Superannuation in Australia
Superannuation in Australia are the arrangements put in place by the Government of Australia to encourage people in Australia to accumulate funds to provide them with an income stream when they retire. A type of employment funded pension, superannuation in Australia is partly compulsory, and is further encouraged by tax benefits. The government has set minimum standards for contributions by employees as well as for the management of superannuation funds. It is compulsory for employers to make superannuation contributions for their employees on top of the employees' wages and salaries. The employer contribution rate has been 9.5% since 1 July 2014, and as of 2015, was planned to increase gradually from 2021 to 12% in 2025.[1] People are also encouraged to supplement compulsory superannuation contributions with voluntary contributions, including diverting their wages or salary income into superannuation contributions under so-called salary sacrifice arrangements.
An avoidable issue with Australia’s superannuation system is employees failing to consolidate multiple accounts, thus being charged multiple account fees. Of Australia’s 15 million superannuation fund members, 40% have multiple accounts, which collectively costs them $2.6 billion in additional fees each year. The federal budget estimates put the number of unnecessary duplicate accounts at 10 million. Plans are in place to facilitate consolidation of these accounts.[2] An individual can withdraw funds out of a superannuation fund when the person meets one of the conditions of release, such as retirement, terminal medical condition, or permanent incapacity, contained in Schedule 1 of the Superannuation Industry (Supervision) Regulations 1994.[3] As of July 1, 2018, members have also been able to withdraw voluntary contributions made as part of the First Home Super Saver Scheme (FHSS).[4]
As of 30 June 2018, Australians have AU$2.7 trillion in superannuation assets, making Australia the 4th largest holder of pension fund assets in the world.[5] As of 30 June 2019, the balance is AU$2.9 trillion.
Introduction
For many years until 1976, what superannuation arrangements were in place were set up under industrial awards negotiated by the union movement or individual unions.
A change to superannuation arrangements came about in 1983 through an agreement between the government and the trade unions. In the Prices and Incomes Accord, the trade unions agreed to forgo a national 3% pay increase which would be put into the new superannuation system for all employees in Australia. This was matched by employers' contributions. Employers' and employees' contributions were originally set at 3% of the employees' income, and has been gradually increased.[6] Though there is general widespread support for compulsory superannuation today, at the time of its introduction it was met with strong resistance by small business groups who were fearful of the burden associated with its implementation and its ongoing costs.[7]
In 1992, under the Keating Labor Government, the compulsory employer contribution scheme became a part of a wider reform package addressing Australia's retirement income dilemma. It had been demonstrated that Australia, along with many other Western nations, would experience a major demographic shift in the coming decades, of the aging of the population, and it was claimed that this would result in increased age pension payments that would place an unaffordable strain on the Australian economy. The proposed solution was a "three pillars" approach to retirement income:[8]
- compulsory employer contributions to superannuation funds,
- further contributions to superannuation funds and other investments, and
- if insufficient, a safety net consisting of a means-tested government-funded age pension.
The compulsory employer contributions were branded "Superannuation Guarantee" (SG) contributions.[9][10]
The Keating Labor Government had also intended for there to be a compulsory employee contribution beginning in 1997-98, with employee contributions beginning at 1%, then rising to 2% in 1998-99 and reaching 3% in 1999-2000.[11] However this planned compulsory 3% employee contribution was cancelled by the Howard Liberal Government when it took office in 1996.[12] The employer SG contribution was allowed to continue to rise to 9%, which it did in 2002-03. The Howard Government also limited employer SG contributions from 1 July 2002 to an employee's ordinary time earnings, which includes wages and salaries, as well as bonuses, commissions, shift loading and casual loadings, but does not include overtime paid.
The SG rate was 9% from 2002-03 to 2013-14 when the Rudd-Gillard Labor Government passed legislation to increase SG contributions slowly to 12% starting on 1 July 2015 and ending on 1 July 2019. However, the succeeding Abbott Liberal Government deferred starting this planned increase by six years, to 1 July 2021.[12] The SG rate has been 9.5% of employee earnings since 1 July 2014, and after 30 June 2021 the rate is planned to increase by 0.5% each year until it reaches 12% in 2025.[13][14]
Operation
Employer contributions
Superannuation guarantee contributions
| 1 July | Minimum contribution percentage[15][16] |
|---|---|
| 1992 | 3 / 4* |
| 1993 | 3 / 5* |
| 1994 | 4 / 5* |
| 1995 | 5 / 6* |
| 1996 | 6 |
| 1998 | 7 |
| 2000 | 8 |
| 2002 | 9 |
| 2013 | 9.25 |
| 2014 | 9.5 |
| 2021 | 10 |
| 2022 | 10.5 |
| 2023 | 11 |
| 2024 | 11.5 |
| 2025 | 12 |
Employers are required to pay superannuation contributions, called "superannuation guarantee" (SG) contributions, to an approved superannuation fund for their employees at 9.5% (as at 2018) of the employees' "ordinary time earnings" (OTE)—which generally consists of wages and salaries, commissions, allowances but not overtime.[17] Employers are not required to make employer contributions for employees earning less than $450 per month, nor for employees aged under 18. However, if an under 18 employee earns over $450 per month before tax or works more than 30 hours per week full-time, part-time or casual, the employer is also required to contribute superannuation. Additionally, if employees aged over 70 years work more than 40 hours in a 30-day period, the employer can also pay contributions. Employer contributions are required to be paid on at least a quarterly basis.
