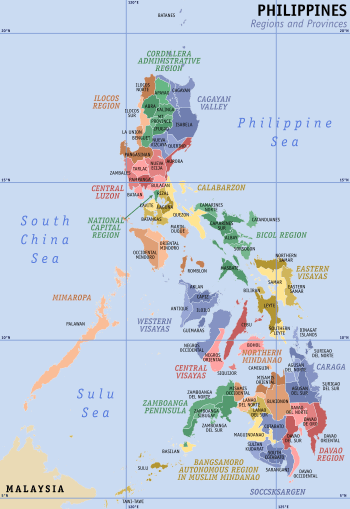
Central Visayas
Central Visayas (Cebuano: Tunga-tungang Kabisay-an) is an administrative region in the Philippines, numerically designated as Region VII. It consists of four provinces (Cebu, Bohol, Negros Oriental, and Siquijor) and three highly urbanized cities (Cebu City, Lapu-Lapu, and Mandaue). Major islands are the eponymous Cebu, Bohol, and Siquijor, together with the eastern part of Negros. The regional center and largest city is Cebu City. The region is dominated by the native speakers of four Visayan languages: Cebuano, Bantayanon, Boholano, and Porohanon. The land area of the region is 15,895.66 km2 (6,137.35 sq mi), and with a population of 7,396,898 inhabitants, it is the second most populous region in the Visayas.
Central Visayas Tunga-tungang Kabisay-an Region VII | |
|---|---|
   From upper-left to bottom-right: Sugar Beach Bantayan, Cebu Metropolitan Cathedral (Cebu); Balinsasayao Twin Lakes Natural Park (Negros Oriental); Chocolate Hills (Bohol); Salagdoong Beach (Siquijor); | |
| Nickname(s): Center of Christianity Rehiyon sa mga Sugboanon (Region of the Cebuanos) | |
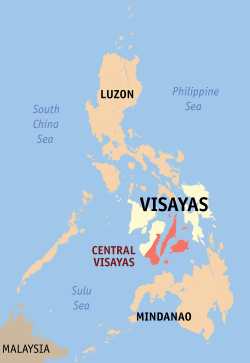 Location in the Philippines | |
| Coordinates: 10°00′N 123°30′E | |
| Country | Philippines |
| Island group | Visayas |
| Regional center | Cebu City (pop. 922,611) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 15,895.66 km2 (6,137.35 sq mi) |
| Area rank | 13th |
| Population (2015 census)[1] | |
| • Total | 7,396,898 |
| • Rank | 4th |
| • Density | 470/km2 (1,200/sq mi) |
| • Density rank | 3rd |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (PST) |
| ISO 3166 code | PH-07 |
| Provinces | |
| Cities | |
| Municipalities | 97 |
| Barangays | 2,446 |
| Cong. districts | 11 |
| Languages | |
On May 29, 2015, the region was redefined, when Central Visayas (Region VII) lost the province of Negros Oriental to the newly formed Negros Island Region. However, the region was dissolved, with Negros Oriental returned to Central Visayas on August 9, 2017.
Etymology

The name of the region was derived to denote the centrality of the islands within the bigger Visayas area. The name was mostly chosen by American colonialists. There have been proposals to rename the current Central Visayas region, which is dominated by the Sebwano ethnic group, into Sugbu region, the former name of the region prior to Spanish colonization in the 16th century. The term is in reference to the former kingdom of the region, the Rajahnate of Cebu, which is simply called as Sugbu in native Sebwano.[2][3]
History
Regions first came into existence on September 24, 1972, when the provinces of the Philippines were organized into 11 regions by Presidential Decree No. 1 as part of the Integrated Reorganization Plan by President Ferdinand Marcos. The provinces of Cebu, Bohol, and Negros Oriental (including its then-subprovince of Siquijor) were grouped together to form the Central Visayas region.
