Shinagawa Station
Shinagawa Station (品川駅, Shinagawa-eki) is a major railway station in the Takanawa and Konan districts of Minato, Tokyo, Japan, operated by East Japan Railway Company (JR East), Central Japan Railway Company (JR Central), and the private railway operator Keikyu. The Tokaido Shinkansen and other trains to the Miura Peninsula, Izu Peninsula, and the Tōkai region pass through here. Though a major station in Tokyo, Shinagawa is not served by the Tokyo subway network. However, it is connected to the Toei Asakusa Line via Keikyu through services.
SGWJT03JO17JK20JY25 KK01 Shinagawa Station 品川駅 | |
|---|---|
 Exterior of Shinagawa Station, May 2011 | |
| Location | 3 Takanawa, Minato, Tokyo Japan |
| Coordinates | 35.628157°N 139.739099°E |
| Operated by |
|
| Line(s) |
|
| Connections | Bus terminal |
| Other information | |
| Station code | KK01 (Keikyu) |
| History | |
| Opened | 1872 |
| Location | |
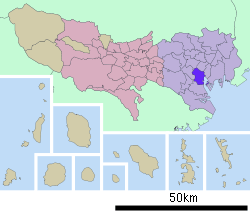
 Shinagawa Station Location within Tokyo  Shinagawa Station Shinagawa Station (Japan) | |
Despite its name, the station is not located in Shinagawa ward. Shinagawa is also commonly used to refer to the business district around the station, which is in Takanawa and Konan neighborhoods of Minato, directly north of Shinagawa ward.
This station is just south of a large yard complex consisting of Shinagawa Carriage Sidings, Shinagawa Locomotive Depot, and Tamachi Depot.
Lines
Shinagawa is served by the following lines:
JR Central
- Tokaido Shinkansen
JR East
- JK Keihin-Tohoku Line
- JT Tokaido Main Line
- JY Yamanote Line
- JO Yokosuka Line
Keikyu
- Keikyu Main Line
JR Central announced in 2011 that Shinagawa will be the terminal for the Chūō Shinkansen, a maglev line under construction and scheduled to begin service to Nagoya in 2027.
Station layout
The main JR station concourse is situated above the platforms running east–west across the breadth of the station. A freely traversable walkway divides the station into two sections. The southerly section contains a number of shops and market-style stalls which form the "e-cute" station complex.
Cross-platform interchange between the Yamanote and Keihin-Tohoku lines is only available from two stations north of this one, Tamachi.
The Keikyu platforms are on the western side of the station at a higher level than the JR platforms. Some Keikyu trains terminate at Shinagawa while others continue on to join the Toei Asakusa Line at Sengakuji.
The Shinkansen platforms were opened on October 1, 2003, to relieve congestion at Tokyo Station. Platforms are on the east side of the station.
JR platforms
| 1 | JY Yamanote Line | for Tokyo, Ueno, and Tabata |
| 2 | JY Yamanote Line | for Shibuya, Shinjuku, and Ikebukuro |
| 3 | ■ Special platform | Temporarily closed |
| 4 | JK Keihin-Tōhoku Line | for Tokyo, Ueno, and Ōmiya |
| 5 | JK Keihin-Tōhoku Line | for Kamata, Yokohama JK Negishi Line for Sakuragichō, and Ōfuna |
| 6-7 | JT Tōkaidō Main Line | for Tokyo JU Utsunomiya Line for Ueno, Ōmiya, Utsunomiya JU Takasaki Line for Takasaki |
| 8 | JJ Ueno–Tokyo Line | Jōban Line for Toride and Katsuta |
| 9 | ■ Ueno–Tokyo Line | Jōban Line Ltd. Express Hitachi/Tokiwa for Iwaki |
| 10-11 | JJ Ueno–Tokyo Line | Jōban Line for Matsudo, Toride, Katsuta, and Narita |
| 11-12 | JT Tōkaidō Main Line | for Kawasaki, Yokohama, Odawara, Atami JT Ito Line for Ito |