Initially, between 1993-1996, a higher contribution rate applied for employers whose annual national payroll for the base year exceeded $1 million, with the employer's minimum superannuation contribution percentage set out in the adjacent table with an asterisk. The contribution rate increased over time. The SG rate was 9.5% on 1 July 2014, and was supposed to increase to 10% on 1 July 2018; and then increase by 0.5% each year until it reached 12% on 1 July 2022. The 2014 federal budget deferred the proposed 2018 SG rate increases by 3 years, with the 9.5% rate remaining until 30 June 2021, and is set to have five annual increases, where the SG rate will increase to 12% by July 2025. However, there have been lobbying that suggests that the SG rate should remain at the current rate of 9.5% or make superannuation voluntary.[18][19]
SG employer superannuation contributions are generally tax deductible to the employer and are not part of the taxable income of the employee. They are subject to a 15% tax in the super fund.
“Defined benefit" superannuation schemes
Special rules apply in relation to employers operating "defined benefit" superannuation schemes, which are less common traditional employer funds where benefits are determined by a formula usually based on an employee's final average salary and length of service. Essentially, instead of minimum contributions, employers need to make contributions to provide a minimum level of benefit.
Salary sacrifices contributions
An employee may request that their employer makes all or part of future payments of earnings into superannuation in lieu of making payment to the employee. Such an arrangement is known as "salary sacrifice", and for income tax purposes the payments are treated as employer superannuation contributions, which are generally tax deductible to the employer, and are not subject to the superannuation guarantee (SG) rules. The arrangement offers a benefit to the employee because the amount so sacrificed does not form part of the taxable income of the employee.
For some purposes, however, such contributions are called "reportable superannuation contributions",[20] and for those purposes they are counted back as a benefit of the employee, such as for calculation of "income for Medicare levy surcharge purposes".
To be valid, a salary sacrifice arrangement must be agreed between employer and employee before the work is performed. This agreement is usually documented in writing in pro forma form.
Personal contributions
People can make additional voluntary contributions to their superannuation and receive tax benefits for doing so, subject to limits. The concessional contribution cap for the 2017 2018 financial year is $25,000. For later financial years, the cap is worked out by indexing annually this amount. Amounts above those limits are called "excess concessional contributions".
Carry-forward concessional contributions Unused concessional contributions cap space can be carried forward from 1 July 2018, if the total superannuation balance is less than $500,000 at the end of 30 June in the previous year. Unused amounts are available for a maximum of five years.
Access to superannuation
Employer and personal superannuation contributions are income of the superannuation fund and are invested over the period of the employees' working life and the sum of compulsory and voluntary contributions, plus earnings, less taxes and fees are paid to the person when they retire.
As superannuation is money invested for a person's retirement, strict government rules prevent early access to preserved benefits except in very limited and restricted circumstances. These include major dental, and drug and alcohol addiction recovery.[21] In general people can seek early release superannuation for severe financial hardship or on compassionate grounds, such as for medical treatment not available through Medicare.
Generally, superannuation benefits fall into three categories:
- Preserved benefits;
- Restricted non-preserved benefits; and
- Unrestricted non-preserved benefits.
Preserved benefits are benefits that must be retained in a superannuation fund until the employee's 'preservation age'. Currently, all workers must wait until they are at least 55 before they may access these funds. The actual preservation age varies depending on the date of birth of the employee. All contributions made after 1 July 1999 fall into this category.
Restricted non-preserved benefits although not preserved, cannot be accessed until an employee meets a condition of release, such as terminating their employment in an employer superannuation scheme.
Unrestricted non-preserved benefits do not require the fulfilment of a condition of release, and may be accessed upon the request of the worker. For example, where a worker has previously satisfied a condition of release and decided not to access the money in their superannuation fund.
