Ram Nath Kovind
Ram Nath Kovind (born 1 October 1945) is an Indian politician serving as the 14th and current President of India since 25 July 2017.[2] Previously he had served as the 26th Governor of Bihar from 2015 to 2017[3][4] and was a Member of Parliament, Rajya Sabha from 1994 to 2006. Kovind was nominated as a presidential candidate by the ruling NDA coalition and won the 2017 presidential election.[5]
Ram Nath Kovind | |
|---|---|
 | |
| 14th President of India | |
| Assumed office 25 July 2017[1] | |
| Prime Minister | Narendra Modi |
| Vice President | Mohammad Hamid Ansari M. Venkaiah Naidu |
| Preceded by | Pranab Mukherjee |
| 26th Governor of Bihar | |
| In office 16 August 2015 – 20 June 2017 | |
| Chief Minister | Nitish Kumar |
| Preceded by | Keshari Nath Tripathi |
| Succeeded by | Keshari Nath Tripathi |
| Member of Parliament, Rajya Sabha | |
| In office 3 April 1994 – 2 April 2006 | |
| Preceded by | Subramanian Swamy |
| Succeeded by | Vinay Katiyar |
| Constituency | Uttar Pradesh |
| Personal details | |
| Born | 1 October 1945[1] Paraunkh, United Provinces, British India (present-day Uttar Pradesh, India) |
| Nationality | Indian |
| Political party | Bharatiya Janata Party |
| Other political affiliations | National Democratic Alliance |
| Spouse(s) | |
| Children | 2 |
| Residence | Rashtrapati Bhavan, New Delhi |
| Alma mater | Kanpur University (B.Com, LL.B.) |
Before entering politics, he was a lawyer for 16 years and practised in the Delhi High Court and the Supreme Court until 1993.[6]
Early life and education
Ram Nath Kovind was born on 1 October 1945, in Paraunkh village in the Kanpur Dehat district of Uttar Pradesh, as the youngest of five brothers and two sisters. His father Maikulal Kovind ran a small shop. Kovind was born in a mud hut, which eventually collapsed. He was only five when his mother died of burns when their thatched dwelling caught fire. Kovind later donated the land to the community.[7] Kovind was born into the Kori caste, considered underprivileged even among the Dalits.[8]
After his elementary school education, he had to walk each day to Kanpur village, 8 km away, to attend junior school, as nobody in the village had a bicycle.[9] He holds a bachelor's degree in commerce and an LLB from DAV College (affiliated with Kanpur University).[10][11][12]
Early Career

Advocate
After graduating in law from DAV College, Kanpur, Kovind went to Delhi to prepare for the civil services examination. He passed this exam on his third attempt, but he did not join because he had only scored high enough to work in an allied service rather than in IAS and thus started practising law.[13]
Kovind enrolled as an advocate in 1971 with the bar council of Delhi. He was Central Government Advocate in the Delhi High Court from year 1977 to year 1979. Between 1977 & 1978, he also served as the personal assistant of Prime Minister of India Morarji Desai.[14] In 1978, he became an advocate-on-record of the Supreme Court of India and served as a standing counsel for the Central Government in the Supreme Court of India from 1980 to 1993. He practised in the Delhi High Court and Supreme Court until 1993. As an advocate, he provided pro-bono aid to weaker sections of society, women and the poor under the Free Legal Aid Society of New Delhi.[10]
BJP member
He joined the BJP in 1991.[14] He was President of the BJP Dalit Morcha between 1998 and 2002 and President of the All-India Koli Samaj. He also served as national spokesperson of the party.[15] He donated his ancestral home in Derapur to the Rashtriya Swayamsevak Sangh.[14] Soon after joining the BJP, he contested for Ghatampur assembly constituency, but lost and later contested for Bhognipur (in 2007) (both in Uttar Pradesh) assembly constituency on the BJP ticket but lost again.[16]
