Timeline of Arizona
The following is a timeline of the history of the area which today comprises the U.S. state of Arizona. Situated in the desert southwest, for millennia the area was home to a series of Pre-Columbian peoples. By 1 AD, the dominant groups in the area were the Hohokam, the Mogollon, and the Ancestral Puebloans (also known as the Anasazi). The Hohokam dominated the center of the area which is now Arizona, the Mogollon the southeast, and the Puebloans the north and northeast. As these cultures disappeared between 1000–1400 AD, other Indian groups settled in Arizona. These tribes included the Navajo, Apache, Southern Paiute, Hopi, Yavapai, Akimel O'odham, and the Tohono O'odham.
Important dates in Arizona's history Flag of Arizona |
|---|
|


The first European presence in the state were the Spanish. In 1539 Marcos de Niza explored the area, followed by Francisco Vásquez de Coronado the following year. Spanish missionaries began to settle in the southern portion of the state, near present-day Tucson, around 1700, but did not move further north. With the construction of the Presidio San Augustin del Tucson, on August 20, 1775, Tucson became the first European city in what would become Arizona. In 1822, Arizona became part of the state of Sonora, Mexico, but most of current Arizona was transferred to the United States as a result of the Mexican–American War, with the rest transferring with the completion of the Gadsden Purchase in 1853. During the American Civil War, both sides laid claim to Arizona, although the North and South split the New Mexico/Arizona area differently: the South split the territory into north and south divisions, creating Confederate Arizona, while the northern section remained part of the United States as the New Mexico Territory; while the North in 1863, after driving Confederate forces from the Tucson area, created the Arizona Territory from the New Mexico Territory by splitting off the western section. Prescott became the territory's first capital, which would transfer to Tucson in 1867, then back to Prescott in 1877, before settling finally in Phoenix in 1889.
Arizona achieved statehood in 1912, becoming the 48th state, with Phoenix remaining the capital of the new state. In the 1900s, the state, particularly the Phoenix Metropolitan area, has seen tremendous population growth. Phoenix currently ranks as the 6th most populous city in the nation.
Pre-Columbian and Spanish eras
Pre-Columbian
- ca. 9,000 BC – Paleo-Indians arrive in the southwest, including Arizona, known as the Clovis culture, they were hunter-gatherers.[1]
- ca. 4,500 BC – Maize is introduced into the southwest United States, including Arizona.[2]
- ca. 1,500 BC – Pre-Columbian Indians begin developing irrigation systems.[2]
- 1,250 BC – Las Capas, slightly north of present-day Tucson, settled by pre-Columbian peoples, centered on an irrigation system.[2]
- 600 BC–550 AD – Ancestral Puebloans begin to settle on the Four Corners area.[3]
- 1–300 AD – Hohokam establish several villages along the Gila River.
- 200 AD – The Mogollon culture begins to appear in the southeast area of Arizona.[4]
- 300 AD – Ceramics appear in the Hohokam culture.[5]
- ca. 450 AD – Pueblo Grande settled.
- 600–1300 AD – Hohokam build large network or irrigation canals throughout the area.[6]
- 875 AD – Patayan peoples appear along the Colorado River.[7]
- 899 AD – Major floods along Salt River disrupt Hohokam irrigation systems.[8]
- 1000 AD – The Kayenta tradition of the Ancestral Puebloans develops in northern Arizona.[9]
- 1100 AD – The Hopi found the village of Oraibi, the oldest continuously inhabited settlement in North America.[10][11]
- 1276–99 AD – Severe drought hits the Colorado Plateau.[12]
- 1276–99 AD – Grasshopper Pueblo founded by the Mogollon and Ancestral Puebloans.[13]
- 1300 AD – Ancestral Puebloans abandon their communities in north Arizona.
- 1300 AD – Hohokam have largest population in the southwest.[5]
- 1300 AD – Awatovi founded by the Hopi.[14]
- 1300 AD – The Yavapai, descended from the Patayan, begin settling in Arizona near the southern extent of the Colorado Plateau.[15]
- 1370s AD – Drought hits the Hopi areas.[16]
- 1300–1450 AD – Periods of drought alternate with flooding in the Salt River area.
- 1400 AD – The Athabaskan ancestors of the Navajo enter Arizona.[17]
- 1430s AD – Drought hits the Hopi areas.[16]
- 1440s AD – Drought hits the Hopi areas.[16]
- ca. 1450 AD – Pueblo Grande abandoned due to drought.
- 1455–65 AD – Drought hits the Hopi areas.[16]
Arrival of the Spanish
- 1539 – Marcos de Niza, a Jesuit Franciscan leads an expedition which passes through eastern Arizona.[18]
- 1540–42 – Francisco Vázquez de Coronado leads an expedition, part of which explores Arizona.[19]
- 1583 – Antonio de Espejo's explores eastern Arizona, discovers mines near present-day Jerome.[20]
- 1598 – Juan de Ornate leads an expedition into Arizona, explores the Verde Valley.[20]
- 1687 – Jesuit priest Eusebio Kino establishes missions among the Tohono O'odham people along the Santa Cruz River.[21]
- 1691 – Kino establishes the Mission Los Santos Ángeles de Guevavi.[22]
- 1694 – Kino explores Arizona, discovers the ruins of Casa Grande.[19]
- 1732 – Mission San Xavier del Bac founded by Jesuits near present-day Tucscon.[23]
- 1736 – Silver discovered on the ranch of the Basque settler, Bernardo de Urrea, near the Guevavi mission. The name of Urrea's ranch was Arizona, meaning "the good oak tree".[24]
- 1751 – The O'odham people rebel against the Spanish, but the rebellion is put down.[25]
- 1752 – In response to the rebellion, the Spanish construct a presidio at Tubac, the first permanent European settlement in Arizona.[25]
- 1757 – Tumacácori Mission established.[26]
- 1768 – Arizona becomes part of the Provincia de las Californias, under Spanish rule.
- 1775 – Southern Arizona explored by Juan Bautista de Anza while leading an expedition from Mexico to San Francisco.[19][25]
- 1776 – Presidio San Augustin del Tucson (military outpost) established, when the presidio of Tubac was relocated.[23][27]
- 1779 – December 6: First Battle of Tucson.
- 1781 – Yuma Indians massacre Spanish settlers and missionaries.[25]
- 1782
- May 1: Second Battle of Tucson.
- December 25: Third Battle of Tucson (1782).
- 1784 – March 21: Fourth Battle of Tucson, Sonora, New Spain.
- 1789 – One of the first Spanish land grants is bestowed to Toribio de Otero, a 63-acre ranch which remained in the Otero family until 1941.[28][29]
- 1804 – The Spanish province of Las Californias is split, and Arizona becomes part of the new province of Alta California.
- 1821 – Mexico achieves independence from Spain.
- 1824 – The Alta California Territory was formed, which included Arizona, under the Mexican Constitution of 1824.
- 1825 – The first people from the fledgling United States enter Arizona, the trapper Sylvester Pattie and his son James; trapping along the San Francisco, Gila, and San Pedro rivers.[30]
- 1846
- December 16: Capture of Tucson, Sonora, Mexico, by United States forces.
- Kit Carson leads an exploration which passes through Arizona on their way from Santa Fe to California.[31]
- Lieutenant Colonel Phillip Cooke led a group of Mormon settlers, known as the "Mormon Battalion" across Arizona on their way to San Diego.[31]
- 1847 – Tucson occupied by "Mormon Battalion."[32]
U.S. possession and territory

1840s
- 1848
- With the end of the Mexican–American War, the area which includes today's Arizona becomes part of the United States, as part of the New Mexico Territory.[34]
- Population of Tucson is 760.[23]
1850s
- 1853
- The most southern section of Arizona becomes part of the United States per Gadsden Purchase.[23][35]
- Lieutenant Amiel Weeks Whipple led a surveying party from Fort Smith, Arkansas, to Los Angeles, through northern Arizona. The party reached Flagstaff by Christmas.[36]
- 1855 – While surveying a road from New Mexico to California, Lieutenant Beale's company camps at the current site of Flagstaff. The location got its name when his men stripped a local tree and ran a flag up the staff.[37]
- 1856 – August 29: Conference held to organize Arizona Territory.
- 1857 – San Antonio-San Diego Mail Line in operation.
- 1859 – Gold is discovered near the confluence of the Gila and Colorado Rivers, creating Arizona's first "gold rush".[38]
1860s
- 1862
- February 14: Confederate Arizona officially becomes a territory of the Confederate States of America, consisting of the portion of the New Mexico Territory below the 34th parallel, with Mesilla, New Mexico as the territorial capital.[39][40]
- February: Tucson occupied by Confederate forces.[23]
- May 20: Capture of Tucson by Union forces.[41]
- Gold is discovered north of Yuma, and the town of La Paz is founded. By the end of the year, it would be the most populous settlement in Arizona, and the capital of Yuma County. The following year, it would be considered for the capital of the Arizona Territory.[38]
- 1863
- February 24: The Arizona Territory is created by splitting the New Mexico Territory virtually in half.[42]
- A party which included Jack Swilling discovers gold along the Hassayampa River, on what is now known as Rich Hill.[43]
- Wickenburg becomes the first town to be established in what is now Maricopa County, Arizona.[44]
- Tully, Ochoa & Co. merchandisers opens in Tucson.[45]
- 1864
- May 30: Prescott founded, and named the capital of the Arizona Territory.[46]
- November 7: Arizona Historical Society founded by an Act of the First Territorial Legislature.[47]
- Fort Whipple moved near Prescott (from Chino Valley, where it had been established the prior year).
