Banjul
Banjul (UK: /bænˈdʒuːl/,[2][3] US: /ˈbɑːndʒuːl/),[2][3][4][5] officially the City of Banjul, is the capital and fourth largest city of The Gambia. It is the centre of the eponymous administrative division which is home to an estimated 400,000 residents, making it The Gambia's largest and densely populated metropolitan area. Banjul is on St Mary's Island (Banjul Island), where the Gambia River enters the Atlantic Ocean. The population of the city proper is 31,301, with the Greater Banjul Area, which includes the City of Banjul and the Kanifing Municipal Council, at a population of 413,397 (2013 census).[6] The island is connected to the mainland to the west and the rest of Greater Banjul Area via bridges. There are also ferries linking Banjul to the mainland at the other side of the river.
Banjul | |
|---|---|
City | |
  Downtown Banjul, Banjul airport, Arch22 | |
 Banjul Location of Banjul in the Gambia  Banjul Banjul (Africa) | |
| Coordinates: 13°27′11″N 16°34′39″W | |
| Country | |
| Division | Banjul |
| Founded | 1816 |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Rohey Malick Lowe |
| Area | |
| • City | 12 km2 (5 sq mi) |
| • Urban | 93 km2 (36 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 0 m (0 ft) |
| Population (2013 census) | |
| • City | 31,301 |
| • Density | 2,600/km2 (6,800/sq mi) |
| • Urban | 413,397 |
| • Urban density | 4,400/km2 (12,000/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC±00:00 (GMT) |
| HDI (2017) | 0.552[1] medium |
Etymology
Banjul takes its name from the Mandé people who gathered specific fibres on the island, which were used in the manufacture of ropes. Bang julo is the Mandinka (Mande) word for rope fibre.
History


In 1651 Banjul was leased by The Duke of Courland and Semigallia (German: Herzog von Kurland und Semgallen) from the King of Kombo, as part of the Couronian colonization.[7]
On 23 April 1816, the King of Kombo ceded Banjul Island to Alexander Grant, the British commandant. Grant founded Banjul as a trading post and base, constructing houses and barracks for controlling entrance to the Gambia estuary and suppressing the slave trade.[8] The British renamed Banjul Island as St. Mary's Island and named the new town Bathurst, after the 3rd Earl Bathurst, Secretary of State for War and the Colonies at the time. Streets were laid out in a modified grid pattern, and named after Allied generals at the Battle of Waterloo. The town became the centre of British activity in the Gambia Colony and Protectorate.[9]
After independence, the town's name was changed to Banjul in 1973.[8] On 22 July 1994, Banjul was the scene of a bloodless military coup d'état in which President Dawda Jawara was overthrown and replaced by Yahya Jammeh. To commemorate this event, Arch 22 was built as an entrance portal to the capital. The gate is 35 metres tall and stands at the centre of an open square. It houses a textile museum.
Culture
Attractions in the city include the Gambian National Museum, the Albert Market, Banjul State House, Banjul Court House, African Heritage Museum.[10]
Sport
Banjul is the destination of the Plymouth-Banjul Challenge, a charity road rally.
Economy
Banjul is the country's economic and administrative centre and includes the Central Bank of the Gambia. Peanut processing is the country's principal industry, but beeswax, palm wood, palm oil, and skins and hides are also shipped from the port of Banjul.[11]
Banjul is also the home of the Gambia Technical Training Institute. GTTI is engaged in a partnership with non-profit organization Power Up Gambia to develop a solar energy training program.

 A street in Banjul
A street in Banjul- Banjul from the International Space Station
Climate
Banjul has a very warm climate year round. Under the Köppen climate classification, Banjul features a tropical wet and dry climate. The city features a lengthy dry season, spanning from November to May and a relatively short wet season covering the remaining five months. However, during those five months, Banjul tends to see heavy precipitation. August is usually the rainiest month, with on average 500 mm of precipitation falling. Temperatures are somewhat constant, though it tends to be warmer during the wet season than the dry season.