In 1997, Kovind joined the protest against certain orders from the Central government that had adverse effects on the SC/ST workers. Later, three amendments were made to the Constitution that revoked the orders, by the NDA government headed by Atal Bihari Vajpayee.[17]
Rajya Sabha
He was elected and became a Rajya Sabha MP from the state of Uttar Pradesh in April 1994. He served a total of twelve years, two consecutive terms, until March 2006. As a member of parliament, he served on the Parliamentary Committee for Welfare of Scheduled Castes/Tribes, Home Affairs, Petroleum and Natural Gas, Social Justice and Empowerment, Law and Justice. He also served as the chairman of the Rajya Sabha House Committee. During his career as a parliamentarian, under the Members of Parliament Local Area Development Scheme, he focused on education in rural areas by helping in construction of school buildings in Uttar Pradesh and Uttrakhand. As a member of parliament, he visited Thailand, Nepal, Pakistan, Singapore, Germany, Switzerland, France, the United Kingdom, and the United States on study tours.[11]
Other appointments
He has served on the Board of management of Dr. B.R Ambedkar University, Lucknow, and as on the Board of Governors of IIM Calcutta. He has also represented India at the UN and addressed the United Nations General Assembly in October 2002.[18]
Governor
On 8 August 2015, the then President of India appointed Kovind as Governor of Bihar.[19] On 16 August 2015, the acting Chief Justice of Patna High Court, Iqbal Ahmad Ansari, administered the oath to Kovind as the 35th Governor of Bihar. The function took place at Raj Bhawan, Patna.[20]

Kovind's appointment was criticised by then Chief Minister of Bihar Nitish Kumar as it came months before State Assembly elections and the appointment was made without consulting State Government as recommended by Sarkaria Commission.[21] However, Kovind's term as Governor, was praised for constituting a judicial commission to investigate irregularities in promotion of undeserving teachers, mis-management of funds and appointment of undeserving candidates in universities.[14] In June 2017, when Kovind was announced as candidate for Presidential election, Nitish Kumar backed Kovind's choice and praised Kovind as being unbiased and working closely with the State Government during his Governorship.[22]
2017 presidency campaign
After nomination for the post of 14th President of India, he resigned from his post as Governor of Bihar, and President of India Pranab Mukherjee accepted his resignation on 20 June 2017.[23] He won election on 20 July 2017.[24]
Ram Nath Kovind received 65.65% of the valid votes, against former Speaker of the Lok Sabha - Meira Kumar, the presidential candidate of the Opposition who received 34.35% of the total votes. Kovind received 2,930 votes (From MPs and MLAs) amounting to Electoral College votes of 702,044 (65.65%) as compared to 1,844 votes with a value of 367,314 (34.35%) votes for Meira Kumar lagging far behind with 367,314 votes, and 77 votes were invalid.[25] He became only the second Dalit representative to become President after K. R. Narayanan, and also is the first BJP candidate to be elected to the post.[26] The tally of votes (367,314) polled by Meira Kumar is only the second highest for a losing candidate, that of Neelam Sanjiva Reddy in the 1969 Presidential elections being the highest ever; he received 405,427 votes as against 420,077 by V V Giri, the winner.
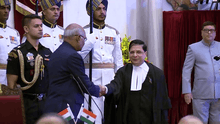
14th President of India

Ram Nath Kovind took the oath as the 14th President of India on 25 July 2017.[27] He is the first leader from Rashtriya Swayamsevak Sangh to occupy the Office of President of India.[28]

List of international trips as president
Kovind made trips to 19 different countries, each for state visit.