- 1865 – Camp McDowell (later Fort McDowell) is set up on the Verde River.[48]
- 1866 – L. Zechendorf & Co. merchandisers opens in Tucson.[45]
- 1867
- November: Jack Swilling, resident of Wickenburg, establishes the Swilling Irrigating and Canal Company with the intent to develop the Phoenix area, which he became impressed with after viewing the area on a visit to Camp McDowell.[49]
- December: Swilling leads a group of 17 miners from Wickenburg to the Phoenix area and begins the process of developing a canal system.[50]
- Territorial capital moved from Prescott to Tucson.[46]
- 1868
- May 4: Phoenix is officially recognized by the Board of Supervisors of Yavapai County, which at that point contained Phoenix.[51]
- June 15: First post office in Phoenix is established, in the Swilling homestead, with Swilling as postmaster.[52]
- Swilling has completed almost 3 miles of his canals in Phoenix.[53]
- Mary Adeline Gray, the first European woman settler in Phoenix, and her husband Columbus, arrive.[53]
- Salt River floods for the first of many times during Phoenix's settlement.[53]
- 1869 – St. Augustine Roman Catholic Church built in Tucson.[32]
1870s
- 1870
- October 20: Town site selected in what is currently downtown Phoenix.[51][54]
- Phoenix is laid out,[55] original town site consists of 320 acres, or 0.5 square miles.[51][56]
- Population of the Salt River Valley reaches 240, the Arizona Territory has 9,658 people.[53]
- 1700 acres under cultivation in the Salt River Valley.[53]
- Maricopa Canal completed.[53]
- Arizona Citizen newspaper begins publication in Tucson.[57]
- J.S. Mansfield news depot opens in Tucson.[45]
- 1871
- February 12: Maricopa County is broken out of Yavapai County, Phoenix becomes the county seat.[41][58]
- July 4: First wheat ground in Salt River Valley at Birchard's Mill.[53]
- First permanent building in Phoenix, the Hancock residence, is constructed at Washington and First Streets.[53]
- The second building in Phoenix, a brewery, is constructed.[53]
- The first store (Hancock's) and the first church (Central Methodist) open in Phoenix.[51][53]
- The Tempe Irrigating Canal Co. is created.[53]
- Tempe founded by Charles T. Hayden.[53]
- Population of Phoenix reaches 500.[53]
- 1872
- September 5: Phoenix public school in session.[51]
- December 19: Fort Grant is established at the foot of Mount Graham.[59]
- Adobe schoolhouse constructed in Phoenix.[53]
- Phoenix's first wedding, between George Buck and Matilda Murray.[53]
- Phoenix's first Chinese settlers arrive.[53]
- The first bookstore and newsstand in Phoenix is opened by Edward Irvine.[53]
- Public School department in Tucson is organized.[32]
- Population of Tucson is 3,500 (estimate).[32]
- 1873
- 1874
- 1875 – Salt River floods.[53]
- 1876
- July 1: Territorial Prison built in Yuma. First prison in Arizona.[59]
- Empire Ranch is founded in southeastern Pima County.[61]
- Salero founded as a mining camp. Currently a ghost town, one of the best preserved in Arizona.[62]
- 1877
- 1878
- Salt River Herald, Phoenix' first newspaper, begins publication.[65]
- The first bank in Phoenix, a branch of the Bank of Arizona, opens.[66]
- Population of Phoenix reaches 1500.[53]
- Brick factory opens in Phoenix.[53]
- Grand Canal completed.[53]
- Mesa is founded.[53][63]
- El Fronterizo newspaper begins publication.[57][67]
- 1879
- Presbyterian church established in Phoenix.[55]
- Salt River Indian Reservation is formed.[53]
- The Southern Pacific railroad reaches Maricopa.[53]
- Arizona Daily Star newspaper begins publication in Tucson.[57]
- Presbyterian Church built in Tucson.[32]
- Town of Terminus is founded as a supply stop for the construction of the Southern Pacific Railroad.[31]
- Colossal Cave is discovered southeast of Tucson.[68]
1880s
- 1880
- Arizona Gazette newspaper begins publication.[65]
- Methodist church established in Phoenix.[55]
- First legal hanging in Maricopa County.[53]
- Southern Pacific Railroad begins operating in Tucson.[32]
- Tucson Library Association organized.[32]
- St. Mary's Hospital opens near Tucson.[32]
- Terminus is renamed Casa Grande. Population by end of year was 33.[31]
- Population of Phoenix reaches 1,800;[55] population of Tucson reaches 7,007.[23]
- Bien/McNatt House is built in Casa Grande.[69]
- Harshaw founded as a mining town. Currently a ghost town.[70]
- 1881
- February 25: Phoenix officially incorporated when Governor John C. Frémont signs "The Phoenix Charter Bill", and instituting a mayor-council form of government.[41][51]
- La Guardia, Phoenix's first Spanish language newspaper, begins publication.[71]
- May 3: John T. Alsap defeated James D. Monihon, 127 to 107, to become the Phoenix's first mayor.[51]
- May 9: City Council begins meeting.[72]
- June 24: Catholic church in Phoenix dedicated.[55]
- Phoenix Rangers organized in response to hostile Apache activity in Tonto Basin.[53]
- Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe railroad begins operating in Tucson.[32]
- Methodist Church built in Tucson.[32]
- AT&SF's subsidiary, the Atlantic & Pacific Railroad constructs line from Albuquerque to California. The line passes through Flagstaff, and many towns in northern Arizona take their names from men working on the line: Kingman, Holbrook, Drake and Winslow.[36]
- 1882
- March 20: Wyatt Earp kills Frank Stilwell in Tucson.
- Kingman founded.
- The Kingman Daily Miner begins publishing. As of 2015, it is still in publication.[73]
- Robles Ranch established. Will become Three Points.[74]
- 1883
- Cotton cultivation is brought to the Salt River Valley.[53]
- Two smallpox outbreaks in Phoenix. City creates the position of Health Officer.[53]
- Mesa City incorporates.[53]
- Tucson chartered. Townsite is bounded by Speedway Boulevard on the north, 22nd Street on the south, 1st Avenue on the east, & on the west by Main Avenue from north of 18th Street, & 10th Avenue from south of 18th Street.[23]
- First church, a Methodist congregation, established in Flagstaff.[75]
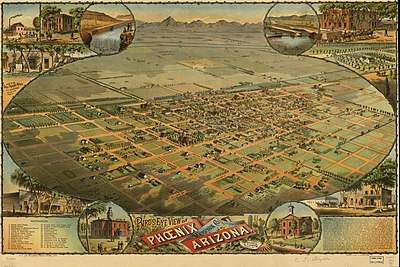
- 1884
- Arizona Industrial Exposition begins.[76][77]
- Valley Bank founded by William Christy.[71]
- The Women's Christian Temperance Union opens a Phoenix branch.[53]
- 1885
- 1886
- A second major fire in Phoenix destroys several buildings and results in approximately $100,000 in damage.[53]
- Phoenix Fire Department established, when bond issue passes establishing 2 fire companies.[53]
- First private gas lighting company established in Phoenix.[56]
- First telephone company opens in Phoenix.[66]
- Phoenix Opera House is completed.[53]
- Arizona Insane asylum's construction is completed.[53]
- Casa Grande suffers from a devastating fire.[31]
- Judge William T. Day House is built in Casa Grande.[69]
- Fire destroys a major portion of Flagstaff on Valentine's Day.[78]
- 1887
- Maricopa-Phoenix railway and horse-drawn Street Railway begin operating.[79]
- Public water system created in Phoenix.[66]
- Public Health Department is established in Phoenix.[53]
- Mule-drawn streetcar system established in Phoenix.[66]
- Salt River Valley News begins weekly publication.[53]
- Philanthropist Mary Tileston Hemenway sponsored an archeological expedition led by Frank Hamilton Cushing which explored the Casa Grande ruins.[19]
- McMillan Building built in Flagstaff.[80]
- 1888
- 1889
- Prescott incorporated.
- Capital of Arizona Territory relocated to Phoenix from Prescott.[83]
- Citrus cultivation is begun in the Salt River Valley by the Arizona Improvement Company.[53]
- The Atlantic & Pacific Railroad constructs a freight depot in Flagstaff.[84]
1890s
- 1890
- Arizona Republican newspaper begins publication.[65]
- Population of Phoenix reaches 3,152;[41] Casa Grande's population was 256.[31]
- Walnut Grove dam bursts, 50 people killed.[53]
- Ladies Benevolent Society formed in Phoenix.[53]
- Shonessy House in Casa Grande is built.[69]
- Dr. Alexander Chandler purchases 80 acres southeast of Phoenix, and establishes a ranch and trading post.[85]
- 1891
- Phoenix Indian School opens.
- Largest flood in the history of the Salt River Valley occurs.[56]
- Telephones come to Phoenix.[53]
- A territorial convention is held in Phoenix. The idea of becoming a state is discussed, but is voted down.[53]
- University of Arizona opens per Morrill Act;[23] Old Main, University of Arizona built.[86]
- 1892
- June 22: Casa Grande Reservation is created by President Benjamin Harrison. The first prehistoric and cultural reserve in the United States.[19]
- The Phoenix Sewer and Drainage Department is created.[56]
- The Phoenix Indian School holds its first classes.[53]
- Mesa Free Press begins publication.[87]
- Flagstaff suffers another major fire.[78]
- 1893
- The Phoenix Street Railway switches over from mule-drawn to electrical streetcars.[56]
- The Arizona Territory passes a law allowing cities, including Phoenix, to annex land surrounding the city, as long as it obtained the permission of the inhabitants of that area.
- Arizona State Museum established in Tucson.
- Casa Grande suffers its second major fire in 6 years.[31]
- The Abineau building, a brick liquor store, was built in Flagstaff.[88]
- 1894
- 1895
- Santa Fe, Prescott and Phoenix Railway begins operating.[58]
- Arizona Gazette newspaper begins publication.[65]
- Phoenix Union High School opens, and the Phoenix Union High School district is created.[51][53]
- Rosson House built in downtown Phoenix.[90]
- Sisters of Mercy Hospital (today called St. Joseph's Hospital and Medical Center) opens in Phoenix.[53]
- In Phoenix, the New York Store is opened by Sam Korrick;[71] Nathan and Isaac Diamond open the Boston Store; and Baron Goldwater opens a branch of his Flagstaff store, M. Goldwater and Brothers.[53]
- 1896
- The Adams Hotel opens in Phoenix.[71]
- Date Palms are introduced into the Salt River Valley.[53]
- Sirrine House built in Mesa.[91]
- The Cathedral of Saint Augustine is constructed.[92]
- 1897
- May 24: Peoria founded.
- The Friday Club begins a movement to open a public library in Phoenix.[53]
- Roman Catholic Diocese of Tucson established; Cathedral of Saint Augustine (Tucson) built.
- Flagstaff suffers its fourth major fire in 11 years.[78]
- The Little Red Schoolhouse is constructed in Kingman.[93]
- 1898
- El Demócrata newspaper begins publication in Phoenix.[65]
- The block of the red-light district is now illegal in Phoenix.[53]
- Doris Opera House Opens in Phoenix.[53]
- First public library opens in Phoenix.[53]
- Casa Grande Hotel opens.[69]
- The Coconino Chop House, an iron building, was constructed in Flagstaff.[78]
- 1899
- Phoenix Library Association created.[53]
- Northern Arizona University (NAU) founded in Flagstaff.[94]
- The second half of the Weatherford Hotel is constructed in Flagstaff, and the hotel would open on New Year's Day, 1900.[95]
- Las Dos Naciones Cigar Company founded, the only cigar company in the southwest.[96]
1900-09
- 1900
- July 14: Most of downtown Prescott is destroyed by fire.[97]
- Dorris Theatre opens in Phoenix (approximate date).[98]
- Phoenix accesses unincorporated lands, area increases from .5 acre to over 2 acres.[53]
- In spite of efforts by the Women's Temperance Union, Phoenix has 28 saloons and 18 casinos.[53]
- First automobiles arrive in Phoenix.[53]
- Population in Phoenix reaches 5,544,[41] population of Tucson is 7,531.[23]
- San Rafael Ranch built south of Patagonia.[99]
- 1901
- 1902 – Evans School for Boys opens; later renamed Mesa Ranch School.
- 1903
- February 7: Salt River Project founded (as the Salt River Valley Water Users' Association).[101][102]
- Voters in Phoenix approve a bond to create a municipal waterworks.[53]
- Desert Laboratory founded in Tucson.[103]
- 1904
- 1905
- 1906
- Construction begins on the Theodore Roosevelt Dam.[105]
- Gambling is outlawed in Phoenix.[53]
- A.J. Chandler purchases 100 ostriches, the beginning of Ostrich farming in Chandler.[106]
- 1907
- 1908
- 1909
- In Phoenix, the Central Avenue bridge over the Salt River is approved.[53]
- The original "Old Main" campus of Mesa High School opens.
- Mesa installs potable waterworks system.
