Illegal drug trade
The illegal drug trade or drug trafficking is a global black market dedicated to the cultivation, manufacture, distribution and sale of drugs that are subject to drug prohibition laws. Most jurisdictions prohibit trade, except under license, of many types of drugs through the use of drug prohibition laws.
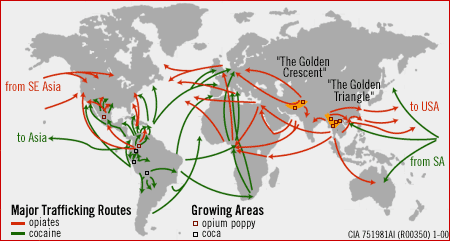
The United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime's World Drug Report 2005 estimates the size of the global illicit drug market at US$321.6 billion in 2003 alone.[1] With a world GDP of US$36 trillion in the same year, the illegal drug trade may be estimated as nearly 1% of total global trade. Consumption of illegal drugs is widespread globally and it remains very difficult for local authorities to thwart its popularity.
History
Chinese authorities issued edicts against opium smoking in 1729, 1796 and 1800.[2] The West prohibited addictive drugs throughout the late 19th and early 20th centuries.[3][4][5]
In the early 19th century, an illegal drug trade in China emerged. As a result, by 1838 the number of Chinese opium-addicts had grown to between four and twelve million.[6] The Chinese government responded by enforcing a ban on the import of opium; this led to the First Opium War (1839-1842) between the United Kingdom and Qing-dynasty China. The United Kingdom won and forced China to allow British merchants to sell Indian-grown opium. Trading in opium was lucrative, and smoking it had become common for the Chinese in the 19th century, so British merchants increased trade with the Chinese. The Second Opium War broke out in 1856, with the British joined this time by the French. After the two Opium Wars, the British Crown, via the treaties of Nanking (1842), and Tianjin (1858), obligated the Chinese government to pay large sums of money for opium they had seized and destroyed, which were referred to as "reparations".
In 1868, as a result of the increased use of opium, the UK restricted the sale of opium in Britain by implementing the 1868 Pharmacy Act.[7] In the United States, control of opium remained under the control of individual US states until the introduction of the Harrison Act in 1914, after 12 international powers signed the International Opium Convention in 1912.
Between 1920 and around 1933 the Eighteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution banned alcohol in the United States. Prohibition proved almost impossible to enforce and resulted in the rise of organized crime, including the modern American Mafia, which identified enormous business opportunities in the manufacturing, smuggling and sale of illicit liquor.[8][9]
The beginning of the 21st century saw drug use increase in North America and Europe, with a particularly increased demand for marijuana and cocaine.[10][11] As a result, international organized crime syndicates such as the Sinaloa Cartel and 'Ndrangheta have increased cooperation among each other in order to facilitate trans-Atlantic drug-trafficking.[12] Use of another illicit drug, hashish, has also increased in Europe.
Drug trafficking is widely regarded by lawmakers as a serious offense around the world. Penalties often depend on the type of drug (and its classification in the country into which it is being trafficked), the quantity trafficked, where the drugs are sold and how they are distributed. If the drugs are sold to underage people, then the penalties for trafficking may be harsher than in other circumstances.