By virtue of Executive Order No. 183 issued on May 29, 2015, by President Benigno Aquino III, the province of Negros Oriental was removed from Central Visayas to form the Negros Island Region along with Negros Occidental and its provincial capital, Bacolod.[4] But later regained Negros Oriental and its capital, Dumaguete City back into Central Visayas on August 9, 2017 when President Rodrigo Duterte dissolved the Negros Island Region, revoking Executive Order No. 183, s. 2015 through the signage of Executive Order No. 38, citing the reason of the lack of funds to fully establish the NIR according to Benjamin Diokno, the Secretary of Budget and Management.[5]
Geography
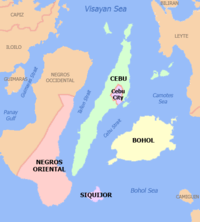
Central Visayas consists of the two major island provinces of Cebu and Bohol, as well as the smaller island of Siquijor and several outlying islands. It also includes the eastern half of the larger island of Negros. The straits of Cebu and Tañon are also part of the region as well. The region is bordered to the north by the Visayan Sea, west by the province of Negros Occidental in Western Visayas, south by the Bohol Sea, and east by the Camotes Sea and the island of Leyte in Eastern Visayas.
Administrative divisions
The Central Visayas region consists of 4 provinces and 3 independent cities:
| Province or HUC | Capital | Population (2015)[1] | Area[6] | Density | Cities | Muni. | Barangay | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| km2 | sq mi | /km2 | /sq mi | |||||||||
| Bohol | Tagbilaran | 21.7% | 1,313,560 | 4,820.95 | 1,861.38 | 270 | 700 | 1 | 47 | 1,109 | ||
| Cebu | Cebu City | 48.6% | 2,938,982 | 4,943.72 | 1,908.78 | 590 | 1,500 | 6 | 44 | 1,066 | ||
| Negros Oriental | Dumaguete | 30.7% | 1,354,995 | 5,385.53 | 2,079.36 | 250 | 650 | 6 | 19 | 557 | ||
| Siquijor | Siquijor | 1.6% | 95,984 | 337.49 | 130.31 | 280 | 730 | 0 | 6 | 134 | ||
| Cebu City | † | — | 15.3% | 922,611 | 315.00 | 121.62 | 2,900 | 7,500 | — | — | 80 | |
| Lapu-Lapu | † | — | 6.8% | 408,112 | 58.10 | 22.43 | 7,000 | 18,000 | — | — | 30 | |
| Mandaue | † | — | 6.0% | 362,654 | 25.18 | 9.72 | 14,400 | 37,000 | — | — | 27 | |
| Total | 7,396,898 | 15,885.97 | 6,133.61 | 470 | 1,200 | 10 | 116 | 3,003 | ||||
|
† Cebu City, Mandaue, and Lapu-Lapu are highly urbanized cities; figures are excluded from Cebu province. | ||||||||||||
- † Regional center
| City | Population (2015)[1] | Area | Density | City class | Income class | Province | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| km2 | sq mi | /km2 | /sq mi | |||||
| Bais | 76,291 | 319.64 | 123.41 | 240 | 620 | Component | 3rd | Negros Oriental |
| Bayawan | 117,900 | 699.08 | 269.92 | 170 | 440 | Component | 2nd | Negros Oriental |
| Bogo | 78,120 | 103.52 | 39.97 | 750 | 1,900 | Component | 6th | Cebu |
| Carcar | 119,664 | 116.78 | 45.09 | 1,000 | 2,600 | Component | 5th | Cebu |
| † Cebu City | 922,611 | 315.00 | 121.62 | 2,900 | 7,500 | Highly urbanized | 1st | Cebu |
| Canlaon | 54,509 | 170.93 | 66.00 | 320 | 830 | Component | 4th | Negros Oriental |
| Danao | 136,471 | 107.30 | 41.43 | 1,300 | 3,400 | Component | 3rd | Cebu |
| Dumaguete | 131,377 | 33.62 | 12.98 | 3,900 | 10,000 | Component | 2nd | Negros Oriental |
| Guihulngan | 95,969 | 388.56 | 150.02 | 250 | 650 | Component | 5th | Negros Oriental |
| Lapu-Lapu | 408,112 | 58.10 | 22.43 | 7,000 | 18,000 | Highly urbanized | 1st | Cebu |
| Mandaue | 362,654 | 25.18 | 9.72 | 14,000 | 36,000 | Highly urbanized | 1st | Cebu |
| Naga | 115,750 | 101.97 | 39.37 | 1,100 | 2,800 | Component | 3rd | Cebu |
| Tagbilaran | 105,051 | 36.50 | 14.09 | 2,900 | 7,500 | Component | 3rd | Bohol |
| Talisay | 227,645 | 39.87 | 15.39 | 5,900 | 15,000 | Component | 3rd | Cebu |
| Tanjay | 80,532 | 276.05 | 106.58 | 290 | 750 | Component | 4th | Negros Oriental |
| Toledo | 170,335 | 216.28 | 83.51 | 790 | 2,000 | Component | 3rd | Cebu |
Demographics
| Year | Pop. | ±% p.a. |
|---|---|---|
| 1990 | 4,594,124 | — |
| 2000 | 5,706,953 | +2.19% |
| 2010 | 6,800,180 | +1.77% |
| 2015 | 7,396,898 | +1.61% |
| Data in 2015 includes Negros Oriental. Source: Philippine Statistics Authority[1][7][8][9] | ||
According to the 2015 census, it had a population of 7,396,898. The population density was 700/km2 (1,800/sq mi). The 2015 census showed an average annual population growth rate of 1.76% from 2010 to 2015, slightly higher than the national average of 1.72%.[1]
Languages
The native languages of Central Visayas are:
- Bantayanon, spoken in Bantayan Islands of Cebu province.
