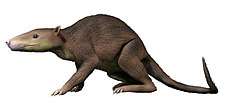
Pantolestidae
Pantolestidae is an extinct family of semi-aquatic, non-placental eutherian mammals that took part in the first placental evolutionary radiation together with other early mammals such as the leptictids.[1] Forming the core of the equally extinct suborder Pantolesta, the pantolestids evolved as a series of increasingly otter-like forms, ranging from the Middle Paleocene (60 mya) Bessoecetor to the Late Eocene (Ergilian) (50-33 mya) Gobiopithecus and Kiinkerishella. They first appear in North America, whence they spread to Europe.[2]
| Pantolestidae | |
|---|---|
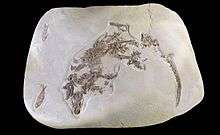 | |
| Palaeosinopa, from Wyoming eocene | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | |
| Suborder: | Pantolesta |
| Family: | Pantolestidae Cope, 1884 |
| Genera | |
|
Bessoecetor | |
Description
The pantolestids were fish predators with a body length of about 50 centimetres (20 in) and a tail about 35 centimetres (14 in) long. The anatomy of these archaic "insectivorous" mammals is best known through well-preserved Middle Eocene Buxolestes specimens found at Messel in Germany and a few other less complete specimens,[1] such as the Palaeosinopa found at Fossil Butte in Wyoming, estimated to have reached body weights of up to 1,400 grams (3 lb), making them relatively large early mammals.[2]
They had moderately strong canines and multi-cusped cutting teeth supported by the strong jaw muscles[1] to which cranial cavities were adapted. This combination of dentition and muscles has been interpreted as an early adaptation to a hard diet such as clams and snails.[2]
Freely articulated forearm bones (radius and ulna) permitted their powerful forelimbs wide rotational movements, while their digits had large bony claws —indicating they could dig and build underground dens. Their powerful hind limbs could not be rotated in the same way, but the prominent transverse processes of the first tail vertebra suggest that they used their powerful tails to propel through the water like modern otters.[1] In later pantolestids there is a prominent cranial crest combined with strong spinal processes, indicating the presence of strong neck muscles needed by swimmers that constantly hold their heads above the water surface.[2]
The youngest pantolestids known are Gobiopithecus khan and Kiinkerishella zaisanica from the Ergilian deposits of Khoer Dzan, Mongolia. These late Asian forms are thought to be one of the few examples of European mammals dispersing into Asia during the Grande Coupure.[3]
Classification
- Family: †Pantolestidae (Cope, 1884)
- Subfamilies
- †Pentacodontinae (Simpson, 1937)
- †Amaramnis
- †Aphronorus
- †Bisonalveus
- †Coriphagus
- †Pentacodon
- †Pantolestinae (Cope, 1884)
- †Bessoecetor
- †Bogbia
- †Bouffinomus
- †Buxolestes
- †Chadronia
- †Galethylax
- †Oboia
- †Palaeosinopa
- †Pagonomus
- †Pantolestes
- †Thelysia
- †Todralestes
- †Dyspterninae (Kretzoi, 1943)
- †Cryptopithecus
- †Dyspterna
- †Gobipithecus
- †Kochictis
Notes
- Agustí 2002, p 5
- Jehle 2005
- Spencer G. Lucas,Kate E. Zeigler,Peter E. Kondrashov, Paleogene Mammals: Bulletin 26, 2004
- Haaramo, Mikko (March 2008). "†Pantolestidae". Mikko's Phylogeny Archive. Retrieved 17 January 2010. (long list including dozens of species)
References
- Agustí, Jordi; Antón, Mauricio (2002). Mammoths, Sabertooths, and Hominids: 65 Million Years of Mammalian Evolution in Europe. New York: Columbia University Press. ISBN 0-231-11640-3.
- Jehle, Martin (December 8, 2005). "Insectivore-like mammals: Tiny teeth and their enigmatic owners". Paleocene Mammals. Retrieved 17 January 2010.
External links
- "Family: Pantolestidae: Occurrence overview". GDIF. Retrieved 17 January 2010.