According to a Gambian government minister, Banjul is at risk of submerging under water by a metre rise in sea levels as a result of climate change and global warming.[12]
| Climate data for Banjul | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 37.2 (99.0) |
38.9 (102.0) |
40.6 (105.1) |
41.1 (106.0) |
41.1 (106.0) |
37.8 (100.0) |
33.9 (93.0) |
33.3 (91.9) |
34.4 (93.9) |
37.2 (99.0) |
35.6 (96.1) |
35.6 (96.1) |
41.1 (106.0) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 31.7 (89.1) |
33.5 (92.3) |
33.9 (93.0) |
33.0 (91.4) |
31.9 (89.4) |
31.9 (89.4) |
30.8 (87.4) |
30.2 (86.4) |
31.0 (87.8) |
31.8 (89.2) |
32.7 (90.9) |
31.9 (89.4) |
32.0 (89.6) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 15.7 (60.3) |
16.6 (61.9) |
17.9 (64.2) |
18.8 (65.8) |
20.3 (68.5) |
22.9 (73.2) |
23.6 (74.5) |
23.3 (73.9) |
22.6 (72.7) |
22.2 (72.0) |
18.8 (65.8) |
16.2 (61.2) |
19.9 (67.8) |
| Record low °C (°F) | 7.2 (45.0) |
10.0 (50.0) |
11.7 (53.1) |
12.2 (54.0) |
13.9 (57.0) |
18.3 (64.9) |
20.0 (68.0) |
20.0 (68.0) |
17.2 (63.0) |
16.1 (61.0) |
12.2 (54.0) |
8.9 (48.0) |
7.2 (45.0) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 0.5 (0.02) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
1.3 (0.05) |
62.7 (2.47) |
232.4 (9.15) |
346.8 (13.65) |
255.1 (10.04) |
75.8 (2.98) |
1.6 (0.06) |
0.7 (0.03) |
976.9 (38.46) |
| Average rainy days | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 14 | 19 | 16 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 60 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 47 | 47 | 50 | 58 | 67 | 73 | 81 | 85 | 84 | 80 | 69 | 55 | 67 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 207.7 | 237.3 | 266.6 | 252.0 | 229.4 | 201.0 | 182.9 | 189.1 | 183.0 | 217.0 | 246.0 | 210.8 | 2,622.8 |
| Mean daily sunshine hours | 6.7 | 8.4 | 8.6 | 8.4 | 7.4 | 6.7 | 5.9 | 6.1 | 6.1 | 7.0 | 8.2 | 6.8 | 7.2 |
| Source 1: World Meteorological Organization[13] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: Deutscher Wetterdienst (extremes, humidity, and sun)[14] | |||||||||||||
Transport
The primary method reaching the city by land is by roadway. A highway connects Banjul to Serrekunda which crosses the Denton Bridge, however ferries provide another mode of transportation.[15] As of May 2014, ferries sail regularly from Banjul across the River Gambia to Barra.[16] The city is served by the Banjul International Airport. Banjul is on the Trans–West African Coastal Highway connecting it to Dakar and Bissau, and will eventually provide a paved highway link to 11 other nations of the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS).
 Banjul International Airport
Banjul International Airport Banjul ferry
Banjul ferry
Districts
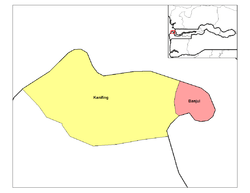
Banjul Division (Greater Banjul Area) is divided into two districts:
Places of worship
Among the places of worship, they are predominantly Muslim mosques. There are also Christian churches and temples : Roman Catholic Diocese of Banjul (Catholic Church), Church of the Province of West Africa (Anglican Communion), Assemblies of God.[18]
See also
- Divisions of the Gambia
- Districts of the Gambia
References
- "Sub-national HDI - Area Database - Global Data Lab". hdi.globaldatalab.org. Retrieved 2018-09-13.
- "Banjul". Collins English Dictionary. HarperCollins. Archived from the original on April 12, 2019. Retrieved April 12, 2019.
- "Banjul" Archived 2019-04-12 at the Wayback Machine (US) and "Banjul". Oxford Dictionaries UK Dictionary. Oxford University Press. Retrieved April 12, 2019.
- "Banjul". The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language (5th ed.). Boston: Houghton Mifflin Harcourt. Retrieved April 12, 2019.
- "Banjul". Merriam-Webster Dictionary. Retrieved April 12, 2019.
- "The Gambia 2013 Population and Housing Census Preliminary Results" (PDF). Gambia Bureau of Statistics. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2018-07-13. Retrieved 2017-12-07.
- Arnold Hughes; David Perfect (2008). "Courland, Duchy Of". Historical Dictionary of The Gambia. Scarecrow Press. pp. 43–4. ISBN 978-0-8108-6260-9.
- "History of Banjul". Accessgambia.com. Retrieved 2012-10-29.
- Arnold Hughes; David Perfect (2008). "Banjul". Historical Dictionary of The Gambia. Scarecrow Press. pp. 15–16. ISBN 978-0-8108-6260-9.
- "Banjul Gambia | Travel information". HappyTellus.com. 2009-06-14. Archived from the original on 2012-10-04. Retrieved 2012-10-29.
- "Gambia, The". State.gov. 2012-07-03. Retrieved 2012-10-29.
- Gambia: Banjul Risks Sinking As Sea Level Rises, Africa: Allafrica.com, 2012, retrieved 11 October 2012
- "World Weather Information Service – Banjul". World Meteorological Organization. Retrieved 10 June 2016.
- "Klimatafel von Banjul-Yundum (Flugh.) / Gambia" (PDF). Baseline climate means (1961-1990) from stations all over the world (in German). Deutscher Wetterdienst. Retrieved 10 June 2016.
- "Denton Bridge bridge, Banjul, Gambia". Gambia. Retrieved 2018-02-12.
- Virtual Tourist, The Gambia Transportation
- "École française de Banjul Bakau, Gambie" (Archive). Agency for French Teaching Abroad. Retrieved on April 27, 2015. "Adresse Atlantic road - Fajara, P.O. Box 4682, Bakau Ville: Bakau Pays: Gambie"
- J. Gordon Melton, Martin Baumann, ‘‘Religions of the World: A Comprehensive Encyclopedia of Beliefs and Practices’’, ABC-CLIO, USA, 2010, p. 1172
Bibliography
- Pierre Gomez; Hassoum Ceesay, eds. (2018). A Geocritical Representation of Banjul (Bathurst): 1816-2016. Global Hands Publishing.
- Matthew James Park, Heart of Banjul: The History of Banjul, The Gambia, 1816-1965. PhD dissertation, Michigan State University, 2016.
- Paul Tiyambe Zeleza; Dickson Eyoh, eds. (2003). "Banjul, Gambia". Encyclopedia of Twentieth-Century African History. Routledge. ISBN 0415234794.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Banjul. |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Banjul. |