| 13-14 | JO Yokosuka Line | for Tokyo JO Sobu Line for Funabashi, Chiba, and Narita Airport (Terminal 2·3 and Terminal 1) |
| ■ Limited express Narita Express for Narita Airport | ||
| 14-15 | JO Yokosuka Line | for Musashi-Kosugi, Yokohama, Ōfuna, and Kurihama |
 The JR Yamanote line platforms, 2020
The JR Yamanote line platforms, 2020
Adjacent stations
| « | Service | » | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tōkaidō Line JT03 | ||||
| Yokohama YHMJT05 |
Saphir Odoriko | Tokyo TYOJT01 | ||
| Kawasaki KWSJT04 |
Odoriko | Tokyo TYOJT01 | ||
| Ōfuna OFNJT07 |
Commuter Rapid | Shimbashi SMBJT02 | ||
| Kawasaki KWSJT04 |
Rapid Acty | Shimbashi SMBJT02 | ||
| Kawasaki KWSJT04 |
Local | Shimbashi SMBJT02 | ||
| Tōkaidō Line-(via Ueno-Tokyo Line)-Jōban Line (Rapid)JT03 | ||||
| Tōkaidō Line-(via Ueno-Tokyo Line)-Jōban Line JT03 | ||||
| Terminus | Hitachi/Tokiwa | Tokyo TYOJT01 | ||
| Terminus | Special Rapid | Shimbashi SMBJT02 | ||
| Terminus | Rapid[Note 1] | Shimbashi SMVJT02 | ||
| Yokosuka Line JO17 | ||||
| Musashi-Kosugi MKGJO15 Shibuya SBYJS19 |
Narita Express | Tokyo TYOJO19 | ||
| Nishi-Ōi JO16 | Local | Shimbashi SMBJO18 | ||
| Keihin-Tōhoku Line JK20 | ||||
| Ōimachi JK19 | Rapid | Takanawa Gateway TGWJK21 | ||
| Ōimachi JK19 | Local | Takanawa Gateway TGWJK21 | ||
| Yamanote Line JY25 | ||||
| Ōsaki OSKJY24 |
- | Takanawa Gateway TGWJY26 | ||
- including medium distance local trains
Shinkansen platforms
| 21, 22 | ■ Tokaido Shinkansen | for Tokyo |
| 23, 24 | ■ Tokaido Shinkansen | for Nagoya, Shin-Osaka, and Hakata |
Adjacent stations
| « | Service | » | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tokaido Shinkansen | ||||
| Tokyo | Nozomi | Shin-Yokohama | ||
| Tokyo | Hikari | Shin-Yokohama | ||
| Tokyo | Kodama | Shin-Yokohama | ||
Keikyu platforms
| 1 | KK Keikyu Main Line | for Keikyū Kawasaki, Keikyū Kamata, Yokohama, Uraga KK Keikyū Airport Line for Haneda Airport (Terminal 3 and Terminal 1·2) KK Keikyū Kurihama Line for Miurakaigan |
| 2 | KK Keikyu Main Line | for Sengakuji A Toei Asakusa Line for Shimbashi, Nihombashi, and Asakusa KS Keisei Main Line for Narita Airport (Terminal 2·3 and Terminal 1) HS Hokuso Railway for Imba-Nihon-Idai KS Narita Sky Access Line for Narita Airport |
| 3 | KK Keikyū Main Line | for Keikyū Kurihama and Misakiguchi (Keikyu Wing) |
| KK Keikyu Main Line | for Kitashinagawa, Samezu (local trains in mornings only) |
 Keikyu platforms
Keikyu platforms
Adjacent stations
| « | Service | » | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Keikyu Main Line KK01 | ||||
| Sengakuji A07 | Morning Wing (Inbound) | Kamiōoka KK44 | ||
| Terminus | Keikyu Wing (Outbound) | Kamiōoka KK44 | ||
| Sengakuji A07 | Airport Limited Express | Haneda Airport Terminal 3 KK16 | ||
| Sengakuji A07 | Limited Express (Kaitoku) | Keikyū Kamata KK11 | ||
| Sengakuji A07 | Limited Express (Tokkyū) | Aomono-yokochō KK04 | ||
| Sengakuji A07 | Airport Express | Aomono-yokochō KK04 | ||
| Terminus | Local | Kitashinagawa KK02 | ||
History


Shinagawa is one of Japan's oldest stations, opened on June 12, 1872, when the service between Shinagawa and Yokohama provisionally started, four months before the inauguration of "Japan's first railway" between Shimbashi and Yokohama through Shinagawa on October 14, 1872. This line is a part of the Tōkaidō Main Line. Nothing remains of the original structure.
