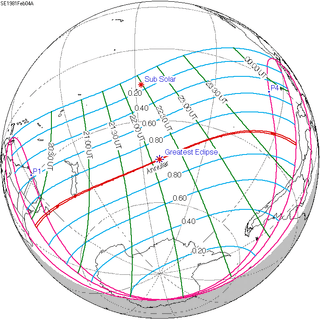
Solar eclipse of February 4, 1981
An annular solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's descending node of the orbit on February 4–5, 1981. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. This annular solar eclipse was large because the Moon covered 99.4% of the Sun, with a path width of only 25 km (15.534 mi, or 82,080.997 feet). It was visible in Australia, crossing over Tasmania and southern Stewart Island of New Zealand near sunrise on February 5th (Thursday), and ended at sunset over western South America on February 4th (Wednesday). Occurring only 4 days before perigee (Perigee on February 8, 1981), the moon's apparent diameter was larger.
| Solar eclipse of February 4, 1981 | |
|---|---|
 Map | |
| Type of eclipse | |
| Nature | Annular |
| Gamma | -0.4838 |
| Magnitude | 0.9937 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Duration | 33 sec (0 m 33 s) |
| Coordinates | 44.4°S 140.8°W |
| Max. width of band | 25 km (16 mi) |
| Times (UTC) | |
| Greatest eclipse | 22:09:24 |
| References | |
| Saros | 140 (27 of 71) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9466 |
The moon's apparent diameter was 7 arcseconds smaller than the July 31, 1981 total solar eclipse.
Related eclipses
Solar eclipses of 1979–1982
This eclipse is a member of a semester series. An eclipse in a semester series of solar eclipses repeats approximately every 177 days and 4 hours (a semester) at alternating nodes of the Moon's orbit.[1] There were 8 solar eclipses between February 26, 1979 and July 20, 1982. Were there: February 26, 1979 (total solar eclipse, 0.8 days after perigee, 103.9%, 0.89811 gamma, saros 120), August 22, 1979 (small annular solar eclipse, 0.6 days before apogee, 93.3%, -0.96319 gamma, saros 125), February 16, 1980 (total solar eclipse, 1 day before perigee, 104.3%, 0.22244 gamma, saros 130), August 10, 1980 (large annular solar eclipse, 5 days before apogee, 97.3%, -0.19154 gamma, saros 135), February 4, 1981 (large annular solar eclipse, 4 days before perigee, 99.4%, -0.48375 gamma, saros 140), July 31, 1981 (total solar eclipse, 3.8 days after perigee, 102.6%, 0.57917 gamma, saros 145), January 25, 1982 (moderate partial solar eclipse, 4.7 days after apogee, 56.6%, -1.23110 gamma, saros 150) and July 20, 1982 (small partial solar eclipse, 0.9 days after perigee, 46.4%, 1.28859 gamma, saros 155).
| Solar eclipse series sets from 1979–1982 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Descending node | Ascending node | |||||
| Saros | Map | Gamma | Saros | Map | Gamma | |
| 120 |  1979 February 26 Total | 0.89811 | 125 |  1979 August 22 Annular | -0.96319 | |
| 130 |  1980 February 16 Total | 0.22244 | 135 |  1980 August 10 Annular | -0.19154 | |
| 140 |  1981 February 4 Annular | -0.48375 | 145 | 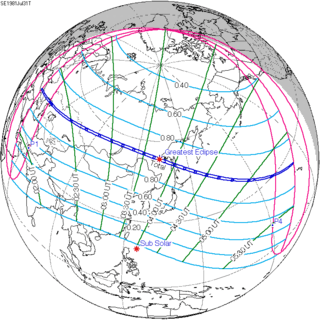 1981 July 31 Total | 0.57917 | |
| 150 | 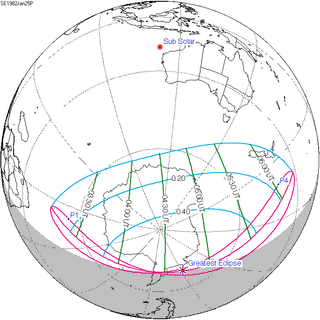 1982 January 25 Partial | -1.23110 | 155 | 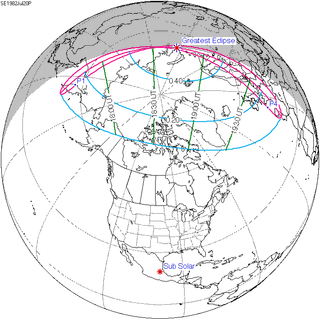 1982 July 20 Partial | 1.28859 | |
| Partial solar eclipses on June 21, 1982 and December 15, 1982 occur in the next lunar year eclipse set. | ||||||
Saros 140
It is a part of Saros cycle 140, repeating every 18 years, 11 days, containing 71 events. The series started with partial solar eclipse on April 16, 1512. It contains total eclipses from July 21, 1656 through November 9, 1836, hybrid eclipses from November 20, 1854 through December 23, 1908, and annular eclipses from January 3, 1927 through December 7, 2485. The series ends at member 71 as a partial eclipse on June 1, 2774. The longest duration of totality was 4 minutes, 10 seconds on August 12, 1692.