Preservation age and conditions of release
| Date of birth | Preservation age |
|---|---|
| Before 1 July 1960 | 55 |
| 1 July 1960 – 30 June 1961 | 56 |
| 1 July 1961 – 30 June 1962 | 57 |
| 1 July 1962 – 30 June 1963 | 58 |
| 1 July 1963 – 30 June 1964 | 59 |
| After 30 June 1964 | 60 |
Benefit payments may be a lump sum or an income stream (pension) or a combination of both, provided the payment is allowed under super law and the fund's trust deed. Withholding tax applies to payments to members who are under 60 or over 60 and the benefit is from an untaxed source.[22] In either case, eligibility for access to preserved benefits depends on a member's preservation age and meeting one of the conditions of release.[23] Until 1999, any Australian could access their preserved benefits once they reached 55 years of age. In 1997, the Howard Liberal Government changed the preservation rules to induce Australians to stay in the workforce for a longer period of time, delaying the effect of population ageing. The new rules progressively increased the preservation age based on a member's date of birth, and came into effect in 1999. The result is that by 2025 all Australian workers would need to be at least 60 years of age to access their superannuation.
To access their super, a member must also meet one of the following "conditions of release".[24] Before age 60, workers must be retired — i.e., cease employment — and sign off that they intend never to work again (not work more than 40 hours in a 30-day period). Those aged 60 to 65 can access super if they cease employment regardless of their future employment intentions, so long as they are not working at the time. Members over 65 years of age can access their super regardless of employment status. Employed individuals who have reached preservation but are under age 65 may access up to 10% of their super under the Transition to Retirement (TRIS) pension rules.[24]
An Australian worker who has transferred funds from their New Zealand KiwiSaver scheme into their Australian superannuation scheme, cannot access the ex-New Zealand portion of their superannuation until they reach the age of 65, regardless of their preservation age. This rule also applies to New Zealand citizens who have transferred funds from their New Zealand Kiwisaver scheme into an Australian superannuation fund.
Reasonable benefit limits
Reasonable benefit limits (RBL) were applied to limit the amount of retirement and termination of employment benefits that individuals may receive over their lifetime at concessional tax rates.[25] There were two types of RBLs - a lump sum RBL and a higher pension RBL. For the financial year ending 30 June 2005, the lump sum RBL was $619,223 and the pension RBL was $1,238,440.[26] RBLs were indexed each year in line with movements in Average Weekly Ordinary Time Earnings published by the Australian Bureau of Statistics. The lump sum RBL applied to most people. Generally, the higher pension RBL applied to people who took 50% or more of their benefits in the form of pensions or annuities that met certain conditions (for example, restrictions on the ability to convert the pension back into a lump sum).[26] RBLs were abolished from 1 July 2007.[27]
Superannuation taxes
Contributions
Contributions made to superannuation, either by an individual or on behalf of an individual, are taxed differently depending on whether that contribution was made from 'pre-tax' or 'post-tax' money. "Pre-tax" contributions are contributions on which no income tax has been paid at time of contribution, and are also known as "before-tax" contributions or as "concessional" contributions. They comprise mainly compulsory employer SG ("Superannuation Guarantee", see above) contributions and additional salary sacrifice contributions. These contributions are taxed by the superannuation fund at a "contributions tax" rate of 15%, which is regarded as "concessional" rate. For individuals who earn more than $250,000, the contributions tax is levied at 30%.[28]
"Post-tax" contributions are also referred to as "after-tax" contributions, "non-concessional" contributions or as "undeducted" contributions. These contributions are made from money on which income tax or contributions tax has already been paid, and typically no further tax is required to be withheld from that contribution when it is made to a fund.
Both contribution types are subject to annual caps. Where the annual cap is exceeded, additional tax is payable, either at the marginal tax rate for concessional contributions, or an additional 31.5% for non-concessional contributions, which is in addition to the standard tax rate of 15% payable on contributions, making a total of 46.5%.
Investments in the fund
Investment earnings of the superannuation fund (i.e. dividends, rental income etc.) are taxed at a flat rate of 15% by the superannuation fund. In addition, where an investment is sold, capital gains tax is payable by the superannuation fund at 15%.
Much like the discount available to individuals and other trusts, a superannuation fund can claim a capital gains tax discount where the investment has been owned for at least 12 months. The discount applicable to superannuation fund is 33%, reducing the effective capital gains tax from 15% to 10%.[29]
These taxes contribute over $6 billion in annual government revenue.[30] Superannuation is a tax-advantaged method of saving as the 15% tax rate on contributions is lower than the rate an employee would have paid if they received the money as income. The federal government announced in its 2006/07 budget that from 1 July 2007, Australians over the age of 60 will face no taxes on withdrawing monies out of their superannuation fund if it is from a taxed source.
