Arizona State Route 202
State Route 202 (SR 202) or Loop 202 is a partial beltway looping around the eastern areas of the Phoenix metropolitan area in central Arizona. It traverses the eastern end of the city of Phoenix, in addition to the cities of Tempe, Mesa, Chandler, and Gilbert, and is a vital route in the metropolitan area freeway system. Loop 202 has three officially designated sections along its route; the Red Mountain Freeway, the SanTan Freeway, and the South Mountain Freeway, also known as the Ed Pastor Freeway. The Red Mountain Freeway runs from the Mini Stack Interchange with Interstate 10 (I-10) and State Route 51 (SR 51) in Phoenix to the SuperRedTan Interchange with U.S. Route 60 (US 60) in Mesa. The SanTan Freeway runs from there to an interchange with Interstate 10 (I-10) in Chandler. The South Mountain Freeway, officially known as the Congressman Ed Pastor Freeway, runs from there to Interstate (I-10) in western Phoenix.
| ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
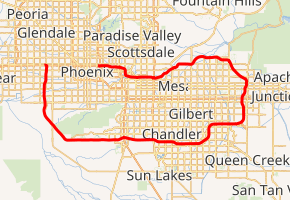
Loop 202 highlighted in red | ||||
| Route information | ||||
| Maintained by ADOT | ||||
| Length | 78 mi[1] (126 km) | |||
| Existed | 1990–present | |||
| Major junctions | ||||
| From | ||||
| To | ||||
| Location | ||||
| Counties | Maricopa | |||
| Highway system | ||||
| ||||
Loop 202 was created after different sections of freeway within the Phoenix metro were given the designation, while the first section was designated in 1990. The SanTan Freeway was completed in 2006, while the Red Mountain Freeway section was completed in 2008. The Ed Pastor Freeway was officially opened on December 21, 2019.[2]
Route description
Red Mountain Freeway
The first section of Loop 202 to open was the Red Mountain Freeway. It runs from the I-10/SR 51 Mini Stack interchange to US 60. It passes over the Salt River and through Tempe and Mesa en route, with an interchange with Loop 101 in Tempe. The final segment of the freeway from Power Road to University Drive opened on July 21, 2008.[3] This opening marked the completion of the original Regional Freeway System as approved by Maricopa County voters in 1985 by Proposition 300.[4]
In 2006, this portion of Loop 202 was used to portray a Saudi Arabian superhighway in the 2007 film, The Kingdom. Filming also took place at Phoenix-Mesa Gateway Airport and the Arizona State University Polytechnic Campus. The city of Mesa received $40,000 for the use of the freeway from NBC Universal.[5]
As of October 2012, HOV lanes on the Red Mountain section run from I-10/SR 51 to Gilbert Road. In 2015, the HOV lanes were extended from Gilbert Road to Broadway Road. HOV lanes are planned to extend to US 60 in Mesa, eventually tying into planned HOV lanes on the SanTan Freeway.
SanTan Freeway
Completed in 2006,[6] the SanTan Freeway serves the southeast valley cities of Chandler, Gilbert, and Mesa. It provides access to Phoenix-Mesa Gateway Airport, the former Williams Air Force Base. Beginning at the SuperRedTan Interchange with US 60 in Mesa, the freeway runs south and turns westward in Gilbert near the airport. A few miles later the SanTan is running in Chandler, where it has a junction with Loop 101 in the vicinity of the Chandler Fashion Center. Following this interchange, the SanTan Freeway section of Loop 202 encounters its terminus at a stack interchange with I-10 near Ahwatukee.[7]
The SanTan section has HOV lanes between I-10 and Gilbert Road. Long-term plans call for HOV lanes to extend to US 60 and to the HOV lanes on the Red Mountain section.