| Year | Country | Areas Visited | Date(s) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | Djibouti City | 3–4 October | [29][30] | |
| Addis Ababa | 5–6 October | [31][32][33] | ||
| 2018 | Port Louis | 11–14 March | [34][35] | |
| Antananarivo | 14–15 March | [34] | ||
| Malabo | 7–9 April | [36] | ||
| Mbabane | 9–10 April | [37] | ||
| Lusaka | 10–12 April | [38][39] | ||
| Athens | 16–19 June | [40][41] | ||
| Paramaribo | 19–21 June | [41][42] | ||
| Havana | 21–23 June | [43][44] | ||
| Nicosia | 2–4 September | [45] | ||
| Sofia | 4–6 September | [45] | ||
| Prague | 6–9 September | [45] | ||
| Dushanbe | 7–9 October | [46] | ||
| Da Nang, Hanoi | 18–21 November | [47][48] | ||
| Sydney, Melbourne | 21–24 November | [47][49] | ||
| 2019 | Zagreb, Croatia | 25–27 March | [50] | |
| Santa Cruz de la Sierra, Bolivia | 28–30 March | [51] | ||
| Santiago, Chile | 30 March – 1 April | [52] |
Personal life
Kovind married Savita Kovind on 30 May 1974. They have a son, Prashant Kumar, and a daughter, Swati Kovind who was an air hostess for Air India.[12][53]. He is a long time practitioner of Heartfulness Meditation. In Feb 2020 he along with his wife inaugurated the new global headquarters 'Kanha Shanti Vanam' of Shri Ram Chandra Mission near Hyderabad, India[54].
Controversy
In 2010, he was reported to have said that "Islam and Christianity are alien to the nation" as spokesperson of the BJP.[55][56] As reported by IANS and published by Hindustan Times, he made this comment in response to the Ranganath Misra Commission which recommended 15 percent reservation for religious and linguistic minorities in government jobs.[57] Although more recently, the issue was raised in the media if whether or not he was misquoted and that he in fact said "Islam and Christianity are alien to the notion (of caste)" as opposed to what was reported as "nation".[58][59]
State honours
| Decoration | Country | Date | Note | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14 March 2018 | The highest civilian honour of Madagascar; in the category of Grand Cross 2nd Class, the highest class that may be bestowed upon foreign dignitaries. | [60] | ||
| 8 April 2018 | Degree of Collar. | [61] | ||
| 9 April 2018 | The highest civilian honour of Eswatini | [62] | ||
| 26 March 2019 | The highest civilian honour of Croatia | [63] | ||
| 26 March 2019 | Grand Collar, The highest civilian honour of Bolivia. | [64] | ||
| 3 August 2019 | Grand Cross The highest civilian honour of Guinea. | [65] | ||
References
- "The President of India". presidentofindia.gov.in. National Informatics Centre. Retrieved 19 July 2020.
- "Ram Nath Kovind takes oath: In inaugural speech, president outlines vision for India as world leader". Firstpost. 25 July 2017. Archived from the original on 2 August 2017. Retrieved 2 August 2017.
- "Press Releases Detail – The President of India". presidentofindia.nic.in. Archived from the original on 27 August 2017.
- Ram Nath Kovind resigns as Bihar Governor (20 June 2017). "Ram Nath Kovind resigns as Bihar Governor". The Hindu. Archived from the original on 8 October 2017. Retrieved 20 June 2017.
- Huizhong Wu (20 July 2017). "Man from India's lowest caste elected president". CNN. Archived from the original on 21 July 2017.
- "Bihar Governor Ram Nath Kovind is NDA nominee for President". The Hindu. The Hindu. 19 June 2017. Archived from the original on 24 June 2017. Retrieved 23 July 2017.
- "कानपुर से ग्राउंड रिपोर्ट : रामनाथ कोविंद के गांव में जश्न, लोग गा रहे हैं- मेरे बाबा की भई सरकार". Archived from the original on 21 July 2017. Retrieved 24 August 2017.
- Najar, Nida (20 July 2017). "India Picks Ram Nath Kovind, ' as President". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved 11 June 2019.
- Tiwari, Vaibhav (20 June 2017). "NDA Presidential nominee Ram Nath Kovind would walk 8 km daily for school". India.com. Archived from the original on 30 July 2017. Retrieved 25 July 2017.
- PTI (19 June 2017). "Ram Nath Kovind: A crusader for the rights of weaker sections". The Economic Times. Archived from the original on 27 August 2017. Retrieved 19 June 2017.
- "Bihar governor Ram Nath Kovind: 10 facts about NDA's Presidential nominee – Times of India". The Times of India. Archived from the original on 27 August 2017. Retrieved 19 June 2017.