Discontinued superannuation surcharge
In 1996, the federal government imposed a "superannuation surcharge" on higher income earners as a temporary revenue measure. During the 2001 election campaign, the Howard Government proposed to reduce the surcharge from 15% to 10.5% over three years. The superannuation surcharge was abolished by the Howard Government from 1 July 2005.
Superannuation co-contribution scheme
From 1 July 2003, the Howard Liberal Government made available incentives of a Government co-contribution with a maximum value of $1,000.[31] From the 2012-2013 financial year to the 2016-2017 financial year, superannuation contributions are available for individuals with income not in excess of $37,000.[32] The Government offsets a maximum of $500 and a minimum of $20, calculated at 15% of a low income earners total superannuation contributions.[33]
As at 1 July 2017, The Low Income Superannuation Contribution (LISC) scheme will be replaced with the renamed Low Income Superannuation Tax Offset (LISTO).[34] Under this new scheme, the minimum amount of Government contributions for low income earners with income not in excess of $37,000 is lowered to $10 but the $500 maximum remains.[35]
Effect on income tax
One of the reasons that people contribute to superannuation is to reduce their income tax liability, and possibly to be able to receive an age pension while still receiving supplementary income.
The following is a general summary of the tax rules relating to superannuation. The full details are extremely complex.
Employer superannuation contributions
Employer superannuation contributions are generally tax deductible if paid to a "complying superannuation fund". This includes compulsory employer contributions as well as "salary sacrifice" contributions. Employees may choose to make additional contributions at the same rate as a "salary sacrifice", but only if their employer agrees to do so.
Taxation of superannuation fund
Employer contributions received by a superannuation fund and income earned in the fund are taxed at the concessional rate of 15%, or more for higher income earners. Additional contributions made without the cooperation of an employer or paid to a non-complying superannuation fund are taxed at the top marginal tax rates and are subject to different rules.
Taxation of Superannuation in America
Under the U.S.-Australia Income Tax Treaty, there is an opportunity to lawfully avoid U.S. taxation on gains within Australian Superannuation Funds.[36][37][38] By taking this legal position, Australia would have exclusive taxing rights over Australian Superannuation Funds, which effectively allows Australian nationals residing in the U.S. to lawfully exclude from their Australian Superannuation Fund from their U.S federal income tax returns any gain within or even future distributions.[39]
Benefits paid
Income retrieved from the fund by a member after preservation age is generally tax free.
Exceeding the concessional contributions cap
The concessional contribution cap for the 2017-2018 financial year is $25,000. For later financial years, the cap is worked out by indexing annually this amount. Excess concessional contribution (ECC) is included in the assessable income for corresponding income year, and the taxpayer is entitled to a tax offset for that income year equal to 15% of the excess concessional contributions (S 291-15 of the Income Tax Assessment Act 1997). This offset cannot be refunded, transferred, or carried forward.
Excess concessional contribution charge
ECC charge is applied to the additional income tax liability arising due to excess concessional contributions included in the income tax return- Division 95 in Schedule 1 to the Taxation Administration Act 1953. The ECC charge period is calculated from the start of the income year in which the excess concessional contributions were made and ends the day before the tax is due to be paid under the first income tax assessment for that year. The compounding interest formula is applied against the base amount (the additional income tax liability) for each day of the ECC charge period. The ECC charge rates are updated quarterly and for January - March 2019 it is 4.94% per annum.
Concessional contributions and taxable income, exceeding the threshold - Division 293 tax
Division 293 tax (additional tax on concessional contributions) is payable if income for surcharge purposes (other than reportable super contributions), plus concessionally taxed super contributions (also known as low tax contributions) are greater than $250,000. Division 293 tax levies 15% tax on either your total concessional contributions, or the amount (Concessional Contributions + Gross Income) that is over the $250,000 threshold – whichever amount is lower.
Non-concessional contributions
Non-concessional contributions include excess concessional contributions for the financial year. They do not include super co-contributions, structured settlements and orders for personal injury or capital gains tax (CGT) related payments that the member has validly elected to exclude from their non-concessional contributions. Non-concessional contributions are made into the super fund from after-tax income. These contributions are not taxed in the super fund. The non-concessional contributions cap is $100,000 for members 65 or over but under 75. Members under 65 years of age will have the option of contributing up to $300,000 over a three-year period depending on their total superannuation balance. If a member’s non-concessional contributions exceed the cap, they are taxed at the top marginal tax rate. [40]
Effect on Age Pensions
Australian resident citizens over 67 years of age are entitled to an Age Pension if their income and assets are below specified levels. The full pension, as at 2014, was $766 every two weeks for singles and $577.40 each for couples. This reduced by 50% of any income over $160 every two weeks for singles or $284 for couples. The pension may also be reduced for 0.15% of assets other than the home over $202,000 or $286,500 for single or couples. The pension is reduced by the maximum of the income and assets test. Assets may also be deemed to earn between 2% and 3% which is counted towards the income test.