- Arizona Overland Telephone Company opens in Flagstaff, giving residents long distance capability for the first time; headquartered in the Telegraph Building, built the same year.[109]
- September 15: Yuma Territorial Prison is closed.[59]
1910s
- 1910
- Speed limit in Phoenix is increased to 12 mph in city limits; city has 329 licensed cars.[53]
- Phoenix city schools establish an official segregation policy.[53]
- In Phoenix, the Adams Hotel is destroyed by fire, but is rebuilt.[53]
- Guidelines concerning surface water rights are established by the Kent decree.[53]
- Population in Phoenix reaches 11,134,[41] Tucson hits 13,193.[23]
- The oldest synagogue in Arizona, Stone Avenue Temple, opens in Tucson. Currently known as Temple Emanu-El.[110]
- 1911
- May 18: Roosevelt Dam dedicated by Theodore Roosevelt, it is the first multi-purpose (electricity and water) dam built under the National Reclamation Act.[105]
- Center Street Bridge in Phoenix opens.[53]
- Mesa takes over irrigation system operation within incorporated city limits.
- Hinchcliffe Court opens near Tucson, the first auto court motel in Arizona.[111]
- 1912
- February 14: Arizona becomes the 48th state of the United States; Phoenix becomes the state capital.[105]
- May 17: Chandler is founded by Alexander Chandler, from the breakup of his ranch.[53][85][112]
- May 21: The Chandler Arizonan begins publication.[113]
- Women are granted the right to vote.[53]
- Casa Grande Dispatch founded.[114]
- Chandler Grammar School opens.[85]
- Fort Grant becomes the State Industrial School for Wayward Boys and Girls.[59]
Statehood through World War II
1910s, continued
- 1913
- November 22: Hotel San Marcos, the first golf resort in the state, opens in Chandler.[112]
- Phoenix adopts council-manager form of government (previously mayor-council), becoming one of the first cities in the country to adopt this form of government.[115]
- 35% of the votes cast in Phoenix were by women.[53]
- Phoenix has 646 registered automobiles.[53]
- Ash Avenue Bridge is completed in Phoenix.[53]
- 1914
- 1915
- St. Mary's Basilica in Phoenix is dedicated.
- Phoenix's first sewer treatment plant is completed.[116]
- Mesa installs sanitary sewer system.
- 1917
- Arizona adopts its state flag.[83]
- Litchfield is founded when the Goodyear Tire Company purchases a tract of land.[116]
- Salt River Valley Water Users Association gains control of the Salt River Project.[116]
- Migrant workers from Mexico are brought in to pick cotton in the Salt River Valley.[116]
- Mesa purchases existing gas and electric utilities from Dr. A.J. Chandler.
- Orpheum Theater opens in Flagstaff.[117]
- 1918
- August 3: Casa Grande Ruins are declared a national monument by President Woodrow Wilson.[19]
- Alfalfa falls to the number two agricultural product, behind cotton in Phoenix.[116]
- The Rialto Theatre opens in Phoenix.[116]
- Spanish flu infects a significant portion of the population in Phoenix.[116]
- 1919
- In anticipation of the upcoming U.S. Census, Phoenix votes to extend the city limits.[116]
- City airfield established in Tucson.
- Hotel Congress opens in Tucson.[118]
- Rialto Theater opens in Tucson.[74]
1920s
- 1920
- Congregation Beth Israel formed in Phoenix.[119]
- The Heard Building, the first skyscraper in Phoenix, is constructed.[51]
- Phoenix Union High School has 2000 students.[83]
- The entirety of the original Phoenix town site is now completely paved.[116]
- A precipitous drop in the price of cotton, from $1.35 to $0.35 a pound, creates a financial crisis in Phoenix.[116]
- Phoenix has over 11,000 registered vehicles.[116]
- Chandler is incorporated.[112][116]
- Rialto Theatre (Arizona) opens in Tucson.
- Phoenix College, one of the oldest community colleges in the United States, and part of the Maricopa Community College District, is established.
- Population in Phoenix reaches 29,053.[51]
- 1921
- Temple Beth Israel, Phoenix's first synagogue, opens.[120]
- "Rich, Resolute, Ready, Phoenix, Salt River Valley" becomes the official tourism slogan of Phoenix.[116]
- Mesa Welfare League founded.
- Casa Grande Union High School is constructed.[69]
- 1922
- Valley and Gila River Banks merge.[116]
- Water from the Verde River becomes available in Phoenix through a 30-mile-long (48 km) wooden pipeline.[116]
- KFAD becomes Phoenix's first radio station (later renamed KTAR; it was followed shortly by KFCB, which today is called KOY.[116]
- Casa Grande Municipal Airport opens (date approximate).[121]
- Chandler High School building is completed, and classes begin there in September.[85]
- 1923
- Cave Creek Dam is completed.[116]
- Salt River Project absorbs the Tempe Irrigating Canal Company.[116]
- Union Station is built in Phoenix.[122]
- Deaconess Hospital (today known as Banner Good Samaritan Medical Center) opens in Phoenix.[116]
- Mesa Tribune newspaper begins publication.[65]
- 1924
- Luhrs Building constructed in Phoenix.
- The depression in Phoenix caused by the drop in the cotton price in 1920 ends.[116]
- Phoenix Sanitarium opens.[116]
- Jokake Inn opens in Phoenix.[116]
- South Mountain Park (originally named Phoenix Mountain Park) is created in Phoenix.[116]
- 1925
- 12 subdivisions are annexed by Phoenix.[116]
- Phoenix Fine Arts Association formed.[123]
- The private electric streetcar system is purchased by the City of Phoenix for $20,000.[122]
- Mormon Flat Dam completed.[116]
- Voters approve a separate high school for blacks in Phoenix.[116]
- First municipal airport in Phoenix is opened, near Christy Road and 59th Avenue.[124]
- Phoenix implements a zoning program.[116]
- The Nogales International newspaper founded.[125]
- 1926
- The Phoenix Main Line of the Southern Pacific Railroad is completed, intercontinental rail will begin being routed through Phoenix the following year.[122]
- Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway builds the passenger terminal in Flagstaff.[126]
- The first Annual Masque of the Yellow Moon is held in Phoenix.[116]
- The segregated Phoenix Union Colored High School opens.[116]
- 1927
- Salt River Canal is diverted underground.[116]
- Phoenix voters approve a $750,000 bond issue to improve the street car system.[122]
- Horse Mesa Dam is completed.[116]
- Mesa Arizona Temple dedicated (first time).[127]
- Charles Lindbergh visits Tucson.
- Temple of Music & Art built in Tucson.[128]
- Casa Grande Stone Church is built.[69]
- Hotel Monte Vista is constructed in Flagstaff.[129]
- 1928
- Hotel San Carlos and Westward Ho hotel open in Phoenix.
- Phoenix completes 2 years of annexation, absorbing 74 subdivisions.[116]
- Construction of Sky Harbor Airport in Phoenix is begun.[130]
- Phoenix Little Theatre is incorporated.[116]
- The first paved road connecting Phoenix with Los Angeles (via Blythe), is completed.[116]
- Phoenix creates a zoning and planning commission.[116]
- First production of the Mesa Arizona Easter Pageant.
- James A. Walsh United States Courthouse built in Tucson.
- Casa Grande Hospital built.[69]
- Chandler Heights Citrus District is founded by Dr. Alexander Chandler.[85]
- Museum of Northern Arizona founded in Flagstaff.[131]
- Flagstaff incorporates as a city[37]
- Sharlot Hall Museum opens in Prescott.[132]
- 1929
- February 23: Arizona Biltmore Hotel opens in Phoenix.[83]
- February 23: Scheduled airline service from Los Angeles to Phoenix begins.[83]
- September 2: Sky Harbor Airport opens in Phoenix.[130]
- Phoenix sells municipal airport.[116]
- Heard Museum opens in Phoenix.[133]
- The Tempe Normal School is renamed Arizona State Teachers College.[134]
- Orpheum Theatre and First Baptist Church are built in Phoenix.
- Tourism revenue in Phoenix tops $10 million for first time.[116]
- Phoenix has over 53,000 registered cars.[116]
- Pima County Courthouse and Consolidated National Bank building constructed in Tucson.
- Pioneer Hotel opens in Tucson.
- Paramount Theatre opens in Casa Grande.[69]
- Fox Theater opens in Tucson.[135]
- The first skyscraper in Tucson, the Valley National Bank Building, is erected.[136]
1930s
- 1930
- March 4: Coolidge Dam dedicated by Calvin Coolidge.[102]
- American Airlines brings passenger and air postal service to Phoenix.[130]
- KTAR in Phoenix becomes an NBC affiliate.[116]
- Stuart Mountain Dam is completed.[116]
- In Phoenix the high school installs lights in its athletic stadium.[116]
- Fox Tucson Theatre and Plaza Theater (Tucson) open.
- Arizona Inn built in Tucson.[137]
- The dwarf planet Pluto is discovered by Clyde Tombaugh at Lowell Observatory.[138]
- Population reaches 48,118 in Phoenix.
- 1931
- Hunt's Tomb built in Papago Park in Phoenix.
- Construction on Tovrea Castle completed in Phoenix.[139]
- Fox Movie Palace opens in Phoenix.[116]
- Mesa town area expanded.[127]
- 1932
- Wrigley Mansion completed in Phoenix.[140]
- State of Arizona repeals state law banning alcohol.[116]
- The inaugural Phoenix Open is held.[116]
- Ike and Eddie Basha Sr. found Bashas' supermarkets.[141]
- 1933
- Since the start of the Great Depression, 33% of banks and savings & loans in Phoenix have failed.[116]
- In Phoenix, over 300 bars have obtained liquor licenses since the repeal of the Arizona state law banning alcohol.[116]
- Pueblo Grande Museum Archaeological Park opens.[116]
- 1934
- Encanto Park opens in central Phoenix.
- The term, "Valley of the Sun" is invented by a local advertising agency.[116]
- 1935
- July 16: The city of Phoenix purchases Sky Harbor Airport, which has been run by the city ever since.[130][142]
- The Federal government becomes the largest employer in Phoenix.[116]
- Saint Anthony's Church and Rectory, a Roman Catholic church, is built in Casa Grande.[69]
- Smoki Museum, housing American Indian artifacts, opens in Prescott.[143]
- 1936 – Federal Building-U.S. Post Office in Phoenix is built.
- 1937
- 1938
- Phoenix Thunderbirds are created by the Chamber of Commerce.[116]
- The First Baptist Church in Casa Grande is built.[69]
- The McCullough-Price House built in Chandler.[145]
- Arizona Snowbowl skiing facility opens near Flagstaff.[146]
- 1939
- Desert Botanical Garden opens in Phoenix.
- Bartlett Dam completed.[116]
- Phoenix's second high school, North High School, opens.[116]
1940s
- 1940
- Civic Center Association formed to raise funds for Phoenix Art Center. It was dissolved in 1955 when all fund raising and archival activities were taken over by the Fine Arts Association.[123]
- Tucson Army Air Field established.
- South Tucson incorporates as a city.
- Population of Phoenix reaches 65,414.
- 1941
- January 2: Construction begins on Thunderbird Field in Glendale (later renamed Thunderbird Field No. 1), funded by a collaborative group of Hollywood personalities, including James Stewart, Henry Fonda, Cary Grant, and Margaret Sullavan. The field opens in April.
- Luke Air Force Base opens, its first class graduating in June.
- Williams Air Force Base opens in December.
- Falcon Field opens in Mesa as a training location for British RAF pilots.[147][148]
- Kingman Airport opens as the Kingman Army Airfield.
- Ernest A. Love Field opens near Prescott.[149]
- Urban renewal project in Phoenix creates 3 new housing developments: Marcos de Niza Project for Mexicans, Matthew Henson Project for Blacks, and Frank Luke Jr. Project for Whites.[116]
- 1942
- April 1: the Desert Training Center, formed by General George S. Patton, is created. The base, located in the Mojave Desert in Southern California and the Sonoran Desert in western Arizona, stretched to within 50 miles of Phoenix.[51][150]
- June 22: Thunderbird Field #2 opens in Scottsdale. Later renamed Scottsdale Airport.
