Shonan Monorail
The Shonan Monorail (湘南モノレール, Shōnan Monorēru) is a suspended SAFEGE monorail in the cities of Kamakura and Fujisawa in Kanagawa Prefecture, Japan. It is operated by the Shonan Monorail Co., Ltd. (湘南モノレール株式会社, Shōnan Monorēru Kabushiki-gaisha), and opened on March 7, 1970, the first monorail of its kind in Japan.[1]
 A 5000 series train in August 2008 | |||
| Overview | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Locale | Kanagawa Prefecture | ||
| Transit type | Suspension railway | ||
| Number of lines | 1 | ||
| Number of stations | 8 | ||
| Operation | |||
| Began operation | March 7, 1970 | ||
| Operator(s) | Shonan Monorail Co, Ltd Wholly owned subsidiary of Michinori Holdings; formerly part of Mitsubishi Group | ||
| Technical | |||
| System length | 6.6 km | ||
| Minimum radius of curvature | 90 m (295 ft) | ||
| Electrification | 1,500 V DC | ||
| Top speed | 75 km/h (45 mph) | ||
| |||
The train is used by commuters that work in Tokyo or Yokohama, tourists visiting Enoshima, and, in summer months, city dwellers who are visiting the parks or baths of Enoshima.[2]
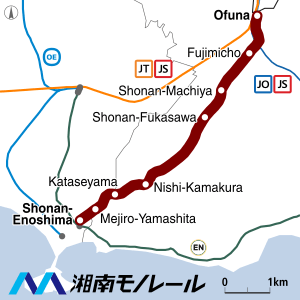
Enoshima Line (江の島線, Enoshima-sen) travels 6.6 km (4.1 mi) every seven to eight minutes between Ōfuna Station and Enoshima, making six stops.[1] The average length of a single trip is 14 minutes.[3] The line includes two tunnels (between Shōnan-Fukasawa and Nishi-Kamakura stations, and between Mejiroyamashita and Shōnan-Enoshima stations).[4]
History
The monorail was built by Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, and the line opened March 7, 1970 between Ōfuna and Nishi-Kamakura. The rest of the line opened on July 1, 1971.[1]
Stations
| Station | Distance (km) |
Transfers | Location | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ōfuna | 0.0 | Kamakura | Kanagawa Prefecture | |
| Fujimichō* | 0.9 | |||
| Shōnan-Machiya | 2.0 | |||
| Shōnan-Fukasawa* | 2.6 | |||
| Nishi-Kamakura* | 4.7 | |||
| Kataseyama | 5.5 | |||
| Mejiroyamashita* | 6.2 | Fujisawa | ||
| Shōnan-Enoshima | 6.6 |
| ||
* Track switching possible at these stations
Rolling stock
- 5000 series 3-car sets (since 2004)
As of July 2016, the line is operated using a fleet of seven three-car aluminium-bodied 5000 series trainsets.[5] The 5000 series is equipped with a VVVF control device and regenerative brake which allows for smooth acceleration and deceleration. The VVVF inverter control reduces the need for inspection and maintenance because unlike a DC motor, there is no commutator brush or contact switch.[6]
 A 5000 series set in October 2009
A 5000 series set in October 2009
Former
 A 400 series set in 2004
A 400 series set in 2004- A 500 series set in April 2008
- 300 series 2/3-car sets (from March 1970 until July 1992)
- 400 series (from 1980 until July 2004)
- 500 series 3-car sets (from 1988 until June 2016)
Services were initially operated using a fleet of six two-car 300 series trainsets built by Mitsubishi Heavy Industries.[1] Two sets were increased to three cars from February 1975 to provide additional capacity.[1] The last of the 300 series sets were withdrawn by July 1992, following the introduction of new 500 series trains.[7] The 500 series trains introduced in 1988 were the first air-conditioned trains on the line.[1] The last 500 series train was withdrawn after its last day in service on 26 June 2016.[5]
See also
- Monorails in Japan
- List of rapid transit systems
References
- Terada, Hirokazu (19 January 2013). データブック日本の私鉄 [Databook: Japan's Private Railways] (in Japanese). Japan: Neko Publishing. p. 80. ISBN 978-4-7770-1336-4.
- "Shonan and Enoden". Retrieved 2007-09-02.
- "Sarukoen 猿公園: July 2007 Archives". Retrieved 2007-09-02.
- "Kamakura-Enoshima Shonan Monorail". Kamakura-Enoshima Shonan Monorail (in Japanese). Retrieved 2019-09-05.
- 湘南モノレール500形が引退 [Shonan Monorail 500 series withdrawn]. Japan Railfan Magazine Online (in Japanese). Japan: Koyusha Co., Ltd. 27 June 2016. Archived from the original on 23 July 2016. Retrieved 23 July 2016.
- "環境保全 | 江の島への近道 湘南モノレール株式会社". www.shonan-monorail.co.jp. Retrieved 2019-09-05.
- 湘南モノレール 300形 [Shonan Monorail 300 series]. Tetsudo Hobidas (in Japanese). Japan: Neko Publishing Co., Ltd. 16 February 2016. Retrieved 21 February 2016.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Shōnan Monorail. |
- Company website (in Japanese)
35°21′08″N 139°31′53″E(Ōfuna)35°18′43″N 139°29′16″E(Shōnan-Enoshima)