Income received from a superannuation fund is considered to be income for pension purposes, and reduces the pension by 50% of the income received that is over the limit. However, if this is received as a "super pension" then the effect on the age pension is discounted by the "cost" of the "super pension". This "cost" is calculated by dividing the total super balance by the life expectancy of the receiver at the time the super pension began. This means that if one withdraws ones super evenly over one's expected life expectancy there is essentially no income test on it. [41]
Assets in a pension fund are deemed to earn income. The assets supporting a "super pension" are also deemed to earn income. (It is difficult to find reliable information on this complex subject, and the above should only be taken as a guide and not relied upon.)
Superannuation funds
Trustee structure
Superannuation funds operate as trusts with trustees being responsible for the prudential operation of their funds and in formulating and implementing an investment strategy. Some specific duties and obligations are codified in the Superannuation Industry (Supervision) Act 1993 - other obligations are the subject of general trust law. Trustees are liable under law for breaches of obligations. Superannuation trustees have, inter alia, an obligation to ensure that superannuation monies are invested prudently with consideration given to diversification and liquidity.
Investments
Other than a few very specific provisions in the Superannuation Industry (Supervision) Act 1993 (largely related to investments in assets related to the employer) funds are not subject to any asset requirements or investment exposure flaws. There are no minimum rate of return requirements, nor a government guarantee of benefits. There are some minor restrictions on borrowing and the use of derivatives and investments in the shares and property of employer sponsors of funds.
As a result, superannuation funds tend to invest in a wide variety of assets with a mix of duration and risk/return characteristics. The recent investment performance of superannuation funds compares favourably with alternative assets such as ten year bonds.
Types of superannuation funds
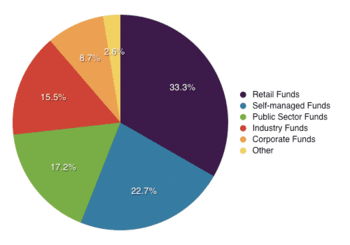
There are about 500 superannuation funds operating in Australia. Of those, 362 have assets totalling greater than $50 million. Superannuation assets totalled $2.7 trillion at the end of the June 2018 quarter, a new record according to the Association of Superannuation Funds of Australia.[42]
There are seven main types of superannuation funds:
- Industry Funds are multiemployer funds run by employer associations and/or unions. Unlike Retail/Wholesale funds they are run solely for the benefit of members, as there are no shareholders.
- Wholesale Master Trusts are multiemployer funds run by financial institutions for groups of employees. These are also classified as Retail funds by APRA.
- Retail Master Trusts/Wrap platforms are funds run by financial institutions for individuals.
- Employer Stand-alone Funds are funds established by employers for their employees. Each fund has its own trust structure that is not necessarily shared by other employers.
- Self Managed Superannuation Funds (SMSFs or Do-It-Yourself Funds) are funds established for a small number of individuals (limited to 4) and regulated by the Australian Taxation Office. Generally the Trustees of the fund are the fund members (where there is a Corporate Trustee, the members are the directors of that company).[43] SMSFs are the most numerous funds in the Australian super industry, with 99% of the number of funds and 31% of the $1.6 trillion total super assets as of 30 June 2013.[44]
Recent changes to the SIS act has allowed SMSFs to borrow under limited recourse borrowing rules. Banks have now developed SMSF loans catering purely for this change to the ACT and to enable SMSF's to borrow for residential property, commercial property and industrial property, however funds cannot acquire vacant land. There are restrictions placed upon the fund that the trustees of the fund cannot gain a personal advantage from asset acquired by the fund, or purchase from what's known as a 'related party'. For example, you would not be able to live in the home that is owned by your SMSF. SMSF loans are generally available to 70% to 80% of the purchase price and attract a slight margin to the interest rate in comparison to standard loans.
- SMSF property investment has gained considerable momentum since the amendment of borrowing provisions to allow for the purchase of residential real estate.[45] The ability to obtain a limited recourse loan to buy income-producing property in a favourably low tax environment has influenced a rapidly emerging incidence of direct property investment within SMSF structures in recent times.
