Wz. 35 anti-tank rifle
The Model 35 antitank rifle (Karabin przeciwpancerny wzór 35, abbreviated "kb ppanc wz. 35") was a Polish 7.9 mm anti-tank rifle used by the Polish Army during the 1939 Invasion of Poland. It was designated model 35 for its design year, 1935: It was also known by its codename "Uruguay", after that country (kb Urugwaj; or kb Ur) and by the name of its designer, Józef Maroszek(pl).
| Karabin przeciwpancerny wz.35 | |
|---|---|
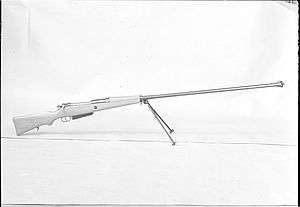 Karabin przeciwpancerny wzór 35 | |
| Type | Anti-tank rifle |
| Place of origin | Poland |
| Service history | |
| Used by | See Users |
| Wars | World War II |
| Production history | |
| Manufacturer | Państwowa Fabryka Karabinów |
| No. built | 3,500 |
| Specifications | |
| Mass | 10 kg (22 lb) (loaded) |
| Length | 1,760 mm (69 in) |
| Barrel length | 1,200 mm (47 in) |
| Cartridge | 7.92×107mm DS |
| Caliber | 7.9mm |
| Action | Bolt action |
| Rate of fire | 8–10 round/min |
| Muzzle velocity | 1,275 m/s (4,180 ft/s) |
| Feed system | 4-round box magazine |
Secrecy
The weapon was initially a top secret project of the Polish Army, and was also known by various codenames. Until mobilization in 1939, the combat-ready rifles were held in closed crates marked: "Do not open! Surveillance equipment!". Another of the rifle's cover names was "Uruguay" (Polish: Urugwaj, hence Ur), the country to which the "surveillance equipment" was supposedly being exported.
After the fall of Poland, the German army captured large numbers of the kb ppanc wz.35 and renamed it "Panzerbüchse 35 (polnisch)" (abbreviated "PzB 35(p)"). The Italian army later received 800 of the captured weapons, renaming them "fucile controcarro 35(P)." Both names translate roughly as "anti-tank rifle model 1935 (Polish)."
In early 1940, one of the rifles, its stock and barrel sawed off, was smuggled out of Poland across the Tatra Mountains into Hungary for the Allies by Krystyna Skarbek and fellow Polish couriers. The rifle never saw service with the Allies, however. The drawings and specifications had been destroyed by the Poles during the invasion of Poland.
Description
It resembled a rifle with a longer-than-normal barrel supported by a bipod at the front of the wooden stock. It was a Mauser style, bolt-action rifle, fed from a 4-round box magazine. The barrel had a muzzle brake to limit recoil. It absorbed about 65% of the shot energy, and the recoil was comparable to a standard Mauser rifle, even though the cartridge carried more than twice the amount of propellant. It had iron sights fixed for a 300-meter range.
Unlike contemporary anti-tank rifles, it lacked a pistol grip and fired a bullet with a lead core rather than an armour-piercing round with a hard core. The full metal jacket bullet weighed 14.579 g and, due to a high muzzle velocity, was effective even under shallow angles, as instead of ricocheting, the bullet would "stick" to the armour and punch a roughly 20 mm diameter hole. Calculated kinetic energy, by shot, before brake was about 11,850 J. The high energy was due to the relatively long barrel, and nitro powder giving a muzzle velocity of 1,275 m/s.[1]
History
Ammunition
In the late 1920s the Polish General Staff started the development of a light anti-tank weapon for the Polish infantry. In 1931 Lt. Colonel Tadeusz Felsztyn from the Institute of Armament Technology in Warsaw started the first tests of various low-calibre cartridges. After the tests of German-made Hagler bullets proved the possibilities of that type ammunition in perforating steel plate, the National Ammunition Factory in Skarżysko-Kamienna was ordered to develop its own 7.92 mm cartridge with a muzzle velocity of over 1,000 meters per second. After a series of tests, the new DS cartridge was proposed.
The DS ammunition was originated from the standard 7.92×57mm cartridge as used by both the Mauser rifle 1898 (wz.98) and its Polish variant the Karabinek wz.29. The length of the cartridge was extended to 131.2 millimetres (5.17 in) and the overall weight was 64.25 grams (2.266 oz). After an additional series of tests the copper cartridge case was replaced with a case made of brass (67% copper/ 23% zinc).
The round's armor-defeating properties were not through penetration, i.e. by punching the core through the armor like a typical penetrator, but through the impact of the bullet flattening against the plate, transferring kinetic energy to the metal. The result was that the bullet would cause spalling on the interior of the armor plate, ideally ejecting an approximately 20mm diameter fragment from the interior surface of the armour at high speed, which would then ricochet around the interior, hopefully killing crew and/or damaging equipment or engines (this is similar in concept to modern HESH anti-tank rounds, albeit less potent). Due to the physics of spalling, the size of this spall was larger than the actual rifle caliber, and could theoretically do more damage ricocheting around inside the vehicle than the bullet itself would if it penetrated. The downside was that since the bullet itself was not designed to penetrate, it could not be filled with an incendiary component and used to ignite fuel tanks, or filled with tear gas (as used by the similar German 7.92×94mm Patronen anti-tank rifle cartridge), which was intended to force the crew to evacuate, or at least greatly reduce their combat effectiveness, even if no-one was hit by the bullet itself.
The Soviet PTRD 14.5×114mm anti-tank rifle also used a bolt based on the Mauser Gewehr 98 rifle, as this design is legendary for its strength and simplicity and has become the most widely adopted and copied designs of all time. The Wz. 35 is itself inspired by the 13.2mm TuF anti-tank rifle, also a scaled-up G98 rifle. The main difference is that while the TuF and PTRD were chambered in a large-caliber round, the Wz. 35 used an oversized cartridge case mated to a rifle-caliber 8mm bullet, giving very high velocity at the expense of hitting power. The Panzerbüchse 39 also used an 8mm bullet, but with an out-sized 8mm Mauser cartridge case known as the 7.92x94mm Patronen, and a special tool-steel cored bullet.
Rifle