- "Governor of Bihar". governor.bih.nic.in. Archived from the original on 3 July 2017. Retrieved 20 June 2017.
- PTI (19 June 2017). "What you should know about BJP's presidential candidate Ram Nath Kovind". Archived from the original on 18 July 2017 – via The Economic Times.
- "Ram Nath Kovind, a lawyer who cracked civils but lost 2 elections – Times of India". The Times of India. Archived from the original on 18 July 2017. Retrieved 20 June 2017.
- "Enact tougher laws to prevent crimes against dalits". The Hindu. 19 January 2003. Archived from the original on 4 October 2011.
- "Ram Nath Kovind, a lawyer who cracked civils but lost 2 elections". Times of India. 20 June 2017. Archived from the original on 18 July 2017. Retrieved 24 July 2017.
- "Ram Nath Kovind is BJP's choice for president: All you need to know about the Dalit leader from UP". Firstpost. 20 July 2017. Archived from the original on 24 July 2017.
- "Ramnath Kovind Profile". Outlook. 19 June 2017. Archived from the original on 27 August 2017. Retrieved 20 June 2017.
- PTI (8 August 2015). "Ram Nath Kovind, Acharya Dev Vrat appointed as Bihar and Himachal Pradesh governors". The Economic Times. Archived from the original on 27 August 2017.
- "36th Governor of Bihar". indiatoday. 16 August 2015. Archived from the original on 17 August 2015. Retrieved 16 August 2015.
- PTI (19 August 2015). "PM Modi praises new Bihar Governor Ram Nath Kovind". Archived from the original on 27 August 2017 – via India TV News.
- IANS (19 June 2017). "Presidential Election 2017: Nitish Kumar praises Ram Nath Kovind, remains mum on party support". Archived from the original on 29 July 2017 – via First Post.
- "Resignation as Governor of Bihar". firstpost. 20 August 2015. Archived from the original on 27 August 2017. Retrieved 20 August 2015.
- "Ram Nath Kovind is the 14th President of India". The Hindu. Archived from the original on 20 July 2017. Retrieved 20 July 2017.
- "With 65 percent votes, Kovind sweeps elections". Times of India. 21 July 2017. Archived from the original on 21 July 2017.
- "Kovind first President from Sangh, cross-voting boosts margin". Times of India. 21 July 2017. Archived from the original on 23 July 2017. Retrieved 23 July 2017.
- "Ram Nath Kovind takes oath as India's 14th President". indtoday.com. 25 July 2017. Archived from the original on 28 July 2017.
- "Kovind First President from RSS".
- "Press Information Bureau". Archived from the original on 5 October 2017. Retrieved 4 October 2017.
- "Press Information Bureau". Archived from the original on 5 October 2017. Retrieved 4 October 2017.
- "Press Information Bureau". Archived from the original on 6 October 2017. Retrieved 5 October 2017.
- "Press Information Bureau". Archived from the original on 6 October 2017. Retrieved 5 October 2017.
- "Press Information Bureau". Archived from the original on 6 October 2017. Retrieved 5 October 2017.
- "President Kovind meets Mauritius counterpart in Port Louis | DD News". www.ddinews.gov.in. Retrieved 12 March 2018.
- "President of India reached Mauritius; Addresses students at Mahatma Gandhi Institute; says India's aspiration is for Mauritius to rise as a leading Economy and a voice for peace and stability in the entire Indian Ocean Region". pib.nic.in. Retrieved 12 March 2018.
- Roche, Elizabeth (5 April 2018). "President Ram Nath Kovind to visit Africa in bid to bolster ties". Mint. Retrieved 13 April 2018.
- "President Ram Nath Kovind to reach Swaziland today". The Financial Express. 9 April 2018. Retrieved 13 April 2018.
- Chaudhury, Dipanjan Roy (5 April 2018). "President Ram Nath Kovind embarks on third official foreign trip". The Economic Times. Retrieved 13 April 2018.
- "President Kovind arrives in Lusaka, accorded ceremonial reception". www.aninews.in. Retrieved 13 April 2018.