- July 20: Gila River War Relocation Center, an internment camp for Japanese-Americans opens southwest of Phoenix, on the Gila River Indian Reservation.[151]
- November 26: Black troops from segregated units riot in Phoenix.[152]
- December: Gila River War Relocation Center is Arizona's fourth largest city, with a population of 13,348.[151]
- Japanese-Americans from Phoenix are relocated to internment camps at Sacaton and Poston.[116]
- Alzona Park in Phoenix is built by the Federal Government as worker housing.[116]
- Williams Auxiliary Army Airfield #5 is built near Chandler. Would become Chandler Memorial Airport, and is currently known as Gila River Memorial Airport.[153]
- 1943
- Camp Papago Park (POW camp) opens in Phoenix in June.[154]
- Litchfield Naval Air Facility opens.[116]
- The new airport at Douglas is designated the first international airport in the United States.[124]
- The Marana Army Air Field opens in Marana as a training site for the Army Air Corps. Currently named the Pinal County Airpark.[155]
- 1944
- December 23: Great Papago Escape of German prisoners, the largest single escape by POW's in any camp in the United States.[156]
- St. Monica's Hospital, the first integrated hospital in Phoenix, opens (today known as Phoenix Memorial Hospital).[116]
- 1945
- November 10: Gila River War Relocation Center is officially closed.[151]
- Arizona State Teachers College becomes Arizona State College.[134]
- Mystery Castle is built in Phoenix.[157]
- Several large factories which were created in Phoenix for war production, begin to close down operations.[116]
Post-war years through the 1960s
1940s, continued
- 1946
- 1947
- October: A fire destroys all but four of Phoenix's electric streetcars. The city begins the process of transitioning to a public bus transit system.[122]
- The Phoenix Charter Revision Committee is formed. The political group, headed by Barry Goldwater, would dominate city politics in the 1950s.[159]
- Phoenix Symphony Orchestra is founded.[158]
- The New York Giants start spring training in Phoenix.[158]
- 1948
- Motorola opens a research and development center for military electronics in Phoenix.[160]
- Phoenix Jewish News begins publication.[65]
- Phoenix establishes its first sales tax.[158]
- KPHO-TV becomes Phoenix's first television station.[158]
- Barry Goldwater elected to the Phoenix city council.[158]
- Mesa Country Club established.[161]
- Falcon Field becomes part of Mesa[148]
- Casa Grande Cotton Kings, a semi-professional ball team were founded.[162]
- Primera Iglesia Baptista, a Church of the Nazarene, was built in Casa Grande.[69]
- Chandler Municipal Airport opens.[163]
- 1949 – Modern wastewater treatment plant built at Riverview in Mesa.
1950s
- 1950s – Widespread use of air-conditioning leads to a construction and population boom in Phoenix.[83]
- 1950
- Catalina Highway constructed in Tucson.
- KTYL-FM radio in Mesa begins broadcasting.
- The Phoenix population reaches 106,818, now 99th most populous city in the United States, and the largest in the Southwest;[158] Mesa's population reaches 16,790; Chandler's population stands at 3,800.[85]
- Flagstaff Symphony Orchestra is formed.[164]
- 1952
- Wright House (residence) built in Phoenix.
- Republican Barry Goldwater elected United States Senator, defeating the Senate Majority Leader Ernest McFarland; Republican John Howard Pyle elected governor
- Arizona Public Service formed by the merger of Central Arizona Light and Power and Northern Arizona Light and Power[158]
- Racial segregation is banned at Sky Harbor Airport.[158]
- Adam Diaz becomes the first Hispanic on the Phoenix city council.[158]
- Arizona-Sonora Desert Museum founded.
- Kingman incorporated.
- 1953
- State courts declare school segregation illegal. Phoenix begins school desegregation.[158]
- KYTL-TV begins operations as an NBC affiliate in Phoenix. Currently KPNX-TV.[158]
- Channel 10 begins broadcasting in Phoenix, currently KSAZ-TV, the Fox affiliate.[158]
- General Motors Desert Proving Grounds opens in Mesa.
- 10 million gallon Pasadena city reservoir completed in Mesa.
- 1954
- 1955
- January 24: Ira Hayes, one of the men made famous by the flag raising on Iwo Jima, and a member of the Pima Indian Tribe, was found dead of exposure near Sacaton.[166]
- Terminal 1 opens at Sky Harbor Airport, built at a cost of $835,000, it represented the most modern and efficient passenger terminals of its time. It was demolished in 1991.[142]
- In Phoenix, Metropolitan Bus Lines is purchased by L.A. Tanner and renamed Valley Transit Line. Tanner was unsuccessful in his attempts to also purchase the city-run municipal bus system.[122]
- Phoenix battles Scottsdale over annexation of unincorporated areas. This battle would last until an agreement was reached regarding "spheres of annexation influence" in 1964.[167]
- KTVK-TV opens operations as an ABC affiliate in Phoenix.[158]
- Agriculture falls to second behind manufacturing in Phoenix's economy.[158]
- Phoenix bans segregation in public housing.[158]
- United States Naval Observatory Flagstaff Station opens.[168]
- 1956 – Tucson Air National Guard Base active.
- 1957
- Park Central Shopping City in business.
- Phoenix Towers built.
- Tempe Airport is closed by the city and razed.[153]
- Radio station KNOT begins airing from Flagstaff.
- 1958
- Phoenix doubles in size through annexation
- Arizona State College becomes Arizona State University.[134]
- The first Cactus Fly-In, a show of vintage aircraft, takes place at Casa Grande Airport.[169]
- Phoenix Flyers Club established.[170]
- Radio station KVNA begins broadcasting on AM from Flagstaff. An FM counterpart would begin broadcasting in 1999.
- 1959
- Phoenix Art Museum opens.[123]
- L.A. Tanner is successful in purchasing the city-owned municipal bus system, merging it into his Valley Transit Line. All bus service in Phoenix is now unified.[122]
- Sunnyslope annexed by Phoenix.[158]
- Deer Valley airport opens.[124]
- The Francisco Grande hotel is opened in Casa Grande as the spring training location for the San Francisco Giants.[171]
1960s
- 1960
- Phoenix Corporate Center built.
- Ben Avery Shooting Facility, begun in 1957 and one of the largest publicly operated shooting ranges, opens.[172]
- University of Arizona Poetry Center founded in Tucson.
- Old Tucson Studios theme park and El Con Mall open in Tucson.
- During the 1950s, Phoenix annexed 94.86 square miles of land.[173]
- Phoenix annexes Maryvale and South Phoenix.[158]
- Population in Phoenix reaches 439,170.
- Del Webb's Sun City opens.[158]
- 1961
- 1962
- Phoenix Zoo opens.
- Phoenix City Square built.
- In Phoenix, city bus drivers participate in an unsuccessful 62-day strike, which precipitates the decline of public transit in Phoenix.[122]
- Terminal 2 opens at Sky Harbor Airport; passengers served passes the 1 million mark.[175]
- Westwood High School opens in Mesa.
- Phoenix Title Building constructed in Tucson.
- Maricopa Community College District is created. It is currently the largest community college district in the United States.
- Arizona Town Hall was established to facilitate semi-annual discussions about topics of major concern to Arizona's future.[176]
- 1963
- March 13: Phoenix Police arrest Ernesto Miranda without informing him of his rights. This leads to the landmark U.S. Supreme Court case Miranda v. Arizona.[158]
- Municipal golf course built in Papago Park in Phoenix.
- Ernest Miranda is arrested. His arrest and confession lead to the landmark Miranda Warning Supreme Court case.[158]
- Tucson International Airport begins operating.
- Lake Havasu City established as a planned community.[177]
- Titan Missile Site 571-7 is made operational south of Tucson.[178]
- 1964
- Phoenix Municipal Stadium opens.
- Barry Goldwater loses the election for President of the United States.
- Tucson Botanical Gardens founded.
- Phoenix International Raceway opens.[179]
- 1965
- Arizona Veterans Memorial Coliseum opens in Phoenix.
- East wing of the Phoenix Art Museum opens, resulting in almost tripling the museum's space.[123]
- Morrison Warren becomes first black on the Phoenix city council.[158]
- Mesa Community College, part of the Maricopa Community College District, and Adelante con Mesa established.[180]
- Yavapai College, a community college in Prescott, opens.
- DeGrazia Gallery built in Tucson.
- Glendale Community College, the second community college in the Maricopa Community College District, is created.
- 1966
- August 9: Phoenix City Council unanimously approves the "Plan for the Phoenix Mountains", thereby creating the Phoenix Mountain Preserve.[181]
- Valley Transit Line is sold to American Transit Systems (headquartered in St. Louis, Missouri), and the transit system is renamed Phoenix Transit System.[122]
- Prescott College founded.
- 1967
- St. Mary's Food Bank established in Phoenix.[182][183]
- Original "Old Main" building of Mesa High School burns to the ground.
- University of Arizona College of Medicine and Reid Park Zoo founded.
- Tucson Federal Savings & Loan Association Building constructed.
- 1968
- Phoenix Suns basketball team formed.
- Phoenix Financial Center is completed.[184]
- President Lyndon B. Johnson signs a bill approving the Central Arizona Project, to bring water from the Colorado River to central Arizona.[83]
- Phoenix purchases Goodyear Airport as a general aviation supplement to Sky Harbor.[124]
- Tri City Mall in business in Mesa.
- KMND radio in Mesa begins broadcasting.
- City of Mesa takes over operations of Falcon Field[148]
- GateWay Community College, part of the Maricopa Community College District, is founded in Phoenix.
- Fred Lawrence Whipple Observatory opens 35 miles south of Tucson, in the Santa Rita Mountains.[185]
- The Central Arizona Project was created by the Colorado River Basin Project Act of 1968, signed by President Lyndon B. Johnson on September 30, 1968.[186][187]
- 1969
- Roman Catholic Diocese of Phoenix established.
- Sante Fe Railway ceases passenger trains to Phoenix in April.[122]
- Phoenix taxes cigarettes and liquor to cover budget shortfall.[158]
- Pima Community College established.
- Central Arizona College, a community college in the Pinal Community College District, opens in Coolidge.[188]
- Scottsdale Community College, part of the Maricopa Community College District, is founded.
1970s through the end of the millennium
1970s
- 1970
- Phoenix Mountains Preservation Council founded in August, to purchase all of the 7000 acres in the Phoenix Mountains Preserve, and a total of 9700 acres.[189]
- Remnants of Tropical Storm Norma slam into Phoenix, causing flooding and resulting in 23 deaths.[158]
- During the 1960s, Phoenix annexed 134.55 square miles of land, now totaling 245.5 square miles.[173]
- Lehi becomes part of Mesa.[190]
- The Fountain, which gives the name to Fountain Hills, is erected.[191]
- The town of Fountain Hills is founded as a master planned community.[192]
- Phoenix population reaches 581,562,[193] city becomes the nation's 20th most populous;[158] Mesa's population reaches 63,049.
- 1971
- May 1: Amtrak takes over intercity rail routes in Phoenix.[122]
- First National Bank Plaza, currently known as the Wells Fargo Plaza, is built in Phoenix.
- The third building, 3838 N. Central Avenue, is built, completing Phoenix City Square.[194]
- Phoenix purchases the Phoenix Transit System from American Transit, who agrees to continue to manage the operation.[122]
- The city adopts the Central Phoenix Plan in an attempt to develop the Central Avenue corridor.[195]
- The first Fiesta Bowl is played.[158]
- Prehab of Mesa (youth-related nonprofit) established.[196]
- Tucson Opera Company founded.[197]
- Tucson Convention Center built.