| Series members 23–53 occur between 1901 and 2450: | ||
|---|---|---|
| 23 | 24 | 25 |
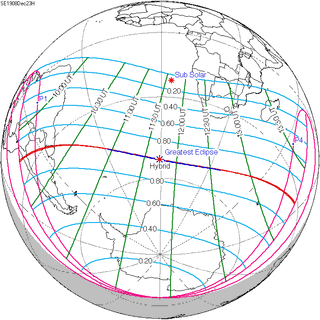 Dec 23, 1908 |
 Jan 3, 1927 |
 Jan 14, 1945 |
| 26 | 27 | 28 |
 Jan 25, 1963 |
 Feb 4, 1981 |
 Feb 16, 1999 |
| 29 | 30 | 31 |
 Feb 26, 2017 |
 Mar 9, 2035 |
 Mar 20, 2053 |
| 32 | 33 | 34 |
 Mar 31, 2071 |
 Apr 10, 2089 |
 Apr 23, 2107 |
| 35 | 36 | 37 |
 May 3, 2125 |
 May 14, 2143 |
 May 25, 2161 |
| 38 | 39 | 40 |
 Jun 5, 2179 |
 Jun 15, 2197 |
 Jun 28, 2215 |
| 41 | 42 | 43 |
 Jul 8, 2233 |
 Jul 19, 2251 |
 Jul 29, 2269 |
| 44 | 45 | 46 |
 Aug 10, 2287 |
 Aug 21, 2305 |
 Sep 1, 2323 |
| 47 | 48 | 49 |
 Sep 12, 2341 |
 Sep 23, 2359 |
 Oct 3, 2377 |
| 50 | 51 | 52 |
 Oct 14, 2395 |
 Oct 25, 2413 |
 Nov 5, 2431 |
| 53 | ||
 Nov 15, 2449 | ||
Tritos series
This eclipse is a part of a tritos cycle, repeating at alternating nodes every 135 synodic months (≈ 3986.63 days, or 11 years minus 1 month). Their appearance and longitude are irregular due to a lack of synchronization with the anomalistic month (period of perigee), but groupings of 3 tritos cycles (≈ 33 years minus 3 months) come close (≈ 434.044 anomalistic months), so eclipses are similar in these groupings.
| Series members between 1901 and 2100 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 September 9, 1904 (Saros 133) |
 August 10, 1915 (Saros 134) |
 July 9, 1926 (Saros 135) | |
 June 8, 1937 (Saros 136) |
 May 9, 1948 (Saros 137) |
 April 8, 1959 (Saros 138) | |
 March 7, 1970 (Saros 139) |
 February 4, 1981 (Saros 140) |
 January 4, 1992 (Saros 141) | |
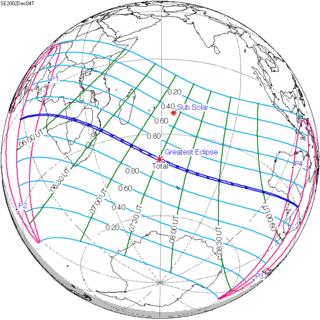 December 4, 2002 (Saros 142) |
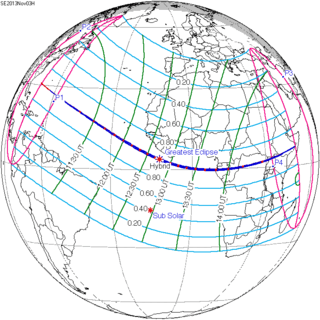 November 3, 2013 (Saros 143) |
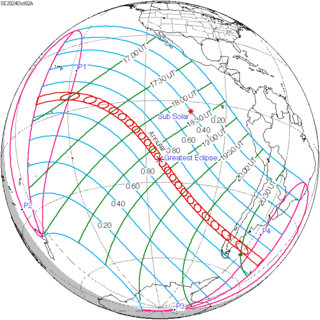 October 2, 2024 (Saros 144) | |
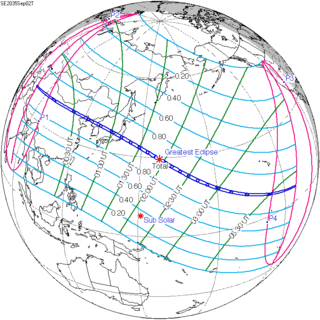 September 2, 2035 (Saros 145) |
 August 2, 2046 (Saros 146) |
 July 1, 2057 (Saros 147) | |
 May 31, 2068 (Saros 148) |
 May 1, 2079 (Saros 149) |
 March 31, 2090 (Saros 150) | |
Metonic series
The metonic series repeats eclipses every 19 years (6939.69 days), lasting about 5 cycles. Eclipses occur in nearly the same calendar date. In addition, the octon subseries repeats 1/5 of that or every 3.8 years (1387.94 days). All eclipses in this table occur at the Moon's descending node.