- Boholano, a Cebuano dialect spoken in Bohol.
- Cebuano, spoken in Cebu, Negros Oriental, Bohol, and Siquijor. It is the regional lingua franca.
- Hiligaynon, spoken in western Negros Oriental.
- Porohanon, spoken in Camotes Islands of Cebu province.
Mass media
Cebu City is the main media hub for both the region. Large media networks – ABS-CBN, GMA Network, 5, People's Television Network, and CNN Philippines – maintain their respective local stations and branches for viewership, commercial and news coverage purposes. Most of these stations broadcast local news and public affairs as well as entertainment and dramas to cater the local viewers.
Aside from the 24 national daily newspapers available, Cebu City also has 20 local newspapers. Among the widely read are Sun.Star Cebu, Cebu Daily News, and The Freeman. The country's main Islamic news journal, The Voice of Islam, was founded in 1961 and published in this city.
Transportation
Ports
The Port of Cebu is the region's main gateway. There are also ports in Tagbilaran in Bohol, Larena in Siquijor, and Sibulan and Dumaguete both in Negros Oriental. Inter-island shipping is served by numerous shipping lines, two of them fastcraft companies which serve all the provinces in the region.
Airports

The Mactan-Cebu International Airport, located in Lapu-Lapu City, is the country's second busiest airport (after Ninoy Aquino International Airport in Metro Manila) and one of the only three airports in the Visayas serving international flights (aside from Kalibo International Airport and Iloilo International Airport). It is the primary airline hub of Cebu Pacific, and secondary hub for Philippine Airlines and its subsidiaries, with flights to locations throughout the country. It also serves international flights to other Asian and intercontinental destinations.[10]
Other airports in the region are Bohol-Panglao International Airport which serves Tagbilaran and the rest of Bohol, and Sibulan Airport which serves Dumaguete and the rest of Negros Oriental.
References
- Census of Population (2015). "Region VII (Central Visayas)". Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay. PSA. Retrieved June 20, 2016.
- "Change in name will be good for Philippines". Inquirer Opinion.
- "Should the Philippines be renamed? Historian weighs in".
- "Executive Order No. 183, s. 2015". Official Gazette (Philippines). May 29, 2015. Retrieved June 5, 2015.
- "Duterte dissolves Negros Island Region". Rappler. August 9, 2017. Retrieved August 10, 2017.
- "PSGC Interactive; List of Provinces". Philippine Statistics Authority. Archived from the original on January 21, 2013. Retrieved April 4, 2016.
- Census of Population and Housing (2010). Population and Annual Growth Rates for The Philippines and Its Regions, Provinces, and Highly Urbanized Cities (PDF). NSO. Retrieved June 29, 2016.
- Census of Population and Housing (2010). "Region VII (Central Visayas)". Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay. NSO. Retrieved June 29, 2016.
- Censuses of Population (1903–2007). "Region VII (Central Visayas)". Table 1. Population Enumerated in Various Censuses by Province/Highly Urbanized City: 1903 to 2007. NSO.
- "Mactan Cebu International Airport - Cebu Pacific - Philippines". Mactan-cebuairport.com.ph. Retrieved April 22, 2013.
External links