Ed Pastor Freeway
The third segment of Loop 202, the South Mountain Freeway, officially known as the Ed Pastor Freeway, received final approval from the Federal Highway Administration on March 10, 2015, with construction completed at the end of 2019.[8][9] The Ed Pastor Freeway has two distinct segments: the "eastern segment" that straddles the Ahwatukee-GRIC border and the "western segment" that parallels 59th Avenue through the southwest Phoenix community of Laveen. Together, these segments form a 21.9-mile (35.2 km) mile bypass around Downtown Phoenix, linking the metropolitan area's southwestern and southeastern suburbs. The freeway begins at the existing four-level symmetrical stack interchange between I-10 and the Santan Freeway on the Chandler-Ahwatukee border and terminates at I-10 and 59th Avenue west of Downtown Phoenix.[10]
A six-mile (9.7 km) stretch of the freeway, from 40th Street to 17th Avenue, includes a 16-foot (4.9 m) wide bike path. The path is on the south side of the freeway and is also open to pedestrians. The path was included because the existing roadway had been a popular cycling route for years.[11]
History

The highway originally was assigned many different route numbers along its path. The portion of the Red Mountain Freeway west of the Pima/Price Freeways was formerly known as the "East Papago Freeway," and it was initially designated SR 217.[12] The remainder of the Red Mountain Freeway was to be SR 216.[13] The San Tan Freeway was originally routed as SR 220.[14] The Ed Pastor Freeway portion, formerly known as the "South Mountain Freeway," was initially supposed to be SR 218.[15] The Loop 202 designation was first assigned on December 18, 1987, along the East Papago and Red Mountain Freeway corridors and the portion of the San Tan Freeway east of Price Road.[16] At that time, the portion of Loop 202 west of Price Road was to become part of Loop 101.[17] But on July 19, 1991, the proposed South Mountain Freeway (Ed Pastor Freeway) was renumbered as part of Loop 202.[18]
Controversy
The Ed Pastor Freeway remains the most controversial[19] segment of Loop 202. Construction was delayed due to tension between three groups: regional transportation planners, who insisted that the freeway was necessary to ensure smooth traffic flow in the coming decades;[20] residents of the adjacent Ahwatukee community, who would have lost 120 homes to eminent domain depending on the road's final alignment; and leaders and residents of the adjoining Gila River Indian Community (GRIC), who have oscillated between opposing and supporting the freeway in recent years.[21]
The specific alignment of the freeway, initially referred to in 1983 as the "Southwest Loop Highway", was revised several times since 1985, when Maricopa County voters originally approved its construction as part of the regional highway network envisioned under Proposition 300.[22] In 1988, the Maricopa Association of Governments (MAG), the region's transportation planning agency, suggested an alignment of the freeway's western segment along 55th Avenue and an alignment of the eastern segment along Pecos Road.[23] A federal study in 2001 required ADOT to reexamine those suggestions, and the task of recommending the final alignment fell to a Citizen's Advisory Team formed in 2002. In April 2006, that panel released their final recommendations to route the western portion of the freeway four miles further west to connect with Loop 101, and to reject the proposed alignment of the eastern portion along Pecos Road, suggesting that the latter be built on Gila River Indian Community land instead.[24][25] Two months later, ADOT overruled the panel's suggestion for the western segment and opted for the current 59th Avenue alignment instead.[23]