- "President Kovind in Greece; Addresses Indian Community in Greece; Urges Indian Community in Greece to Help Enhance Economic, Cultural and People-to-People Links between the two Countries". Retrieved 11 July 2018.
- "President Kovind leaves on 3-nation visit to Greece, Suriname, Cuba - Times of India". The Times of India. Retrieved 11 July 2018.
- "Address by the Hon'ble President Of India Shri Ram Nath Kovind on the occasion of the International Day of Yoga celebrations in Suriname". pib.nic.in. Retrieved 11 July 2018.
- "President of India in Cuba, pays tributes to National Heroes of Cuba to address students at University of Havana". pib.nic.in. Retrieved 11 July 2018.
- "President Ram Nath Kovind to visit Greece, Suriname, Cuba". The New Indian Express. Retrieved 11 July 2018.
- "Ram Nath Kovind embarks on 3-nation tour". The New Indian Express.
- "President Ram Nath Kovind to visit Tajikistan from October 7–9". The Economic Times. 6 October 2018. Retrieved 29 November 2018.
- "President Kovind on six-day visit to Vietnam, Australia from November 18". The Indian Express. 17 November 2018. Retrieved 29 November 2018.
- "President Ram Nath Kovind to visit Vietnam from 18 to 21 November, will address National Assembly - Firstpost". www.firstpost.com. Retrieved 29 November 2018.
- "President Kovind To Begin Four-Day Australia Tour From November 21". NDTV.com. Retrieved 29 November 2018.
- "President Kovind visiting the capital city of croatia". croatiaweek.com. Retrieved 27 March 2019.
- "Press Statement by President during State Visit to Bolivia". Retrieved 29 March 2019.
- "State Visit of the President of India to Croatia, Bolivia and Chile". Retrieved 22 March 2019.
- "President's Daughter Moved To Ground Duties At Air India For Security Reasons". NDTV.com. 12 November 2017. Retrieved 20 March 2020.
- "Address by the President Of India, Shri Ram Nath Kovind on the Occasion of Inauguration of the New Global Headquarters 'Kanha Shanti Vanam' of Shri Ram Chandra Mission". www.presidentofindia.gov.in. 2 February 2020. Retrieved 29 July 2020.
- "Why is India's next president so unknown?". BBC. Archived from the original on 21 July 2017. Retrieved 20 July 2017.
- "When NDA Presidential pick Kovind said Islam, Christianity are alien to India". The New Indian Express. Archived from the original on 28 July 2017. Retrieved 20 July 2017.
- "Islam, Christianity alien, so cannot get quota: BJP". Hindustan Times. Archived from the original on 27 August 2017. Retrieved 20 July 2017.
- "Ram Nath Kovind's 'Islam, Christianity' statement triggers nation vs notion row". Hindustan Times. 27 June 2017. Archived from the original on 25 July 2017. Retrieved 24 July 2017.
- "ईसाइयों और मुसलमानों पर कोविन्द के चौंकाने वाले विचार". 20 June 2017. Archived from the original on 27 August 2017. Retrieved 24 August 2017.
- "Press Release on State Visit of President to Madagascar (March 14-15, 2018)". Retrieved 1 June 2019.
- "India-Equatorial Guinea Joint Statement during the State Visit of President of India to Equatorial Guinea". Retrieved 14 June 2019.
- "India-Swaziland Joint Statement during State Visit of President to Swaziland (April 9-10, 2018)". Retrieved 14 June 2019.
- "Press Statement by President during State Visit to Croatia". Retrieved 26 March 2019.
- "Press Statement by President during State Visit to Bolivia". Retrieved 29 March 2019.
- "President Ram Nath Kovind honoured with Guinea's highest award". India Today. 4 August 2019. Retrieved 21 September 2019.
External links

| Government offices | ||
|---|---|---|
| Preceded by Keshari Nath Tripathi |
Governor of Bihar 2015–2017 |
Succeeded by Keshari Nath Tripathi |
| Political offices | ||
| Preceded by Pranab Mukherjee |
President of India 2017–present |
Incumbent |