- London Bridge opens in Lake Havasu City, after being transported from London, England.[198]
- 1972
- Phoenix Symphony Hall opens.
- Chase Tower in Phoenix is built.
- Salt River floods several times, killing 8.[158]
- Mesa High School reopens at a new location (farther east and south).
- Mesa Central High School opens at site of original Mesa High campus.
- Planetary Science Institute founded in Tucson.
- Inaugural Copperstate Fly-In, an annual vintage airshow, held at Casa Grande Airport.[199]
- 1973
- Voters approve a $23.5 million bond issue, to fund the Phoenix Mountain Preserve.[158]
- Dobson Ranch planned community began selling homes in the first phase of its 26-year development.
- A boiling liquid expanding vapor explosion (BLEVE) kills 11 firefighters in Kingman.[200]
- Fort Grant becomes an Arizona state prison.[59]
- Construction of the Central Arizona Project began.[201]
- 1975
- Phoenix elects its first female mayor: Margaret Hance.[158]
- Papago Freeway is passed by the voters of Phoenix.[158]
- After extensive renovations, the Mesa Arizona Temple is rededicated
- The Park of the Canals in Mesa is added to the National Register of Historic Places; work then commences for developing park facilities and later the botanical garden.
- Chandler Unified School District is created by combining the Chandler Elementary and High School Districts.[85]
- 1976
- Margaret Hance becomes mayor of Phoenix.
- U.S. Bank Center and Hyatt Regency are built in Phoenix.
- Construction begins on Terminal 3 at Sky Harbor Airport.[202]
- Tourism moves ahead of agriculture into the number two largest economic sector in Phoenix.[158]
- Mountain View High School opens.
- 1977
- Mesa Southwest Museum (later renamed the Arizona Museum of Natural History) founded.
- The original Hohokam Park opens in Mesa.
- Bank of America Plaza (Tucson) built.
- Arizona Museum of Natural History is founded in Mesa, originally exhibiting in the City Hall.[203]
- 1978
- March 9: Wesley Bolin Memorial Plaza established in Phoenix.[204]
- Prescott Valley incorporates.[205]
- Phoenix Transit begins to offer "Dial-a-Ride" services in low-population density areas.[122]
- Arizona Street Railway Museum opens in Phoenix.[206]
- Western Design Center is founded by Bill Mensch.
- Arizona State Prison Complex – Tucson opens.
- Rio Salado College and South Mountain Community College, part of the Maricopa Community College District, are established in Tempe and Phoenix, respectively.
- Lake Havasu City incorporates.
- 1979
- Terminal 3 at Sky Harbor Airport opens.[202]
- City adopts the Phoenix Concept 2000 plan, which split the city into urban villages.[207]
- Fiesta Mall opens.
- Mesa Amphitheatre built.
- Mesa Weekly News begins publication.[65]
- Radio station KMLE begins broadcasting from Chandler.
1980s
- 1980
- February: Salt River floods, washing away most of the bridges spanning it.[122]
- 3300 Tower built in Phoenix.
- During the 1970s, Phoenix annexed 75.53 square miles of land, now totaling 321.03 square miles.[173]
- Arizona Museum for Youth opens in Mesa.
- Population in Phoenix reaches 789,704; population in Mesa is at 152,453.[208]
- South Mountain Community College, part of the Maricopa Community College District, is established in Phoenix.
- The Arizona Museum for Youth, the only children's museum in the United States focusing on fine art, is founded. Now known as the I.d.e.a. Museum.[209]
- 1981
- President Ronald Reagan appoints Sandra Day O'Connor to the U.S. Supreme Court.[83]
- Mesa Sister Cities Association founded.[210] and Mesa United Way[211]
- Champlin Fighter Museum opens in Mesa.
- 1982
- Phoenix voters expand the city council from 6 citywide members to 8 members, each representing a distinct area.[212]
- Federal Correctional Institution, Tucson opens.
- Tucson Mall and Casas Adobes Foothills Mall (Arizona) open in Tucson.
- 1983
- August 4: Riordan Mansion State Historic Park in Flagstaff, is opened to the public.[213]
- America West Airlines is formed by valley investors.[212]
- Terry Goddard elected mayor of Phoenix.[212]
- Dobson High School opens in Mesa.
- Arizona Railway Museum is opened in Chandler.[214]
- Firebird International Raceway (currently Wild Horse Motorsports Park), opens.[215]
- Radio station KNAU, run by NAU, begins airing in Flagstaff.
- 1984
- Arizona State University West campus established by the legislature.
- Arizona Science Center opens in Phoenix.
- Deer Valley Petroglyph Preserve opens in Phoenix.[216]
- The Public Transportation Administration becomes an official department of Phoenix.[122]
- Al Brooks becomes mayor of Mesa.
- 1985
- Valley Metro Regional Public Transportation Authority formed, after passage of Proposition 300, tasked to create a regional transit plan and system in the Salt River Valley.[122]
- Great American Tower built in Phoenix.
- First water from the Central Arizona Project reaches Maricopa County.[83]
- Tucson Historic Preservation Foundation established.[217]
- Chandler–Gilbert Community College, part of the Maricopa Community College District, is founded in Chandler.[218]
- Compadre Stadium is built in Chandler for the Milwaukee Brewers Spring training, who begin playing there in 1986.[219]
- Paradise Valley Community College, part of the Maricopa Community College District, is established in Phoenix.
- 1986
- In Phoenix, city urban village divisions created: Ahwatukee, Alhambra, Camelback East, Central City, Deer Valley, Desert View, Encanto, Estrella, Laveen, Maryvale, North Gateway, North Mountain, Paradise Valley, Rio Vista, and South Mountain.
- Renaissance Square Tower 1 built in Phoenix.
- Ballet Arizona headquartered in Phoenix.
- Palo Verde Nuclear Generating Station opens, with two of three units on-line. It is the largest nuclear power plant (by net generation) in the United States.[220]
- Radio station KMGN begins airing from Flagstaff.
- 1987
- Phoenix receives visits from both Pope John Paul II and Mother Teresa.[221]
- Mesa Historical Museum opens.[222]
- 1988
- Cardinals football team relocates to Phoenix.
- Telephone Pioneers of America Park, the first barrier-free park in the United States, for disabled Americans, opens in Phoenix.[223]
- Red Mountain High School opens in Mesa.
- Titan Missile Museum, site of Titan Missile Site 571-7, opens, the only remaining Titan ICBM complex in the United States.[178]
- 1989
- Sunnyslope Historical Society founded in Phoenix.[224]
- Arizona Center built.
- Herberger Theater Center (HTC) opens in Phoenix.[225]
- Voters in Phoenix turn down a $10 billion referendum for a valley-wide rapid transit system, due to the cost and dissatisfaction with the elevated portions of the proposed system.[122]
- Phoenix Grand Prix is run in Downtown Phoenix in June.[212]
- Annual Ostrich Festival begins in Chandler.[85]
- Chandler Center for the Arts opens.[85]
- Fountain Hills is incorporated.
1990s
- 1990
- The Barry Goldwater Terminal (terminal 4) opens at Sky harbor airport with 5 concourses and 44 gates.[226]
- November 10: The Desert Sky Pavilion (currently named the Ak-Chin Pavilion) opens in Phoenix. Billy Joel is its first act.[227]
- The Stack (road interchange) and Papago Freeway Tunnel open in Phoenix.
- Superstition Springs Center opens in Mesa.
- First section of Arizona State Route 202 opens; downtown Lehi was removed to make way for it.
- During the 1980s, Phoenix annexed 99.33 square miles of land, now totaling 420.36 square miles.[173]
- Population in Phoenix reaches 983,403;[193] population of Mesa hits 288,091;[193] population of Tucson reaches 405,390;[193] population of Chandler stands at 90,533.[85]
- 1991
- Viad Tower built in Phoenix.
- Phoenix transit implements a Bus Card Plus Program, allowing participants reduced fares.[122]
- East Valley Institute of Technology Main campus opens in Mesa.
- Biosphere 2 built in Tucson.
- Coconino County Community College opens in Flagstaff.[228]
- 1992
- America West Arena opens in Phoenix.
- Bike racks become available on all almost all buses citywide in Phoenix.[122]
- Joe Arpaio elected Maricopa County Sheriff.[212]
- Estrella Mountain Community College, part of the Maricopa Community College District, is established.
- 1993
- September 30: Williams Air Force Base closes after 52 years of military service.
- RPTA adopts the name, Valley Metro, for the regional transit system. Phoenix and Mesa become the first two systems in the valley to agree to the name.[122]
- Phoenix wins the Carl Bertelsmann Prize, for the best run city government in the world.[51]
- Arpaio creates Tent City, to help alleviate crowding.[212]
- Salt River floods and destroys the new Mill Avenue Bridge in Phoenix.[212]
- Steve Benson, a cartoonist for the Arizona Republic, wins the Pulitzer Prize.[212]
- Construction of the Central Arizona Project was completed.[229]
- 1994
- John B. Nelson becomes mayor if Phoenix, succeeded by Thelda Williams and Skip Rimsza.
- The 20-story Phoenix City Hall opens.[230]
- Williams Gateway Airport in operation.
- Low-floor buses are added to the Valley Metro fleet.[122]
- Radio station KSED begins broadcasting out of Flagstaff.
- Peoria Sports Complex opens.[231]
- 1995
- Burton Barr Central Library opens in Phoenix.
- Valley Metro becomes the first municipal bus service in the country to accept credit cards.[122]
- Robotic Lunar Observatory opens in Flagstaff.
- 1996
- Amtrak discontinues service to Phoenix.[122]
- September 24: Construction begins on a new Central Station for Valley Metro, near Central and Van Buren Avenues.[122]
- Arizona State University at the Polytechnic campus opens on the former Williams Air Force Base.
- Sun Valley High School opens in Mesa.
- Goodricke-Pigott Observatory dedicated in Tucson.
- Museum of Contemporary Art, Tucson founded.
- 1997
- Hayden Flour Mill, which in the late 1800s supplied most of the flour for the state of Arizona, closes after 123 years.[212]
- Phoenix Lights, alleged UFO sighting, seen over the city.[212]
- The new HoHoKam Stadium opens in Mesa.
- 1998
- Sixth concourse added to the Barry Goldwater Terminal at Sky Harbor airport.[226]
- Arizona Diamondbacks begin play in the National League as an expansion team.
- Bank One Ballpark, currently called Chase Field, opens in Phoenix.[212]
- Anthem, Arizona, just north of Phoenix, is begun.[212]
- Hamilton High School, the second high school in Chandler, opens.[85]
- Maryvale Baseball Park, Spring training venue for the Milwaukee Brewers, opens.[232]
- Radio station KWMX begins broadcasting out of Williams.
- 1999
- Tempe Town Lake is completed.[212]
- Skyline High School opens in Mesa.
- Chandler Fire Department becomes one of only 14 fire departments in the world accredited by the Commission on Fire Accreditation International.[144]
- San Rafael State Natural Area created on site of San Rafael ranch.[233]
21st century
2000–09
- 2000
- Bank of America Tower built in Phoenix.