In February 2012, a non-binding referendum was held in the Gila River Indian Community on whether the eastern portion of the freeway should be built on community land several miles south of Pecos Road. Options in the referendum were to build on community land, off community land, or not at all. The "no build" option won a plurality of votes, receiving 720 votes out of a total 1,481 cast.[26] MAG sent out a press release soon after making it clear that construction of the freeway would move forward as planned along the Pecos Road alignment.[20] Expecting this outcome, MAG and ADOT had previously (in 2010) shrunk the freeway's footprint from 10 lanes to eight to minimize its impact on Ahwatukee.[27] Fearing the worst possible outcome of the freeway being built without exits onto community land (as would be the case with the Pecos Road alignment), Gila River Indian Community residents quickly formulated plans for a new referendum that would exclude the "no build" option, leaving only "yes on Gila River or no on Gila River."[28] The tribal government rejected this proposal in July 2013.[29]
As late as September 2013, the freeway still faced active opposition. A non-profit group called the Gila River Alliance for a Clean Environment filed a civil-rights complaint with ADOT in July, claiming the freeway would disproportionately and adversely affect tribe members. A freeway opposition group called Protecting Arizona's Resources and Children planned an environmental lawsuit.[30] And the Environmental Protection Agency in August 2013 raised several objections to the state's 12-year, $21 million draft environmental impact statement that had deemed construction of the freeway to be more beneficial to the environment, by improving traffic flow and thus reducing pollution, than building no freeway at all. The EPA claimed that the statement contained overly optimistic traffic projections, did not sufficiently address air quality concerns, and could harm neighboring communities and environmental resources.[31]
By April 2017, ADOT had purchased 1,387 acres (561 ha), or 90% of the land needed for the freeway. While construction was underway in 2017 on both ends of the freeway segment, no work had occurred on a five-mile (8 km) center segment adjacent to South Mountain until a final decision was made by the Ninth Circuit Court of Appeals. A ruling was released in mid-2018 in the action brought by the Gila River Indian Community.[32] The Ninth Circuit Court of Appeals rejected Gila River Indian Community's claims in December 2017.[33]
Construction
In March 2015, the Federal Highway Administration (FHWA) issued a Record of Decision approving the project and selecting a build alternative. ADOT immediately thereafter commenced right-of-way acquisition and the procurement of final design and construction services in the form of a design-build-maintain contractor or "developer." The developer will have been selected at the end of 2015 (actual date was a couple months after) and freeway construction will have begun in early 2016 (construction started later that same year), with the Chandler Boulevard extension project to facilitate local access beginning in summer 2015. The freeway opened to traffic in late 2019 as originally planned with construction being finalized in early 2020.[34] However, new lawsuits in June 2015 from the group Protecting Arizona's Resources and Children, the Sierra Club, and the Gila River Indian Community threatened to delay the freeway's construction.[35][36]
On August 26, 2015, ADOT started demolition of the first houses along the route for the South Mountain Freeway.[37]
On February 27, 2016, the contract to design, build, and maintain the freeway was awarded to Connect 202 Partners, a joint venture led by Fluor Corporation, with Fluor, Granite Construction, Ames Construction, and Parsons Brinckerhoff being responsible for the final design and construction, and with Fluor and DBi Services, LLC being responsible for maintenance for 30 years.[38]
The first phase of construction of the South Mountain Freeway began on September 19, 2016, with improvements to the I-10/Loop 202 (Santan Freeway) interchange.[39]
In early 2017, ADOT announced an updated design for the freeway, including Arizona's first diverging diamond interchanges at Desert Foothills Parkway and 17th Avenue; a reconfiguration near 51st Avenue that moved the freeway interchange to Estrella Drive in order to avoid a GRIC well; and a pedestrian bridge to connect the Del Rio subdivisions bisected by the freeway.[40][41]
Naming
On October 22, 2019, the South Mountain Freeway was officially renamed the Congressman Ed Pastor Freeway, in honor of longtime U.S. Representative Ed Pastor (D-AZ).[42]
Exit list
The entire route is in Maricopa County.
