Planina Cave]. In Šmid Hribar, Mateja; Golež, Gregor; Podjed, Dan; Kladnik, Drago; Erhartič, Bojan; Pavlin, Primož; Ines, Jerele (eds.). Enciklopedija naravne in kulturne dediščine na Slovenskem [Encyclopedia of Natural and Cultural Heritage in Slovenia] (in Slovenian). Archived from the original on 19 April 2012. Retrieved 17 May 2012.
- https://www.britannica.com/place/Southampton-England
- "Caronoco: confluencia de los rios Caroní y Orinoco". Parques Nacionales Venezuela. Retrieved 4 March 2019.
- The U.S. Army Corps of Engineers refers to the confluence of the Assawoman Canal with the Bethany Loop Canal in Delaware. See: "CENAP-OP-R-Quarterly Report, 2004-05-12". Philadelphia Engineer District. Archived from the original on 2004-10-17. Retrieved 2006-03-11.
- Engineers in New Orleans refer to the confluence of the 17th Street Canal and Lake Pontchartrain. See: "Interim Closure Structure at 17th St. Canal". Task Force Guardian. Archived from the original on 2006-06-25. Retrieved 2006-03-11.
- Vladimir Kotlyakov and Anna Komarova (2006) Elsevier's Dictionary of Geography: in English, Russian, French, Spanish and German. Elsevier. Passage cited may be accessed on Google Books.
References
- Letizia, Chiara (2017) "The Sacred Confluence, between Nature and Culture," in Marie Lecomte-Tilouine (ed.) Nature, Culture and Religion at the Crossroads of Asia. Routledge. Extracts available on line at Google Books.