Simultaneous to the development of the ammunition, a young graduate of the Warsaw University of Technology, Józef Maroszek, was ordered to design an anti-tank rifle. On August 1, 1935, the Committee of Equipment and Armament officially ordered the rifle and in October the first tests of the new weapon commenced.
The rifle was based on the Mauser Gewehr 98, with the action modified to sustain the higher pressure and length of the new cartridge and the barrel lengthened significantly. The first tests carried out in Brześć and Pionki showed that the new weapon was capable of penetrating a 15 mm steel plate at a distance of 300 metres with similar results against angled steel plate. Initially the barrel could withstand only about 30 shots, after which it had to be replaced with a new one. However, this drawback was soon corrected and the final prototype could fire approximately 300 shots. The committee accepted the new design on November 25, 1935, and in December the Ministry of Military Affairs ordered the delivery of 5 rifles, 5000 cartridges and a set of spare barrels for further tests.
After the tests carried out by the Centre of Infantry Training in Rembertów proved the effectiveness and reliability of kbk ppanc wz.35, the Ministry ordered 7610 rifles to be delivered to the Polish Army by the end of 1939. It is uncertain how many rifles were actually produced, but it is estimated that there were more than 6,500 delivered by September 1939.
Use

The rifle was the main anti-tank weapon of an infantry platoon. Each infantry company and cavalry squadron was to be equipped with three rifles, each operated by a team of two soldiers. Additional anti-tank teams were to be created at a later stage. Although the weapon was successively introduced to the units, it remained a top secret. The rifles were kept in closed wooden crates, each marked with a number and a notice do not open; surveillance equipment. The teams were trained in secret military facilities just before the war, beginning in July 1939, and had to swear to preserve the secret.
The rifle was carried by the leader of the two-man rifle team on a carrying strap. The other member of the squad was his aide and provided him with cover while he was reloading. The weapon was usually fired from prone supported position with the bipod attached to the barrel. However, it could be also used in other positions, like prone unsupported and crouch. The effective range was 300 metres and the weapon was effective against any German tank of the period, including Panzer III and Panzer IV. It could penetrate all lightly armored vehicles in any range. It could penetrate 15 mm of armor, sloped at 30° at 300 m distance, or 33 mm of armor at 100 m.[2]
Panzerbüchse 35(p)

The Karabin przeciwpancerny wz.35 was extensively used during the Invasion of Poland of 1939 by most Polish units. After Poland was overrun by Germany and the Soviet Union, large numbers of the weapon were captured. By 1940, Germany had pressed 800 into service as Panzerbüchse 35 (polnisch) (PzB 35(p)) and later PzB 770(p), and sped up work on their own simplified, one-shot anti-tank rifle Panzerbüchse 39 (PzB 39). Germany replaced some of the captured Polish DS ammunition with their own 7.92 mm hardened-steel-core bullets.[2]
Hungary confiscated some of these guns from Polish forces withdrawn into the Magyar land. Finland bought 30 of them in March 1940 but they arrived after the end of the Winter War. They performed poorly during the Continuation War and were used for training.[3]
In 1941, Germany transferred PzB 35 (p) to the Italian armed forces[2], which used them in combat under the designation Fucile Controcarro 35(P) until the end of World War II. The German Army recaptured some of these rifles after the Italian armistice and designated them as PzB 770 (i).[2]
Users
Survivors
There are at least three in the United Kingdom. One is on exhibit in Poland, at Warsaw's Polish Army Museum; another is located in Armament Museum in Poznań Citadel, another is in Museum of the Second World War in Gdańsk, and one is in Australian War Memorial in Canberra. The Norwegian Armed Forces Museum holds several specimens of the Wz. 35.
See also
- Anti-tank rifle
- Boys Anti-tank Rifle
- Krystyna Skarbek
- Saboted light armor penetrator, a possible descendant
Notes
- http://heksan.umcs.lublin.pl/obliczarka/index.php
- Zaloga 2018, p. 13.
- Zaloga 2018, p. 58.
- Zaloga 2018, p. 43.
References
- Departament Broni Piechoty (1938). Dodatek do instrukcji o broni piechoty. Część I. Karabin wzór 35. Polish Ministry of War.
- Gwóźdź, Zbigniew; Zarzycki, Piotr (1993). Polskie konstrukcje broni strzeleckiej. SIGMA NOT. ISBN 978-83-85001-69-0.
- Smoliński, Aleksander (1992). "Wybrane problemy z historii karabinu przeciwpancernego wz. 35". MWP Bulletin.
- Sadowski, Jerzy (1995). "Karabin przeciwpancerny wz.35 w fortyfikacjach II RP". Nowa Technika Wojskowa. 11.
- Nowakowski, Tadeusz (1995). "Karabin przeciwpancerny wz. 35". Nowa Technika Wojskowa. 6.
- Zaloga, Steven J. (2018). The Anti-Tank Rifle. Oxford, UK: Osprey Publishing. ISBN 978-1-4728-1722-8.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Wz.35. |