| Location | mi [1][43][44] | km | Exit | Destinations | Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phoenix | 0.00 | 0.00 | Counterclockwise terminus; exit 147A on I-10 | |||
| 0.28 | 0.45 | 1A | Mini Stack; westbound exit and eastbound entrance; south end of SR 51 | |||
| 0.31 | 0.50 | — | HOV interchange; westbound exit and eastbound entrance; exit 147C on I-10 | |||
| 0.75 | 1.21 | 1B | 24th Street | |||
| 1.76 | 2.83 | 1C | 32nd Street | |||
| 3.27 | 5.26 | 2 | 40th Street / 44th Street | |||
| 3.51 | 5.65 | 3 | Eastbound exit and westbound entrance; exit 5 on SR 143 | |||
| 4.37– 4.52 | 7.03– 7.27 | 4 | 52nd Street / Van Buren Street | |||
| Tempe | 5.35 | 8.61 | 5 | Westbound exit and eastbound entrance; access via unsigned SR 202 Spur | ||
| 5.71– 6.37 | 9.19– 10.25 | 6 | Priest Drive / Center Parkway | |||
| 7.73 | 12.44 | 7 | Scottsdale Road / Rural Road | |||
| Salt River | 8.22 | 13.23 | West end of bridge | |||
| 8.70 | 14.00 | 8 | McClintock Drive | Eastbound exit and westbound entrance | ||
| 9.22 | 14.84 | East end of bridge | ||||
| Mesa | 9.66– 9.92 | 15.55– 15.96 | 9 | Exit 51 on Loop 101 | ||
| 11.07 | 17.82 | 10 | Dobson Road | |||
| 12.07 | 19.42 | 11 | Alma School Road | |||
| 12.73 | 20.49 | 12 | McKellips Road | Eastbound exit and westbound entrance | ||
| 13.23 | 21.29 | 13 | ||||
| 16.55 | 26.63 | 16 | Gilbert Road | Eastbound exit and westbound entrance | ||
| 18.10 | 29.13 | 17 | McDowell Road | Westbound exit and eastbound entrance | ||
| 19.05 | 30.66 | 19 | Val Vista Drive | |||
| 20.07 | 32.30 | 20 | Greenfield Road | |||
| 21.08 | 33.92 | 21 | ||||
| 22.17 | 35.68 | 22 | Recker Road | |||
| 22.95 | 36.93 | 23A | Power Road | Eastbound exit and westbound entrance | ||
| Cardinal direction change: Northern quadrant (west–east) / Eastern quadrant (north–south) | ||||||
| 23.73 | 38.19 | 23B | McDowell Road | Northbound exit and southbound entrance | ||
| 24.91 | 40.09 | 25 | McKellips Road | |||
| 26.39 | 42.47 | 26 | Brown Road | |||
| 27.86 | 44.84 | 27 | University Drive to Apache Trail / Main Street | Signed northbound as University Drive only | ||
| 28.92 | 46.54 | 28 | Broadway Road | |||
| 30.42– 30.60 | 48.96– 49.25 | 30A-B | Signed as exits 30A (east) and 30B (west); SuperRedTan Interchange; exit 190 on US 60 | |||
| Red Mountain Freeway transitions to SanTan Freeway | ||||||
| 31.01 | 49.91 | 31 | Baseline Road | Northbound exit and southbound entrance | ||
| 32.05 | 51.58 | 32 | Guadalupe Road | |||
| 33.05 | 53.19 | 33 | Elliot Road | |||
| 33.95 | 54.64 | 34A | West end of SR 24; southbound exit and northbound entrance | |||
| Cardinal direction change: Eastern quadrant (north–south) / Southern quadrant (west–east) | ||||||
| 34.15– 34.85 | 54.96– 56.09 | 34B | ||||
| 35.25 | 56.73 | 34A | West end of SR 24; eastbound exit and westbound entrance | |||
| Mesa–Gilbert line | 36.55 | 58.82 | 36 | Also serves ASU Polytechnic Campus | ||
| Gilbert | 38.55 | 62.04 | 38 | Higley Road | ||
| 40.75 | 65.58 | 40 | Williams Field Road | Serves Santan Village Mall and Power Center | ||
| 41.75 | 67.19 | 41 | Santan Village Parkway | Eastbound exit and westbound entrance | ||