Later on March 1, 1885, the Yamanote Line started operation. Takanawa station of the Keikyu Line (then Keihin Railway Line) opened on March 11, 1924 across the street from Shinagawa station. Takanawa station was renamed Shinagawa station and moved to the current site on April 1, 1933.
The station concourse on the eastern side of the station (located above the platforms) was extensively redeveloped in 2003 in connection with the construction of the Shinkansen platforms and also to improve access to the new commercial development "Shinagawa Intercity".
Passenger statistics
In fiscal 2017, the JR East station was used by an average of 378,566 passengers daily (boarding passengers only), making it the fifth-busiest station operated by JR East.[1] The passenger figures for previous years are as shown below.
| Fiscal year | Daily average |
|---|---|
| 2000 | 253,575[2] |
| 2005 | 302,862[3] |
| 2010 | 321,711[4] |
| 2011 | 323,893[5] |
| 2012 | 329,679[6] |
| 2013 | 335,661[7] |
| 2014 | 342,458[8] |
| 2015 | 361,466[9] |
| 2016 | 371,787[10] |
| 2017 | 378,566[1] |
Surrounding area
West side (Takanawa Exit)
- Takanawa Keikyu Hotel
- Takanawa Tobu Hotel
- Grand Prince Hotel Takanawa
- Shinagawa Prince Hotel
- Aqua Park Shinagawa
- National Route 15
East side (Konan Exit)
- Shinagawa Inter City
- Tokyo University of Marine Science and Technology
Bus services
Services are provided by Toei Bus, Tokyu Bus, Keikyu Bus, Airport Transport Service, and others.
References
- 各駅の乗車人員 (2017年度) [Station passenger figures (Fiscal 2017)] (in Japanese). Japan: East Japan Railway Company. Retrieved 4 June 2019.
- 各駅の乗車人員 (2000年度) [Station passenger figures (Fiscal 2000)] (in Japanese). Japan: East Japan Railway Company. Retrieved 24 September 2012.
- 各駅の乗車人員 (2005年度) [Station passenger figures (Fiscal 2005)] (in Japanese). Japan: East Japan Railway Company. Retrieved 24 September 2012.
- 各駅の乗車人員 (2010年度) [Station passenger figures (Fiscal 2010)] (in Japanese). Japan: East Japan Railway Company. Retrieved 24 September 2012.
- 各駅の乗車人員 (2011年度) [Station passenger figures (Fiscal 2011)] (in Japanese). Japan: East Japan Railway Company. Retrieved 31 August 2014.
- 各駅の乗車人員 (2012年度) [Station passenger figures (Fiscal 2012)] (in Japanese). Japan: East Japan Railway Company. Retrieved 31 August 2014.
- 各駅の乗車人員 (2013年度) [Station passenger figures (Fiscal 2013)] (in Japanese). Japan: East Japan Railway Company. Retrieved 31 August 2014.
- 各駅の乗車人員 (2014年度) [Station passenger figures (Fiscal 2014)] (in Japanese). Japan: East Japan Railway Company. Retrieved 4 June 2019.
- 各駅の乗車人員 (2015年度) [Station passenger figures (Fiscal 2015)] (in Japanese). Japan: East Japan Railway Company. Retrieved 4 June 2019.
- 各駅の乗車人員 (2016年度) [Station passenger figures (Fiscal 2016)] (in Japanese). Japan: East Japan Railway Company. Retrieved 4 June 2019.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Shinagawa Station. |
- Shinagawa Station information (JR East) (in Japanese)
- Shinagawa Station information (JR Central) (in Japanese)
- Shinagawa Station information (Keikyu) (in Japanese)