- Ro Ho En, the Japanese friendship garden between Phoenix and its sister-city, Himeji City, Japan, opens.[234]
- Sandra Day O'Connor United States Courthouse opens in Phoenix.[212]
- During the 1990s, Phoenix annexed 54.79 square miles of land, now totaling 475.15 square miles.[173]
- "Transit 2000" proposition passes, approving construction of 24 miles of light rail with Phoenix city limits, named Valley Metro Rail.[122]
- Tempe city council passes motion approving an additional 5 miles of light rail to be constructed and linked to the Phoenix light rail system.
- Population of Phoenix reaches 1,321,045;[235] population in Mesa reaches 396,375.[236]
- 2001
- Glendale voters approve a sales tax increase to fund transportation improvements, including 5 miles of light rail to connect with the Metro Light Rail.[122]
- Arizona Diamondbacks defeat the New York Yankees in the World Series.[212]
- Anselmo Valencia Tori Amphitheater opens in Tucson.
- Casa Verde High School opens in Casa Grande as a charter high school.[188]
- 2002
- Comerica Theatre opens in Phoenix.
- Desert Ridge High School opens; physically located in Mesa, it is part of Gilbert Public Schools.
- Basha High School, named for Eddie Basha, Jr., opens in Chandler.[237]
- 2003
- Construction begins on Metro Light Rail in Phoenix.[122]
- Arizona Roller Derby headquartered in Phoenix.
- Jobing.com Arena, currently known as the Gila River Arena, opens in Glendale.[212]
- 2004
- Phil Gordon becomes mayor.[238]
- Maricopa County voters approve a 20-year continuation of the 1985 sales tax to fund transportation needs. The plan includes almost $25 billion in funding for: freeways, bus transit expansion, light rail, city streets, and bike and pedestrian paths.[122]
- The Translational Genomics Research Institute opens in downtown Phoenix.[212]
- Mini Stack (road interchange) built in Phoenix.
- 2005
- The seventh concourse is added to the Barry Goldwater Terminal at Sky Harbor airport, bringing the total number of gates in the terminal to 84.[226]
- America West and US Airlines merge, creating the nation's fifth-largest airline.[212]
- Mesa Arts Center built.
- Mesa Miners baseball team is founded.
- Mesa adopts city flag.
- Jewish History Museum (Tucson) established.
- Southern Arizona Transportation Museum dedicated in Tucson.[239]
- 2006
- Phoenix Metropolitan Opera founded.
- Phoenix Art Museum expansion, which includes a wing for modern art and a sculpture garden, opens.[123]
- Cardinals Stadium, now titled State Farm Stadium, opens.[212]
- Phoenix-Mesa Gateway Airport begins operations on the site of the closed Williams AFB.[212]
- Peoria Center for the Performing Arts opens.[240]
- 2007
- July 27: News helicopter collision.
- Phoenix Mercury win the WNBA championship.[212]
- Mesa Riverview opens.
- United States Penitentiary, Tucson in operation.
- Perry High School opens in Gilbert. It is the fourth high school in the Chandler Unified School District.[241]
- 2008
- Valley Metro Rail begins operation in Phoenix.[122]
- Sycamore Drive and Main Street Valley Metro Rail station opens, in front of the former Tri City Mall location; it is the first Metro Light Rail station in Mesa.
- 44 Monroe built in Phoenix.
- Super Bowl XLII played at University of Phoenix Stadium. The New York Giants defeat the New England Patriots.[212]
- In Phoenix, Squaw Peak is renamed Piestewa Peak, in honor of the first Native American woman killed in combat, Lori Piestewa.[212]
- 2009
- Phoenix Civic Space Park opens.
- Freeport-McMoRan Center built in Phoenix.
- Arizona Cardinals lose to the Pittsburgh Steelers in Super Bowl XLIII.[212]
- Desert Proving Ground Yuma opens, replacing the General Motors Desert Proving Grounds in Mesa.
2010s
- 2010
- 2011
- January 8: Shooting of U.S. Representative Gabrielle Giffords and eighteen others in Casas Adobes, Tucson.
- July 5: Major sandstorm (haboob) hits Phoenix.[245]
- University of Arizona's Center for Social Cohesion active.[246]
- East Valley Institute of Technology East campus opened, adjacent to ASU Polytechnic.
- Chandler Museum opens in the McCullough-Price House.[145]
- 2012
- Greg Stanton becomes mayor of Phoenix.[247]
- CityScape building constructed in Phoenix.
- February 22: Republican Party presidential primaries debate held.[248]
- 2013
- Mesa Grande Cultural Park opens.[249]
- Matt Salmon becomes U.S. representative for Arizona's 5th congressional district and Kyrsten Sinema becomes U.S. representative for Arizona's 9th congressional district.[250]
- Population in Phoenix estimate of 1,513,367.[251]
- 2014 – Cubs Park opens in Mesa.
- 2015
- January 1: The Lowell Discovery Telescope, constructed with funding from the Discovery Channel, and owned by Lowell Observatory becomes fully operational.[252]
- Renovations begin on Terminal 3 at Sky Harbor airport, part of a 3-phase redevelopment of the terminal expected to be completed in 2020.[253]
- Casteel High School opens. First class will begin attending school in September.[254]
See also
- Cities in Arizona
References
- Sheridan 2012, pp. 11–12.
- Sheridan 2012, p. 6.
- Sheridan 2012, p. 18.
- Sheridan 2012, p. 26.
- "The Hohokam". Arizona Museum of Natural History, City of Mesa. Archived from the original on 30 November 2012. Retrieved 30 November 2012.
- Sheridan 2012, pp. 22–24.
- Cordell, Linda S. (1984). Prehistory of the Southwest. New York: Academic Press. ISBN 0-12-188220-9.
- Sheridan 2012, p. 25.
- Sheridan 2012, p. 19.
- "Hopi Places". Cline Library, Northern Arizona University.
- Casey, Robert L. Journey to the High Southwest. Guilford, Connecticut: Globe Pequot Press, 2007: 382. ISBN 978-0-7627-4064-2.
- Sheridan 2012, p. 22.
- Sheridan 2012, p. 29.
- Malotki, Ekkehart. 2002. Hopi Tales of Destruction. Bison Books. pp. 230
- Braatz 2003, p. 27.
- Sheridan 2012, p. 31.
- "Nahanni National Park Reserve". Great Canadian Parks. Retrieved 2007-07-02.
- "The journey of Coronado, 1540–1542: from the city of Mexico to the Grand ..." By Pedro de Castañeda de Nájera, Antonio de Mendoza, Juan Camilo, p. 5 (Google Books ISBN 1-55591-066-1)
- "A Brief History of the Casa Grande Ruins". National Park Service. Retrieved June 30, 2015.
- Sheridan 2012, p. 38.
- Sheridan 2012, p. 41.
- Kessell, John L. (1970). Mission of Sorrow: Jesuit Guevavi and the Pimas, 1691–1767. Tucson, Arizona: University of Arizona Press.
- "Tucson". Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). New York. 1910. OCLC 14782424.
- Sheridan 2012, p. 42.
- Sheridan 2012, p. 43.
- "Agua Linda Ranch (Farm)" (PDF). Archeology Southwest. p. 255. Retrieved July 5, 2015.
- Sheridan 2012, p. 46.
- Sheridan 2012, p. 57.
- "Agua Linda Ranch (Farm)" (PDF). Archeology Southwest. p. 207. Retrieved July 5, 2015.
- Sheridan 2012, p. 52.
- "Casa Grande History". City of Casa Grande. Archived from the original on July 1, 2015. Retrieved June 30, 2015.
- "Tucson P.O.", Arizona Business Directory and Gazetteer, San Francisco: W.C. Disturnell, 1881
- A. Leonard Meyer (1888), Meyer's Business Directory of the City of Phoenix, Arizona, Phoenix, Ariz, OL 7233806M
- Spencer C. Tucker (2012). The Encyclopedia of the Mexican–American War: A Political, Social, and Military History. ABC-CLIO. p. 255. ISBN 978-1851098545.
- "The Actual Treaty". Official Gadsden Purchase Web Site. Retrieved July 10, 2015.
- "The History of the Railroad in Flagstaff" (PDF). ity of Flagstaff. Retrieved July 1, 2015.
- "Community Profile". City of Flagstaff. Retrieved July 1, 2015.
- "A History of Mining in AZ" (PDF). Arizona Mining Association. p. 6. Retrieved July 11, 2015.
- "Ordinance of Secession of the Arizona Territory". The Confederate War Department. Archived from the original on June 22, 2015. Retrieved July 10, 2015.
- "Historical Development of Arizona and New Mexico Boundaries" (PDF). Arizona State University. Archived from the original (PDF) on March 22, 2015. Retrieved July 10, 2015.
- "Phoenix", Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.), New York, 1910, OCLC 14782424
- Poston, Charles Debrille (September 17, 2011). "History of the Arizona Territory". Sharlot Hall Museum. Retrieved July 10, 2015.
- "A History of Mining in AZ" (PDF). Arizona Mining Association. p. 8. Retrieved July 11, 2015.
- "Town of Wickenburg History". Wickenburg, Arizona. Retrieved 25 February 2014.
- Directory of the City of Tucson. San Francisco: G.W. Barter. 1881.
- "Historic Preservation Master Plan" (PDF). City of Prescott. p. 5. Retrieved July 5, 2015.
- "History of the Arizona Historical Society". Arizona Historical Society. Retrieved July 1, 2015.
- "Fort McDowell – In the Midst of the Apache Wars". Legends of America.
- Grady 2012, pp. 1, 5.
- VanderMeer 2010, p. 15.
- "City of Phoenix History". City of Phoenix. Archived from the original on April 4, 2015. Retrieved June 28, 2015.
- Gober 2006, p. 17.
- "Arizona: Territorial, statehood timelines". The Arizona Republic. June 24, 2011. Retrieved June 30, 2015.
- Grady 2012, pp. 61–65.
- "Phoenix P.O.", Arizona Business Directory and Gazetteer, San Francisco: W.C. Disturnell, 1881
- VanderMeer 2010, p. 28.
- "US Newspaper Directory". Chronicling America. Washington, D.C.: Library of Congress. Retrieved April 2, 2013.
- "Phoenix Valley History". The Natural American. Retrieved June 28, 2015.
- "Early ADC History". Arizona Department of Corrections. Retrieved July 5, 2015.
- Hubert Howe Bancroft (1889), History of Arizona and New Mexico, 1530–1888, San Francisco: History Company, OL 14012406M
- "Agua Linda Ranch (Farm)" (PDF). Archeology Southwest. p. 222. Retrieved July 5, 2015.
- "Salero Mine and Camp". Visit Tubac. Retrieved July 5, 2015.
- Walsh, Jim (October 7, 2010). "A roving monument, a proud history". The Arizona Republic. Retrieved July 5, 2015.
- "A History of Mining in AZ" (PDF). Arizona Mining Association. pp. 10–11. Retrieved July 11, 2015.
- "US Newspaper Directory". Chronicling America. Washington, D.C.: Library of Congress. Retrieved March 25, 2013.
- VanderMeer 2010, p. 20.
- Libraries. "Chicano/a Research Collection: Timeline". Research Guides. Arizona State University. Archived from the original on February 22, 2014. Retrieved February 7, 2014.
- "Agua Linda Ranch (Farm)" (PDF). Archeology Southwest. p. 216. Retrieved July 5, 2015.
- "Main Street District Historic Sites". Casa Grande Main Street. Retrieved July 1, 2015.
- "Agua Linda Ranch (Farm)" (PDF). Archeology Southwest. p. 227. Retrieved July 5, 2015.
- Nilsen, Richard (June 24, 2011). "People who built Phoenix: 1865–1912". Arizona Republic. Retrieved June 30, 2015.