- Small APRA Funds (SAFs) are funds established for a small number of individuals (fewer than 5) but unlike SMSFs the Trustee is an Approved Trustee, not the member/s, and the funds are regulated by APRA. This structure is often used for members who want control of their superannuation investments but are unable or unwilling to meet the requirements of Trusteeship of an SMSF.
- Public Sector Employees Funds are funds established by governments for their employees.
Retail and Wholesale Master Trusts are the largest sector of the Australian Superannuation Market.
Choice of superannuation funds
From 1 July 2005, many Australian employees have been able to choose the fund their employer's future superannuation guarantee contributions are paid into. Employees may change a superannuation fund. They may choose to change funds, for example, because:[46]
- one when their current fund is not available with a new employer,
- consolidate superannuation accounts to cut costs and paperwork,
- a lower-fee and/or better service superannuation fund, or
- a better performing superannuation fund.
Where an employee has not elected to choose their own fund, employers must since 1 January 2014 make "default contributions" only into an authorised MySuper product, which is designed to be a simple, low-cost superannuation fund with few, standardised fees and a single balanced investment option.
Superannuation industry
Legislation
Superannuation funds are principally regulated under the Superannuation Industry (Supervision) Act 1993 and the Financial Services Reform Act 2002. Compulsory employer contributions are regulated via the Superannuation Guarantee (Administration) Act 1992
Superannuation Industry (Supervision) Act 1993 (SIS)
The Superannuation Industry (Supervision) Act sets all the rules that a complying superannuation fund must obey (adherence to these rules is called compliance). The rules cover general areas relating to the trustee, investments, management, fund accounts and administration, enquiries and complaints.
SIS also:
- regulates the operation of superannuation funds; and
- sets penalties for trustees when the rules of operation are not met.
In June 2004 the SIS Act and Regulations were amended to require all superannuation trustees to apply to become a Registrable Superannuation Entity Licensee (RSE Licensee) in addition each of the superannuation funds the trustee operates is also required to be registered. The transition period is intended to end 30 June 2006. The new licensing regime requires trustees of superannuation funds to demonstrate to APRA that they have adequate resources (human, technology and financial), risk management systems and appropriate skills and expertise to manage the superannuation fund. The licensing regime has lifted the bar for superannuation trustees with a significant number of small to medium size superannuation funds exiting the industry due to the increasing risk and compliance demands.
MySuper
MySuper is part of the Stronger Super[47] reforms announced in 2011 by the Julia Gillard Government for the Australian superannuation industry. From 1 January 2014, employers must only pay default superannuation contributions to an authorised MySuper product. Superannuation funds have until July 2017 to transfer accrued default balances to MySuper.
A MySuper default is one which complies to a regulated set of features, including:
- a single investment option (although lifecycle strategies are permitted),
- a minimum level of insurance cover,
- an easily comparable fee structure, with a short prescribed list of allowable fee types,
- restrictions on how advice is provided and paid for, and
- rules governing fund governance and transparency.[48]
The Financial Services Reform Act 2002 (FSR)
The Financial Services Reform Act covers a very broad area of finance and is designed to provide standardisation within the financial services industry. Under the FSR, to operate a superannuation fund, the trustee must have a licence to run a fund and the individuals within the funds require a licence to perform their job.
With regard to superannuation, FSR:
- provides licensing of 'dealers' (providers of financial products and services);
- oversees the training of agents representing dealers;
- sets out the requirements regarding what information must be provided on any financial product to members and prospective members; and
- sets out the requirements that determine good-conduct and misconduct rules for superannuation funds.
Regulatory bodies
Four main regulatory bodies keep watch over superannuation funds to ensure they comply with the legislation:
- The Australian Prudential Regulation Authority (APRA) is responsible for ensuring that superannuation funds behave in a prudent manner. APRA also reviews a fund's annual accounts to assess their compliance with the SIS.
- The Australian Securities and Investments Commission (ASIC) ensures that trustees of superannuation funds comply with their obligations regarding the provision of information to fund members during their membership. ASIC is also responsible for consumer protection in the financial services area (including superannuation). It also monitors funds' compliance with the FSR. MoneySmart is a website run by the Australian Securities and Investments Commission (ASIC) to help people make smart choices about their personal finances. They provide a number of tools such as the Superannuation Calculator.
- The Australian Taxation Office (ATO) ensures that self-managed superannuation funds adhere to the rules and regulations. It also makes sure that the right amount of tax is taken from the superannuation savings of all Australians.
- The Superannuation Complaints Tribunal (SCT) administers the Superannuation (Resolution of Complaints) Act. This Act provides the formal process for the resolution of complaints. The SCT will try to resolve any complaints between a member and the superannuation fund by negotiation or conciliation. The SCT only deals with complaints when no satisfactory resolution has been reached.