| 42.41 | 68.25 | 42 | Val Vista Drive | Serves Mercy Gilbert Hospital | ||
| 43 | Lindsay Road | Proposed[45] | ||||
| Gilbert–Chandler line | 44.48 | 71.58 | 44 | Gilbert Road | Serves Gilbert Crossroads Power Center | |
| Chandler | 45.48 | 73.19 | 45 | |||
| 46.48 | 74.80 | 46 | McQueen Road | |||
| 47.55 | 76.52 | 47 | Serves Downtown Chandler | |||
| 48.56 | 78.15 | 48 | Alma School Road | |||
| 49.56 | 79.76 | 49 | Dobson Road | Westbound exit and eastbound entrance | ||
| 50.58 | 81.40 | 50A | Clockwise end of Loop 101; exits 61B-C on Loop 101 | |||
| 50.65 | 81.51 | 50B | Price Road | Serves Chandler Fashion Center | ||
| 50.74 | 81.66 | 50C | Westbound exit and eastbound entrance via HOV lanes; exit 61D on Loop 101 | |||
| 51.65 | 83.12 | 51 | McClintock Drive / Chandler Village Drive | Eastbound exit and westbound entrance | ||
| 53.65 | 86.34 | 53 | Kyrene Road | |||
| Chandler–Phoenix line | 55.16– 55.30 | 88.77– 89.00 | 55A-B | Signed as exits 55A (west) and 55B (east); exits 161A–B on I-10 | ||
| 55C | HOV interchange; westbound exit and eastbound entrance; exit 161C on I-10 | |||||
| SanTan Freeway transitions to Ed Pastor Freeway | ||||||
| Phoenix | 57.17 | 92.01 | 56 | 40th Street | Opened on September 7, 2019[46] | |
| 58.17 | 93.62 | 57 | 32nd Street | Planned diamond interchange; to open October 2020[47] | ||
| 59.17 | 95.22 | 58 | 24th Street | Opened on November 18, 2019[48] | ||
| 60.97 | 98.12 | 60 | Desert Foothills Parkway | Half diverging diamond interchange; opened on November 18, 2019[48] | ||
| 62.97 | 101.34 | 62 | 17th Avenue | Half diverging diamond interchange; opened on November 18, 2019[48] | ||
| Cardinal direction change: Southern quadrant (west–east) / Western quadrant (north–south) | ||||||
| 67 | Vee Quiva Way | Opened on December 22, 2019 | ||||
| 68 | Estrella Drive | Double roundabout interchange[40] | ||||
| 69 | Elliot Road | [40] | ||||
| 70 | Dobbins Road | [40] | ||||
| 71 | Baseline Road | [40] | ||||
| 72 | Southern Avenue | [40] | ||||
| Second bridge over the Salt River | ||||||
| Planned interchange with the eastern terminus of SR 30[40] | ||||||
| 73 | Broadway Road | [40] | ||||
| 74 | Lower Buckeye Road | Diamond interchange with 59th Avenue frontage roads[40] | ||||
| 76 | Buckeye Road | Diamond interchange with 59th Avenue frontage roads[40] | ||||
| 77 | Van Buren Street | Northbound exit and southbound entrance with 59th Avenue frontage roads[40] | ||||
| — | HOV ramps; northbound exit and southbound entrance[40] | |||||
| 78 | Tri-stack interchange; clockwise terminus; exit 138 on I-10; signed as 78A (west) & 78B (east)[40] | |||||
1.000 mi = 1.609 km; 1.000 km = 0.621 mi
| ||||||
Spur route
Arizona Spur 202 is an unsigned state highway located in Phoenix. It begins at the Red Mountain Freeway (Loop 202) at exit 5. It continues west, intersecting the Hohokam Expressway (SR 143) and ends at Phoenix Sky Harbor International Airport. This is an unsigned route, marked by westbound exit signs from Loop 202 as Sky Harbor Boulevard. The spur route was commissioned in 1993.[1]
Major intersections
The entire route is in Maricopa County. All exits are unnumbered.