- "History". City of Phoenix. Archived from the original on April 5, 2013. Retrieved March 25, 2013.
- "About The Kingman Daily Miner". Western News&Info, Inc. Retrieved July 5, 2015.
- "Agua Linda Ranch (Farm)" (PDF). Archeology Southwest. p. 243. Retrieved July 5, 2015.
- "Methodist Episcopal Church". Historical Marker Database. Retrieved July 1, 2015.
- James H. McClintock (1916), Arizona: Prehistoric, Aboriginal, Pioneer, Modern, Chicago: S.J. Clarke Publishing Co., OL 7024158M v.2
- Premium list; Fourth Annual Exhibit, Arizona Industrial Exposition Association, October 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, Phoenix, Maricopa County, Arizona, Phoenix: Arizona Industrial Exposition Association, 1887, OL 7208542M
- "Coconino Chop House". Historical Marker Database. Retrieved July 1, 2015.
- "Busy Railroad in a Rich Country: the Arizona Eastern ..." Southern Pacific Bulletin. San Francisco. August 1921.
- "McMillan Building". Historical Marker Database. Retrieved July 1, 2015.
- "Phoenix: History". City-Data.com. Retrieved 4 February 2014.
- "Babbitt Brothers Building". Historical Marker Database. Retrieved July 1, 2015.
- "Phoenix Valley History". The Natural American. Archived from the original on June 29, 2015. Retrieved June 28, 2015.
- "Flagstaff Amtrak Station". Waymarking.com. Retrieved July 1, 2015.
- "History of Chandler and Chandler High School". City of Chandler. Retrieved July 1, 2015.
- "Agua Linda Ranch (Farm)" (PDF). Archeology Southwest. p. 238. Retrieved July 5, 2015.
- "US Newspaper Directory". Chronicling America. Washington, D.C.: Library of Congress. Retrieved February 18, 2014.
- "Aubineau / Andreatos Building". Historical Marker Database. Retrieved July 1, 2015.
- "History". Lowell Observatory. Retrieved July 1, 2015.
- "The Rosson House". Heritage Square. Retrieved June 29, 2015.
- Rob Rachowiecki (1995), "Phoenix: Mesa", Southwest, Lonely Planet, OL 24220208M
- "Agua Linda Ranch (Farm)" (PDF). Archeology Southwest. p. 250. Retrieved July 5, 2015.
- "Little Red Schoolhouse – Kingman, AZ". Waymarking.com. Retrieved July 5, 2015.
- "By the numbers: key facts and university statistics". Northern Arizona University. Retrieved July 1, 2015.
- "Weatherford Hotel". Historical Marker Database. Retrieved July 1, 2015.
- "Agua Linda Ranch (Farm)" (PDF). Archeology Southwest. p. 232. Retrieved July 5, 2015.
- "Historic Preservation Master Plan" (PDF). City of Prescott. p. 6. Retrieved July 5, 2015.
- Julius Cahn's Official Theatrical Guide. 1900.
- "Agua Linda Ranch (Farm)" (PDF). Archeology Southwest. p. 246. Retrieved July 5, 2015.
- "Agua Linda Ranch (Farm)" (PDF). Archeology Southwest. p. 214. Retrieved July 5, 2015.
- "Salt River Project: Historical timeline". Srpnet.com. Retrieved 2012-06-19.
- "This Day in Arizona History". AZ100Years.org. Archived from the original on 2 February 2014. Retrieved 4 February 2014.
- "Agua Linda Ranch (Farm)" (PDF). Archeology Southwest. p. 220. Retrieved July 5, 2015.
- "Riordan Mansion State Historic Park". DesertUSA. Retrieved July 1, 2015.
- "Phoenix History". Hello Phoenix. Retrieved 4 February 2014.
- "Ostrich Trust Secures More Valuable Birds in Arizona". The Copper Era. August 2, 1906. Retrieved July 1, 2015.
- "Agua Linda Ranch (Farm)" (PDF). Archeology Southwest. p. 245. Retrieved July 5, 2015.
- "Pioneer Museum (Flagstaff)". Arizona Historical Society. Retrieved July 1, 2015.
- "Telegraph Building". Historical Marker Database. Retrieved July 1, 2015.
- "Agua Linda Ranch (Farm)" (PDF). Archeology Southwest. p. 252. Retrieved July 5, 2015.
- "Agua Linda Ranch (Farm)" (PDF). Archeology Southwest. p. 228. Retrieved July 5, 2015.
- "The Story of Chandler, Arizona". City of Chandler. Retrieved July 1, 2015.
- "05-21-1912 - Page 1". Chandlerpedia. Retrieved July 1, 2015.
- "About Us". Casa Grande Valley Newspapers. Retrieved July 1, 2015.
- "Out of the Ashes, Establishing a Council-Manager Government City of Phoenix". Phoenix.gov. Archived from the original on 2014-02-14. Retrieved 2012-06-19.
- "Timeline: The Valley 1912–45". The Arizona Republic. July 22, 2011. Retrieved June 30, 2015.
- "Orpheum Theater: History". The Orpheum Presents. Retrieved July 1, 2015.
- "Agua Linda Ranch (Farm)" (PDF). Archeology Southwest. p. 229. Retrieved July 5, 2015.
- "History". Arizona Jewish Historical Society. Retrieved March 25, 2013.
- "Cutler Plotkin Jewish Heritage Center". Discover Phoenix. Retrieved June 29, 2015.
- "Casa Grande, AZ". Davis-Monthan Aviation Field Register. Retrieved July 1, 2015.
- "A Brief History Of Public Transportation in Metro Phoenix". The Phoenix Trolley Museum. Archived from the original on August 29, 2014. Retrieved June 29, 2015.
- "History & Mission". Phoenix Art Museum. Archived from the original on September 5, 2015. Retrieved June 29, 2015.
- "Airport History Timeline". City of Chandler. Retrieved June 30, 2015.
- "About Us". Nogales International. Retrieved July 5, 2015.
- "Flagstaff". Amtrak. Retrieved July 1, 2015.
- Federal Writers’ Project (1966). Arizona, the Grand Canyon State. American Guide Series (4th ed.). New York: Hastings House. p. 351. OL 5989725M.
- "Arizona Historic Theatres". Maryland: League of Historic American Theatres. Archived from the original on July 21, 2013. Retrieved April 2, 2013.
- "The Historic Hotel Monte Vista". Hotel Monte Vista. Retrieved July 1, 2015.
- "1935 and The Farm – Sky Harbor's Early Years and Memories". skyharbor.com. 30 August 1930. Retrieved 5 February 2014.
- "About MNA". Museum of Northern Arizona. Retrieved July 1, 2015.
- "Who We Are". Sharlott Hall Museum. Retrieved July 5, 2015.
- "Heard Museum History". Heard Museum. Archived from the original on March 11, 2013. Retrieved March 25, 2013.
- "Tempe Normal School Records, 1885–1930 MSS-149". azarchivesonline.org. Arizona Archives Online. 2014. Retrieved May 27, 2014.
- "Agua Linda Ranch (Farm)" (PDF). Archeology Southwest. p. 224. Retrieved July 5, 2015.
- "Agua Linda Ranch (Farm)" (PDF). Archeology Southwest. p. 256. Retrieved July 5, 2015.
- "In Tucson, an Unsung Architectural Oasis", New York Times, June 14, 2015
- "The Pluto Telescope". Lowell Observatory. Retrieved July 1, 2015.
- "An Arizona Fairy Tale". National Trust for Historic Preservation. Retrieved June 29, 2015.
- "Everyday Extraordinary". Wrigley Mansion Club. Retrieved June 29, 2015.
- "Prominent Arizona grocer Eddie Basha dies at 75". CBS5AZ. Retrieved July 1, 2015.
- "Where is Terminal 1?". Sky Harbor Airport. Archived from the original on February 4, 2014. Retrieved June 29, 2015.
- Campbell, Marty (2002). Arizona Family Field Trips. AZ Adventures. p. 53. ISBN 0972228608. Retrieved July 5, 2015.
- "Chandler Fire, Health & Medical Department". City of Chandler. Retrieved July 1, 2015.
- Jensen, Edythe (June 9, 2011). "Chandler's McCullough-Price House to be archive center". The Arizona Republic. Retrieved July 1, 2015.
- "About Us". Arizona Snowball. Retrieved July 1, 2015.
- Mesa Public Library, Brief History of Mesa, Arizona, City of Mesa, archived from the original on March 7, 2012, retrieved February 18, 2014
- "Falcon Field History", MesaAz.gov, City of Mesa, retrieved 2012-05-05
- "History of Ernest A. Love Field" (PDF). Prescott Municipal Airport. Retrieved July 5, 2015.
- Henley, David C. (1992). The Land That God Forgot: The Saga of Gen. George Patton's Desert Training Camp (revised ed.). Fallon, Nevada: Western Military History Association. p. 54. OCLC 76951993.
- "Gila River Relocation Center, Arizona". javadc.org. Retrieved June 30, 2015.
- "Phoenix's Thanksgiving Day Riot, 1942". BlackPast.org. Retrieved June 29, 2015.
- Freeman, Paul. "Arizona: Southeastern Phoenix area". Abandoned & Little-Known Airfields. Retrieved July 1, 2015.
- "Papago Park (Arizona) USA POW Camp". World and Military Notes.com. Archived from the original on June 29, 2015. Retrieved June 29, 2015.
- Randall, Susan (August 4, 2014). "County changing Pinal Airpark". Casa Grande Dispatch. Retrieved July 1, 2015.
- "The Not-So-Great Escape: German POWs in the U.S. during World War II". HistoryNet. Archived from the original on March 21, 2015. Retrieved June 29, 2015.
- "Imagination is more important than knowledge..." Mystery Castle. Retrieved June 29, 2015.
- "Timeline: Postwar, 1946–80". AZCentral.com. Retrieved June 29, 2015.
- Robert Alan Goldberg, Barry Goldwater (1995), 76–82
- "Growing into a Metropolis". The Natural American. Archived from the original on February 1, 2015. Retrieved 5 February 2014.
- "Mesa Country Club". Retrieved February 18, 2014.
- "Established 1948". Casa Grande Cottone Kings. Retrieved June 30, 2015.
- "Chandler Municipal Airport – Your Community Airport for More Than 60 Years". City of Chandler. Retrieved July 1, 2015.
- "About FSO: Mission & History". Flagstaff Symphony Orchestra. Archived from the original on August 16, 2015. Retrieved July 1, 2015.
- "The History of Peoria, Arizona". City of Peoria. Retrieved July 5, 2015.
- "Looking Back In History, 1/28/15". Coolidge Examiner. January 28, 2015. Retrieved July 1, 2015.
- Heim, Carl E. Border Wars: Tax Revenues, Annexation, and Urban Growth in Phoenix. University of Massachusetts. p. 17. Retrieved June 30, 2015.
- "Naval Observatory Flagstaff Station Celebrates First Half Century". Space Ref. September 30, 2005. Retrieved July 1, 2015.
- Valinski, Steven. "2015 Cactus Fly-In : A Showcase of Vintage Aircraft". Aviation Photography Digest. Retrieved July 1, 2015.
- "Welcome to Arizona's Best Flying Club". Phoenix Flyers Club. Retrieved July 1, 2015.
- "History". Francisco Grande. Retrieved June 30, 2015.
- "Ben Avery Shooting Facility". Arizona Game and Fish Department. Retrieved June 29, 2015.
- Heim, Carl E. Border Wars: Tax Revenues, Annexation, and Urban Growth in Phoenix. University of Massachusetts. p. 56. Retrieved June 30, 2015.