Similar schemes in other countries
- Registered Retirement Savings Plan (RRSP) and Tax-Free Savings Account (TSFA) (Canada)[49]
- Individual Retirement Account (IRA) and 401K (United States)
- Self-Invested Personal Pension (SIPP) and Stakeholder Pension (United Kingdom)
- KiwiSaver (New Zealand) – Australia and New Zealand have a reciprocal agreement allowing Australians moving to New Zealand to transfer their KiwiSaver funds to an approved Australian superannuation scheme, and vice versa.[50]
- Nippon Individual Savings Account (NISA) (Japan)
- Mandatory Provident Fund (Hong Kong)[51]
- Vanuatu National Provident Fund (Vanuatu) - The Vanuatu National Provident Fund is a compulsory savings scheme for Employees who receive a salary of Vt3, 000 or more a month, to help them financially at retirement.
- Central Provident Fund (Singapore)[52]
- Employees Provident Fund (Malaysia)[53]
- Pensions in Chile
Criticism
The interaction between superannuation, tax and pension eligibility is complex.[54]
The Australian superannuation industry is under fire for re-investing funds into questionable investments, to benefit related parties ahead of the investor. Thus, a conflict of interest exists with the parent entity re-investing funds into funds related to the parent entity. Thus the best rate of return is never sought out, and the bank or entity investing the money is not seeking the highest rate of return.[55]
Most non-self managed funds only provide very minimal information to the account holders about how their money has been invested. Usually only vague categories are provided, such as "Australian Shares", with no indication of which shares were purchased. This makes the fund's management largely unaccountable to their members.
Losses to the superannuation funds from the global financial crisis have also been a cause for concern, said to be around $75 billion.[56]
Initial financial discussions determined that the Australian economy would be at risk if citizens were allowed to immediately access and withdraw Superannuation, further confirming the belief that mandatory Superannuation may not be a viable long term fiscal management tool. This was compounded by a lack of proper industry regulation, allegations of fraud and financial misconduct and a host of other issues currently plaguing the industry as a whole - "Thousands of superannuation fund members defrauded in Trio Capital scandal"[57]
See also
- Industry superannuation fund
- Australian Government Future Fund
- German pensions
- Pension system
- Social Security (Australia)
- UK pensions
- US pensions
References
- "Liberals slow down SG increase until July 2025". Retrieved 9 December 2015.
- The avoidable super fees stinging almost half Australia’s workforce
- Superannuation Industry (Supervision) Regulations 1994 - Schedule 1, Commonwealth Consolidated Regulations, www.austlii.edu.au, accessed 3 October 2011.
- Office, Australian Taxation. "First Home Super Saver Scheme". www.ato.gov.au. Retrieved 21 August 2019.
- "Superannuation Statistics". The Association of Superannuation Funds of Australia.
- Main, Andrew (20 August 2011). "Paul Keating vision proves a super saviour". The Australian. News Limited.
- Patrick Collinson (2004) Australia may hold key to pensions, The Guardian, 12 October 2004, retrieved 21 July 2006.
- "Chapter 2: Australia's three-pillar system", Retirement Income Strategic Issues Paper, Australian Government, archived from the original on 28 February 2015
- Cook, Trevor (28 March 2012). "Compulsory super: it's good, it works and we want more of it". The Conversation. Archived from the original on 13 September 2015.
- "Super guarantee". Australian Taxation Office. 12 May 2017.
The super guarantee requires employers to provide sufficient super support for their employees. Employers are obliged to contribute a minimum percentage of each eligible employee's earnings (ordinary time earnings) to a complying super fund or retirement savings account (RSA).
- Dinnison, Ian (August 1995). "Australia adds to corporate burden". International Tax Review.
- Keating, Paul (3 September 2014). "This isn't their first superannuation betrayal". Australian Broadcasting Corporation.
- "Super guarantee percentage". Australian Taxation Office. 12 May 2017.
- Section 19 of the Superannuation Guarantee (Administration) Act 1992
- "Super guarantee charge percentage (%)". ato.gov.au. Retrieved 31 December 2013.
- "SUPERANNUATION GUARANTEE (ADMINISTRATION) ACT 1992, Section 21, History". ato.gov.au. Retrieved 31 December 2013.
- Superannuation guarantee: meaning of the terms 'ordinary time earnings' and 'salary or wages'
- "Superannuation Guarantee rate remains at 9.5% for 2015/2016 year". SuperGuide. 21 June 2015. Retrieved 31 October 2015.
- "The great superannuation debate: raise it, freeze it or do away with it altogether". The Guardian. 23 November 2019. ISSN 0261-3077. Retrieved 12 December 2019.