| Location | mi[1] | km | Destinations | Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phoenix | 1.22 | 1.96 | Continuation beyond western terminus | ||
| 1.20– 1.10 | 1.93– 1.77 | 44th Street south | Former SR 153 (Sky Harbor Expressway); eastbound exit and westbound left entrance | ||
| 44th Street north | Former SR 153 (Sky Harbor Expressway); eastbound left exit and westbound entrance | ||||
| Phoenix–Tempe line | 1.03 | 1.66 | No exit ramps to SR 143 north; no eastbound entrance from SR 143 south; exits 3A–B on SR 143 | ||
| Tempe | 0.30 | 0.48 | Priest Drive / Center Parkway – Downtown Tempe | Eastbound exit and westbound entrance | |
| 0.00 | 0.00 | Eastern terminus; exit 5 on Loop 202 | |||
| 1.000 mi = 1.609 km; 1.000 km = 0.621 mi | |||||
See also


- Metropolitan Phoenix Freeways
- Loop 101
- Loop 303
- Public-private partnerships in the United States
References
- Roadway Inventory Management Section, Multimodal Planning Division (December 31, 2013). "2013 State Highway System Log" (PDF). Arizona Department of Transportation. Retrieved January 16, 2016.
- Maryniak, Paul (December 21, 2019). "Congressman Ed Pastor Freeway opens". East Valley Tribune. Times Media Group. Retrieved January 4, 2020.
- "Freeway opening scheduled for July 21". The Arizona Republic. Phoenix, AZ. Retrieved July 10, 2008.
- Staff. "Loop 202 Power to University". Arizona Department of Transportation. Retrieved February 2, 2008.
- "Is that Loop 202?". The Arizona Republic. Retrieved March 5, 2008.
- Staff. "Loop 202 (Santan Freeway)". Arizona Department of Transportation. Retrieved February 2, 2008.
- Project Map L202 (Map). Cartography by ADOT. Arizona Department of Transportation. Retrieved February 2, 2008.
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on March 12, 2015. Retrieved March 11, 2015.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- "ADOT given green light to construct new freeway". Azcentral.com. March 10, 2015. Retrieved April 17, 2017.
- "SR-202L ? South Mountain Freeway Design Review Summary" (PDF). Azmag.gov. Retrieved April 17, 2017.
- Copolla, Chris (April 5, 2016). "South Mountain Freeway to include a bike path in Ahwatukee". The Arizona Republic. Retrieved April 5, 2016.
- Breyer, Joe. "Right-of-Way Resolutions - Route Number: 217". Arizona Highway Data. Works Consulting LLC. Retrieved March 2, 2016.
- Breyer, Joe. "Right-of-Way Resolutions - Route Number: 216". Arizona Highway Data. Works Consulting LLC. Retrieved March 2, 2016.
- Breyer, Joe. "Right-of-Way Resolutions - Route Number: 220". Arizona Highway Data. Works Consulting LLC. Retrieved March 2, 2016.
- Breyer, Joe. "Right-of-Way Resolutions - Route Number: 218". Arizona Highway Data. Works Consulting LLC. Retrieved March 2, 2016.
- Breyer, Joe. "Right-of-Way Resolutions - Route Number: 202L". Arizona Highway Data. Works Consulting LLC. Retrieved March 2, 2016.
- Breyer, Joe. "Right-of-Way Resolutions - Route Number: 101L". Arizona Highway Data. Works Consulting LLC. Retrieved March 2, 2016.
- Breyer, Joe. "Arizona DOT Right-of-Way Resolution 1991-07-A-056". Arizona Highway Data. Works Consulting LLC. Retrieved March 2, 2016.
- Caitlin Cruz. "Gila River landowners' signatures back South Mountain Freeway". Arizona Republic. Retrieved October 15, 2012.
- "MAG News". Azmag.gov. February 8, 2012. Archived from the original on April 2, 2015. Retrieved April 17, 2017.