| 22 eclipse events between September 12, 1931 and July 1, 2011. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| September 11-12 | June 30-July 1 | April 17-19 | February 4-5 | November 22-23 |
| 114 | 116 | 118 | 120 | 122 |
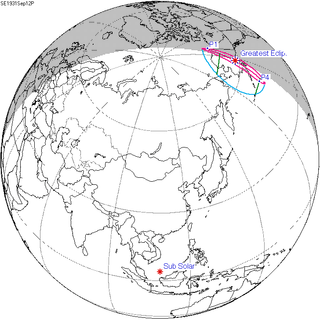 September 12, 1931 |
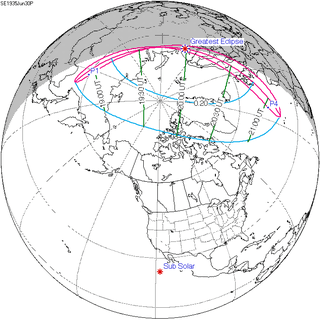 June 30, 1935 |
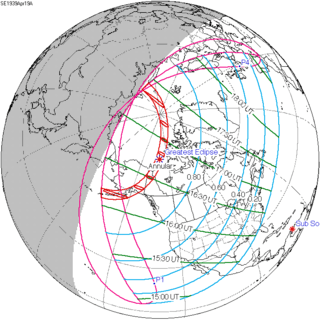 April 19, 1939 |
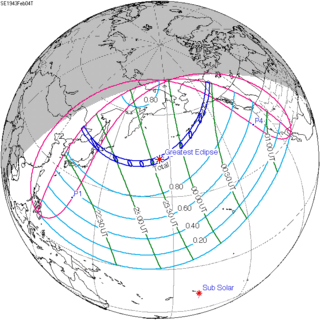 February 4, 1943 |
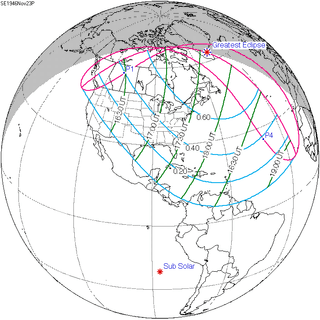 November 23, 1946 |
| 124 | 126 | 128 | 130 | 132 |
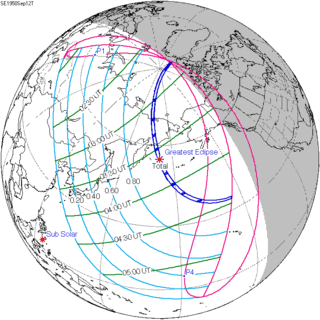 September 12, 1950 |
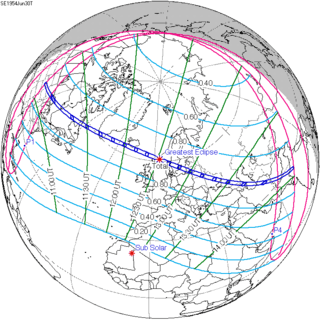 June 30, 1954 |
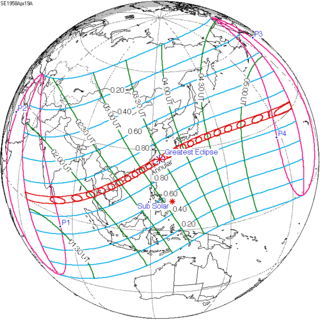 April 19, 1958 |
 February 5, 1962 |
 November 23, 1965 |
| 134 | 136 | 138 | 140 | 142 |
 September 11, 1969 |
 June 30, 1973 |
 April 18, 1977 |
 February 4, 1981 |
 November 22, 1984 |
| 144 | 146 | 148 | 150 | 152 |
 September 11, 1988 |
 June 30, 1992 |
 April 17, 1996 |
 February 5, 2000 |
 November 23, 2003 |
| 154 | 156 | 158 | 160 | 162 |
 September 11, 2007 |
 July 1, 2011 |
April 18, 2015 | February 4, 2019 | November 23, 2022 |
Notes
- van Gent, R.H. "Solar- and Lunar-Eclipse Predictions from Antiquity to the Present". A Catalogue of Eclipse Cycles. Utrecht University. Retrieved 6 October 2018.
References
- Earth visibility chart and eclipse statistics Eclipse Predictions by Fred Espenak, NASA/GSFC
- Annular Solar Eclipse Observed for Solar Radius Determination Observed from Tasmania, by Fiala, A. D., Herald, D., & Dunham, D. W, Bulletin of the American Astronomical Society, Vol. 13, p. 552
- Correcting predictions of solar eclipse contact times for the effects of lunar limb irregularities Observations from Tasmania by Herald, D. Journal of the British Astronomical Association, vol.93, no.6, p. 241–246
.jpg)
