Karasuyama Line
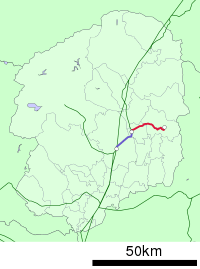
The Karasuyama Line (烏山線, Karasuyama-sen) is a railway line in Tochigi Prefecture, Japan, owned and operated by East Japan Railway Company (JR East). It connects Hōshakuji in the town of Takanezawa with Karasuyama in Nasukarasuyama.
| Karasuyama Line | |||
|---|---|---|---|
An EV-E301 series BEMU on the Karasuyama Line in March 2015 | |||
| Overview | |||
| Type | Regional rail | ||
| System | JR East | ||
| Locale | Tochigi Prefecture | ||
| Termini | Hōshakuji Karasuyama | ||
| Stations | 8 | ||
| Operation | |||
| Opened | 15 April 1923 | ||
| Owner | JR East | ||
| Rolling stock | EV-E301 series BEMU | ||
| Technical | |||
| Line length | 20.4 km (12.7 mi) | ||
| Number of tracks | 1 | ||
| Track gauge | 1,067 mm (3 ft 6 in) | ||
| Electrification | None | ||
| |||
Services
Trains run approximately once every hour, traveling the entire length of the line. Some trains travel through onto the Utsunomiya Line (Tohoku Main Line) to Utsunomiya Station.
Stations
| Station | Japanese | Distance (km) | Transfers | Location | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Between stations |
Total | ||||
| Hōshakuji | 宝積寺 | - | 0.0 | JU Utsunomiya Line (Some through trains to Utsunomiya Station) | Takanezawa, Shioya District |
| Shimotsuke-Hanaoka | 下野花岡 | 3.9 | 3.9 | ||
| Niita | 仁井田 | 2.0 | 5.9 | ||
| Kōnoyama | 鴻野山 | 2.4 | 8.3 | Nasukarasuyama | |
| Ōgane | 大金 | 4.4 | 12.7 | ||
| Kobana | 小塙 | 2.6 | 15.3 | ||
| Taki | 滝 | 2.2 | 17.5 | ||
| Karasuyama | 烏山 | 2.9 | 20.4 | ||
Rolling stock
- EV-E301 series BEMU (since 15 March 2014)
From the start of the revised timetable on 15 March 2014, a new EV-E301 series two-car battery electric multiple unit (BEMU) was introduced on the Karasuyama Line and Tohoku Main Line between Utsunomiya and Karasuyama.[1] Developed from the experimental "Smart Denchi-kun" battery electric railcar also tested on this line since 2012, the EV-E301 series train is recharged at a special recharging facility built at Karasuyama Station, and operates on battery power over the non-electrified Karasuyama Line tracks.[2]
All of the remaining KiHa 40 series diesel trains used on the line were withdrawn on 3 March 2017, and replaced with EV-E301 series battery electric units from the start of the revised timetable on 4 March 2017.[3]
 EV-E301 series BEMU set
EV-E301 series BEMU set
Former rolling stock
- KiHa 40 series DMUs (until 3 March 2017)
 A KiHa 40-1000 series DMU in January 2011
A KiHa 40-1000 series DMU in January 2011
History
The line opened on 15 April 1923.[4] With the privatization of Japanese National Railways (JNR) on 1 April 1987, the line came under the control of JR East.[4]
Wanman driver only operation commenced on the line on 10 March 1990, using KiHa 40 series DMUs.[5]
References
- 烏山線でEV-E301系が営業運転を開始 [EV-E301 series enters revenue service on Karasuyama Line]. Japan Railfan Magazine Online (in Japanese). Japan: Koyusha Co., Ltd. 16 March 2014. Retrieved 17 March 2014.
- JR東日本 烏山線に新型蓄電池電車導入 [JR East to introduce new battery train on Karasuyama Line]. Tetsudo Hobidas (in Japanese). Japan: Neko Publishing Co., Ltd. 6 November 2012. Retrieved 6 November 2012.
- JR烏山線のディーゼル車「キハ40形」 「たらこ色」の車両ラストラン [Last run on JR Karasuyama Line for red KiHa 40 diesel cars]. Sankei News (in Japanese). Japan: The Sankei Shimbun & Sankeu Digital. 4 March 2017. Archived from the original on 4 March 2017. Retrieved 4 March 2017.
- Ishino, Tetsu, ed. (1998). 停車場変遷大辞典 国鉄・JR編 [Station Transition Directory - JNR/JR] (in Japanese). I. Japan: JTB. p. 106. ISBN 4-533-02980-9.
- JR気動車客車編成表 '04年版 [JR DMU & Coaching Stock Formations - 2004]. Japan: JRR. 1 July 2004. p. 197. ISBN 4-88283-125-2.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Karasuyama Line. |
- JR East Karasuyama Line information (in Japanese)
.svg.png)