- Cathryn Creno. "184 homes in South Mountain Freeway path, planners say". Arizona Republic. Retrieved October 15, 2012.
- "2011 Annual Report" (PDF). Azmag.gov. Retrieved April 17, 2017.
- "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on March 4, 2016. Retrieved October 16, 2012.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- "Central District Projects". Azdot.gov. Retrieved April 17, 2017.
- "Central District Projects". Azdot.gov. Retrieved April 17, 2017.
- Holstege, Sean (February 7, 2012). "Gila River tribe appears to reject South Mountain Freeway". Azcentral.com. Retrieved April 17, 2017.
- "Central District Projects". Azdot.gov. Retrieved April 17, 2017.
- Seligman, Allie (February 8, 2012). "Tribal vote may not end South Mountain Freeway struggle". Azcentral.com. Retrieved April 17, 2017.
- Holstege, Sean. "No new tribal vote on South Mountain Freeway". Azcentral.com. Retrieved April 17, 2017.
- Holstege, Sean. "Feds: South Mountain Freeway impact study flawed". Azcentral.com. Retrieved April 17, 2017.
- "National Environmental Policy Act | US EPA" (PDF). Epa.gov. Retrieved April 17, 2017.
- Guzzom, John; Weil, Karen (May 29, 2017). "Construction Revs Up on P3 Freeway Project in Phoenix". Engineering News Record. p. 12.
- "Federal court rejects latest attempt to stop South Mountain Freeway". Azcentral.com. December 8, 2017. Retrieved April 6, 2018.
- "Loop 202 (South Mountain Freeway) Project Homepage". Azdot.gov. Retrieved April 17, 2017.
- "Opponents sue to stop Loop 202 South Mountain Freeway". Azcentral.com. Retrieved April 17, 2017.
- "Gila River tribe sues to prevent South Mountain Freeway". Azcentral.com. Retrieved April 17, 2017.
- "State begins to remove homes in path of Phoenix freeway expansion - ABC15 Arizona". Abc15.com. August 27, 2015. Archived from the original on August 29, 2015. Retrieved April 17, 2017.
- "Fluor-Led Joint Venture Awarded Loop 202 South Mountain Freeway Project". Business Wire. February 29, 2016. Retrieved March 1, 2016.
- "South Mountain Freeway construction scheduled at I-10/Loop 202 interchange". Arizona Department of Transportation. September 15, 2016. Retrieved September 20, 2016.
- "South Mountain Freeway Flyover Visualization". ADOT (via YouTube). March 15, 2017. Retrieved March 27, 2017.
- Reiser, Lindsey (March 17, 2017). "New South Mountain Freeway to utilize "diverging diamond interchange"". AZFamily. Retrieved March 27, 2017.
- Fuenmayor, Alexa (October 24, 2019). "New section of Loop 202 to be named after late Congressman Ed Pastor". Arizona Republic. Phoenix: Gannett Co. Retrieved November 18, 2019.
- Google (January 16, 2016). "Arizona State Route 202" (Map). Google Maps. Google. Retrieved January 16, 2016.
- Google (January 16, 2016). "Pecos Road" (Map). Google Maps. Google. Retrieved January 16, 2016.
- "Gilbert moves forward on new Loop 202 exit, expanding future jobs hub". The Arizona Republic. June 26, 2017. Retrieved January 21, 2019.
- Powell, Kim (September 6, 2019). "40th Street Interchange at Loop 202 South Mountain Freeway opens after 4 months of construction". AZFamily. azfamily.com. Retrieved November 21, 2019.
- "Shared-use path, 32nd Street interchange expected to open in October". Arizona DOT. ADOT. August 12, 2020. Retrieved August 16, 2020.
- Rodewald, Matt; Fox 10 Staff (November 18, 2019). "Half-Diverging Diamond Interchanges open on South Mountain Freeway". KSAZ-TV. NW Communications of Phoenix, Inc. Retrieved November 18, 2019.