- Office, Australian Taxation. "Guide for employees and self-employed - reportable superannuation contributions". www.ato.gov.au. Retrieved 4 April 2018.
- "Sydney man says Thai rehab clinic saved his life after addiction battle". NewsComAu. 17 November 2019. Retrieved 6 February 2020.
- Office, Australian Taxation. "Lump sum and income stream (pension)". www.ato.gov.au. Retrieved 4 April 2018.
- Office, Australian Taxation. "Preservation of super". www.ato.gov.au. Retrieved 4 April 2018.
- Office, Australian Taxation. "Conditions of release". www.ato.gov.au. Retrieved 4 April 2018.
- DIY Funds and Reasonable Benefit Limits by Ross Stephens, KPMG
- What are RBLs?, Australian Taxation Office, 5 June 2007, accessed 3 October 2011
- RBLs were abolished from 1 July 2007, however there were still RBL obligations for superannuation benefits paid up to 30 June 2007.
Superannuation and reasonable benefit limits, Australian Taxation Office, 4 August 2011, accessed 3 October 2011. - "Division 293 tax - information for individuals". ATO. Retrieved 29 April 2016.
- "What is Superannuation?". MoneyGeek. Retrieved 6 April 2014.
- 2006/07 Estimates of Revenue, 2006-07 Budget, Australian Government, 2006, retrieved 21 July 2006
- Superannuation (Government Co-contribution for Low Income Earners) Act 2003, section 10.
- Tax Laws Amendment (Stronger, Fairer, Simpler and Other Measures) Act 2012, section 12C(b).
- Tax Laws Amendment (Stronger, Fairer, Simpler and Other Measures) Act 2012, section 12E.
- Treasury Laws Amendment (Fair and Sustainable Superannuation) Act.
- Treasury Laws Amendment (Fair and Sustainable Superannuation) Act 2016 section 12E(c).
- "U.S. Tax Treatment of Australian Superannuation Funds". Castro & Co. Retrieved 18 December 2019.
- Castro, John (5 March 2018). "U.S. Tax Treatment of Australian Superannuation". Nevada Law Journal Forum. 2 (1).
- Cochrane, George (9 November 2019). "Franking credit refund mystery explained". The Sydney Morning Herald. Retrieved 28 February 2020.
- Reilly, Peter J. "Wrong Signature Voids Million-Dollar Plus Refund Claim". Forbes. Retrieved 28 February 2020.
- https://www.ato.gov.au/Individuals/Super/
- Newnham, Max (18 February 2010). "Superannuation can affect age pension payments". The Sydney Morning Herald. Retrieved 4 April 2018.
- "Quarterly Superannuation Performance". August 2018. Retrieved 22 May 2019.
- What is a SMSF? SMSF Works. Retrieved on 7 November 2013.
- "Self-managed superannuation funds: A statistical overview 2011-2012 | Australian Taxation Office". Ato.gov.au. 30 June 2012. Retrieved 31 October 2015.
- "Guide To SMSF Property Investment". June 2015. Retrieved 30 June 2015.
- "How to add thousands of dollars a year to your super balance". NewsComAu. 27 August 2019. Retrieved 28 August 2019.
- Federal Government (1 July 2011). "Stronger Super Overview of Reforms". Retrieved 21 February 2013.
- APRA (12 January 2013). "Superannuation reforms 2011-2013". Retrieved 21 February 2013.
- Agency, Canada Revenue. "Registered Retirement Savings Plan (RRSP) - Canada.ca". www.canada.ca. Retrieved 10 October 2018.
- "KiwiSaver - KiwiSaver". www.kiwisaver.govt.nz. Retrieved 10 October 2018.
- "MPFA". www.mpfa.org.hk. Retrieved 10 October 2018.
- "CPFB Members Home". www.cpf.gov.sg. Retrieved 15 October 2018.
- "KWSP - Home - KWSP". www.kwsp.gov.my (in Malay). Retrieved 15 October 2018.
- Super for Dummies
- "The great super scam". Australian Financial Review. Fairfax Media. 13 April 2013. Retrieved 31 October 2015.
- Main, Andrew (22 October 2011). "Markets forcing retirees to work after $75bn paper loss in superannuation". The Australian.
- Ryan, Siobhain (13 April 2011). "Super bailout excludes DIY investors". The Australian.
External links
- ASIC's consumer and investor website MoneySmart - Superannuation and Retirement
- Australian Taxation Office - Superannuation
- Super bailout of $59m - excludes DIY investors
- Government compensates most trio capital losses
- Business Spectator - Legality and Constitutional grounds for Mandatory Superannuation in Australia
- Road Map Release My Super