Potassium amide
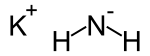
Potassium amide is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula KNH2, i.e. it is composed of a potassium cation, and the conjugate base of ammonia. Like other alkali metal amides, it is a white solid that hydrolyzes readily.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Potassium amide | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.037.508 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| H2KN | |
| Molar mass | 55.121 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | yellowish brown solid |
| Odor | ammonia-like |
| Density | 1.57 g/cm 3 |
| Melting point | 338 °C (640 °F; 611 K) |
| reacts | |
| Solubility | ammonia: 3.6 g/100 mL |
| Thermochemistry | |
Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
-128.9 kJ/mol |
| Related compounds | |
Other cations |
Lithium amide Sodium amide |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Production
Potassium amide is produced by the reaction of liquid ammonia with potassium.[1]
gollark: What day?
gollark: Amazing how it came out *worse* than a thing on Bad Ideas!
gollark: You forgot to add "without pagination and with poorly thought out rules".
gollark: Wow
gollark: Pillow would be better.
References
- O. Glemser, H. Sauer (1963). "Silver Amide". In G. Brauer (ed.). Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry, 2nd Ed. 1. NY,NY: Academic Press. p. 1043.
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.