- "Town of Paradise Valley History". Town of Paradise Valley. Retrieved July 5, 2015.
- "Terminal 2". Sky Harbor. Archived from the original on February 2, 2014. Retrieved June 29, 2015.
- http://ecorp.azcc.gov/Details/corp?corpid=%2000594437; http://aztownhall.org/page-1646000
- "About Us". Lake Havasu City. Archived from the original on August 23, 2015. Retrieved July 5, 2015.
- "Agua Linda Ranch (Farm)" (PDF). Archeology Southwest. p. 236. Retrieved July 5, 2015.
- "Phoenix International Raceway". AutoRacing.com. Retrieved June 30, 2015.
- "MesaCAN: Timeline". Mesa, Arizona: A New Leaf. Retrieved February 18, 2014.
- Gilbert, Dorothy V. (September 19, 1966). "Recreation Gets Priority in North Phoenix Plan" (PDF). The Phoenix Gazette. p. 26. Archived from the original (PDF) on June 29, 2015. Retrieved June 29, 2015.
- "St. Mary's Food Bank". Retrieved October 2014. Check date values in:
|accessdate=(help) - "Arizona Food Banks". Food Bank Locator. Chicago: Feeding America. Retrieved October 2014. Check date values in:
|accessdate=(help) - "Phoenix Financial Center". Defining Downtown. Retrieved June 29, 2015.
- "Agua Linda Ranch (Farm)" (PDF). Archeology Southwest. p. 225. Retrieved July 5, 2015.
- "September (1968)". Lyndon B. Johnson Centennial Celebration. Archived from the original on 2010-01-31. Retrieved 2012-07-24.
- "Morris Udall Papers – Central Arizona Project". University of Arizona Library – Special Collections. Archived from the original on 2016-03-20. Retrieved 2010-05-12.
- "Schools / Education". Casa Grande Chamber of Commerce. Archived from the original on July 1, 2015. Retrieved July 1, 2015.
- "About Us". Phoenix Mountains Preservation Council. Archived from the original on June 29, 2015. Retrieved June 29, 2015.
- D.L. Turner (2006). "Forgotten City of the Saints: Mormons, Native Americans, and the Founding of Lehi". Journal of Arizona History. 47 (1): 57–82. JSTOR 41696951.
- "The Fountain". Fountain Hills Guide. Retrieved July 1, 2015.
- "About Fountain Hills". City of Fountain Hills. Retrieved July 1, 2015.
- Population of the 100 Largest Cities and Other Urban Places in the United States: 1790 to 1990, US Census Bureau, 1998
- "Phoenix City Square". Emporis. Retrieved June 29, 2015.
- John Carl Warnecke and Associates (1967). Central Phoenix plan, first stage : work program for a planning and economic study of downtown-midtown Phoenix. John Carl Warnecke and Associates. OCLC 19485397.
- "About Us". Mesa, Arizona: A New Leaf. Retrieved February 18, 2014.
- "NCGA Co-ops: Arizona". Iowa: National Cooperative Grocers Association.
- "London Bridge". Structurae. Retrieved July 5, 2015.
- "Copperstate Fly-in". Casa Grande Dispatch. October 23, 2014. Retrieved July 1, 2015.
- "The Disaster Story". Kingman Arizona Historic District. Retrieved July 5, 2015.
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2016-03-20. Retrieved 2016-08-12.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- "Terminal 3". Sky Harbor Airport. Archived from the original on July 30, 2013. Retrieved June 29, 2015.
- "About the Museum". Arizona Museum of Natural History. Retrieved July 1, 2015.
- "HB 2104". Arizona House of Representatives. Retrieved June 29, 2015.
- "History". Town of Prescott Valley. Retrieved July 5, 2015.
- "About the Museum". Phoenix Trolley Museum. Retrieved June 29, 2015.
- "Phoenix Concept Plan 2000: A Program for Planning". Phoenix Planning Department. 1979. Retrieved June 29, 2015.
- United States Census Bureau (1984), County and City Data Book, 1983, Statistical Abstract, Washington, D.C., OL 14997563M
- "Our Story". i.d.e.a. Museum. Retrieved July 5, 2015.
- "About". Mesa Sister Cities Association. Retrieved February 18, 2014.
- "History". Mesa AZ: Mesa United Way. Retrieved February 18, 2014.
- "Timeline: 1980-2010". AZCentral.com. Retrieved June 29, 2015.
- "History of Riordan Mansion State Historic Park". Arizona State parks. Retrieved July 1, 2015.
- "ARM Founders and Board of Directors". Arizona Railway Museum. Retrieved July 1, 2015.
- Jovanelly, Joshua. "Firebird races on hold". Gila River Indian Community. Retrieved July 1, 2015.
- Hedding, Judy. "Deer Valley Petroglyph Preserve". About Travel. Retrieved June 29, 2015.
- "Tucson Historic Preservation Foundation". Retrieved April 2, 2013.
- "Visitors & Friends". Maricopa Community Colleges. Retrieved July 1, 2015.
- Powell, Brian (February 27, 2005). "Abandoned Chandler field going to seed". East Valley Tribune. Retrieved July 1, 2015.
- "Palo Verde – Arizona". Nuclear Tourist. Retrieved June 29, 2015.
- "Arizona Centennial". The Arizona Republic/AZCentral.com. Retrieved June 29, 2015.
- "History of the Mesa Historical Museum". Mesa Historical Museum. Retrieved July 5, 2015.
- "Telephone Pioneers of America Park". AZCentral.com. Retrieved June 29, 2015.
- "Sunnyslope Historical Society". Phoenix, Arizona. Archived from the original on December 7, 2013. Retrieved March 25, 2013.
- "Herberger Theater Center". DiscoverPhoenixArizona.com. Archived from the original on February 21, 2014. Retrieved June 29, 2015.
- "Terminal 4". Sky Harbor Airport. Archived from the original on July 24, 2014. Retrieved June 29, 2015.
- "Joel "Starts the Fire" for Pavilion". Deseret News. November 11, 1990. Retrieved June 29, 2015.
- "CCC At a Glance". Coconino County Community College. Retrieved July 1, 2015.
- http://www.cap-az.com/about-us/background
- "Phoenix City Hall". SkyscraperPage.com. Retrieved June 29, 2015.
- "Facility History and Facts" (PDF). Peoria Sports Complex. Archived from the original (PDF) on October 6, 2014. Retrieved July 5, 2015.
- "Maryvale Baseball Park". City of Phoenix. Retrieved July 1, 2015.
- "San Rafael State Natural Area". Arizona State Parks. Archived from the original on December 27, 2014. Retrieved July 5, 2015.
- "About Us". Japanese Friendship Garden of Phoenix. Retrieved June 29, 2015.
- U.S. Census Bureau, "Mini-Historical Statistics: Population of the Largest 75 Cities: 1900 to 2000" (PDF), Statistical Abstract of the United States: 2003
- "Mesa (city)". Arizona QuickFacts. U.S. Census Bureau. Archived from the original on March 9, 2005. Retrieved February 18, 2014.
- "Basha High School". City of Chandler. Retrieved July 1, 2015.
- "Office of the Mayor". City of Phoenix. Archived from the original on June 6, 2004. Retrieved April 2, 2013.
- "Southern Arizona Transportation Museum". Archived from the original on October 10, 2013. Retrieved April 2, 2013.
- "History". Theater Works. Retrieved July 5, 2015.
- "Perry High School". Retrieved July 1, 2015.
- Nilsen, Richard (April 18, 2010). "Former Target CEO Bob Ulrich orchestrates creation of MIM". The Arizona Republic. Retrieved June 29, 2015.
- "Largest Urbanized Areas With Selected Cities and Metro Areas (2010)". US Census Bureau. 2012.
- "Mesa (city), Arizona". State & County QuickFacts. U.S. Census Bureau. Archived from the original on March 9, 2005. Retrieved February 18, 2014.
- "Phoenix Dusts Off After Giant Sandstorm Whips Through". New York Times. July 6, 2011. Retrieved March 25, 2013.
- Center for Social Cohesion, Phoenix, Arizona, archived from the original on August 2, 2011
- "Meet the Mayors". Washington, D.C.: United States Conference of Mayors. Archived from the original on June 27, 2008. Retrieved March 30, 2013.
- "About Last Night". New York Times. February 23, 2012. Retrieved February 18, 2014.
- "Mesa Indian ruins open after decades of effort". USA Today. January 18, 2013. Retrieved February 18, 2014.
- Civic Impulse, LLC. "Members of Congress". GovTrack. Washington, D.C. Retrieved February 18, 2014.
- "The 15 Cities with the Largest Numeric Increase from July 1, 2012 to July 1, 2013" (PDF). US Census Bureau. 2014.
Vintage 2013 Population Estimates
- "Lowell's flagship instrument is the 4.3-meter Discovery Channel Telescope". Lowell Observatory. Retrieved July 1, 2015.
- Brown, Brandon (April 7, 2015). "Terminal 3 renovations start at Sky Harbor, airlines relocate". Phoenix Business Journal. Retrieved June 29, 2015.
- "Casteel High School". Retrieved July 1, 2015.
Bibliography
- Braatz, Timothy (2003). Surviving Conquest. University of Nebraska Press. ISBN 978-0-8032-2242-7.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Sheridan, Thomas E. (2012). Arizona. Tucson: University of Arizona Press.
Further reading
- Published in the 19th century
- Patrick Hamilton (1881), "Chief Towns: Phoenix", Resources of Arizona, Prescott, Ariz
- Published in the 20th century
- Maricopa County (Ariz.). Board of Supervisors (1908), "Phoenix", Salt River Valley, Arizona, offers productive lands, a healthful climate and rare opportunities to the investor and homeseeker, New York: Norman Pierce Co., OCLC 16818598
- George Wharton James (1917), "Phoenix and Salt River Valley", Arizona, the Wonderland, Boston: Page Company
- Federal Writers’ Project (1966). "Phoenix". Arizona, the Grand Canyon State. American Guide Series (4th ed.). New York: Hastings House. p. 216+. OL 5989725M.
- James E. Buchanan (1978), Howard B. Furer (ed.), Phoenix: a chronological & documentary history, 1865-1976, American Cities Chronology Series, Dobbs Ferry, N.Y.: Oceana Publications, ISBN 0379006170
- Lykes, Aimee de Potter. "A Hundred Beers of Phoenix History", in G. Wesley Johnson, Jr., ed. Phoenix in the Twentieth Century: Essays in Community History (1993) pp 220–236, to 1981
- Published in the 21st century
- Matthew C. Whitaker (2009). "Great expectations: African American and Latino relations in Phoenix since World War II". In Kenneth L. Kusmer and Joe W. Trotter (ed.). African American Urban History since World War II. Historical Studies of Urban America. University of Chicago Press. ISBN 978-0-226-46512-8.
- American Cities Project (2013). "Phoenix". America's Big Cities in Volatile Times: City Profiles. Washington, D.C.: Pew Charitable Trusts.
- Joseph Galaskiewicz; et al. (2013). "Studying the role of nonprofits, government, and business in providing activities and services to youth in the Phoenix Metropolitan Area". In Mario Luis Small; et al. (eds.). Reconsidering the Urban Disadvantaged: The Role of Systems, Institutions, and Organizations. Sage. ISBN 978-1-4833-0656-8.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to History of Arizona. |
- "Collection Directory". Arizona Memory Project. Retrieved March 25, 2013.
- Phoenix Public Library. Arizona Room (local history)