Drug smuggling carries severe penalties in many countries. Sentencing may include lengthy periods of incarceration, flogging and even the death penalty (in Singapore, Malaysia, Indonesia and elsewhere). In December 2005, Van Tuong Nguyen, a 25-year-old Australian drug smuggler, was hanged in Singapore after being convicted in March 2004.[13] In 2010, two people were sentenced to death in Malaysia for trafficking 1 kilogram (2.2 lb) of cannabis into the country.[14] Execution is mostly used as a deterrent, and many have called upon much more effective measures to be taken by countries to tackle drug trafficking;[15] for example, targeting specific criminal organisations that are often also active in the smuggling of other goods (i.e. wildlife) and even people.[16][17] In many cases, links between politicians and the criminal organisations have been proven to exist.[18]
Societal effects
The countries of drug production and transit are some of the most affected by the drug trade, though countries receiving the illegally imported substances are also adversely affected. For example, Ecuador has absorbed up to 300,000 refugees from Colombia who are running from guerrillas, paramilitaries and drug lords. While some applied for asylum, others are still illegal immigrants. The drugs that pass from Colombia through Ecuador to other parts of South America create economic and social problems.[19]
Honduras, through which an estimated 79% of cocaine passes on its way to the United States,[20] has the highest murder rate in the world.[21] According to the International Crisis Group, the most violent regions in Central America, particularly along the Guatemala–Honduras border, are highly correlated with an abundance of drug trafficking activity.[22]
Violent crime
In many countries, the illegal drug trade is thought to be directly linked to violent crimes such as murder. This is especially true in all developing countries, such as Honduras, but is also an issue for many developed countries worldwide.[23][24] In the late 1990s in the United States the Federal Bureau of Investigation estimated that 5% of murders were drug-related.[23] In Colombia, drug violence can be caused by factors such as the economy, poor governments, and no authority within law enforcement.[25]
After a crackdown by US and Mexican authorities in the first decade of the 21st century as part of tightened border security in the wake of the September 11 attacks, border violence inside Mexico surged. The Mexican government estimates that 90% of the killings are drug-related.[26]
A report by the UK government's Drug Strategy Unit that was leaked to the press, stated that due to the expensive price of highly addictive drugs heroin and cocaine, drug use was responsible for the great majority of crime, including 85% of shoplifting, 70–80% of burglaries and 54% of robberies. It concluded that "[t]he cost of crime committed to support illegal cocaine and heroin habits amounts to £16 billion a year in the UK" [27]
Drug trafficking routes

South America
Venezuela has been a path to the United States and Europe for illegal drugs originating in Colombia, through Central America, Mexico and Caribbean countries such as Haiti, the Dominican Republic, and Puerto Rico.
According to the United Nations, there was an increase of cocaine trafficking through Venezuela since 2002.[28] In 2005, the government of Hugo Chávez severed ties with the United States Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA), accusing its representatives of spying.[29] Following the departure of the DEA from Venezuela and the expansion of DEA's partnership with Colombia in 2005, Venezuela became more attractive to drug traffickers.[30] Between 2008 and 2012, Venezuela's cocaine seizure ranking among other countries declined, going from being ranked fourth in the world for cocaine seizures in 2008[31] to sixth in the world in 2012.[32]
On 18 November 2016, following what was known as the Narcosobrinos incident, Venezuelan President Nicolás Maduro's two nephews were found guilty of trying to ship drugs into the United States so they could "obtain a large amount of cash to help their family stay in power".[33]
In August 2019, former Dominican players of the MLB, Octavio Dotel and Luis Castillo were suspected of being involved with a massive drug-trafficking ring, alleged to be run by César Emilio Peralta. Authorities claim that they ran narcotics from South America into the United States and Europe.[34]
According to a research conducted by the Abba Eban Institute as part of an initiative called Janus Initiative, the main routes that Hezbollah uses for smuggling drugs are from Colombia, Venezuela and Brazil into West Africa and then transported through northern Africa into Europe. This route serves Hezbollah in making a profit in the cocaine smuggling market to leverage it for terrorist activities.[35]
West Africa
Cocaine produced in Colombia and Bolivia increasingly has been shipped via West Africa (especially in Cape Verde, Mali, Benin, Togo, Nigeria, Cameroon, Guinea-Bissau and Ghana).[36] The money is often laundered in countries such as Nigeria, Ghana and Senegal.
According to the Africa Economic Institute, the value of illicit drug smuggling in Guinea-Bissau is almost twice the value of the country's GDP.[36] Police officers are often bribed. A police officer's normal monthly wage of $93 is less than 2% of the value of 1 kilogram (2.2 lb) of cocaine (€7000 or $8750). The money can also be laundered using real estate. A house is built using illegal funds, and when the house is sold, legal money is earned.[37] When drugs are sent over land, through the Sahara, the drug traders have been forced to cooperate with terrorist organizations, such as Al Qaida in Islamic Maghreb.[38][39]
Eastern and Southern Africa
Heroin is increasingly trafficked from Afghanistan to Europe and America through eastern and southern African countries. This path is known as the “southern route” or “smack track.” Repercussions of this trade include burgeoning heroin use and political corruption among intermediary African nations.[40]
Asia
Drugs in Asia traditionally traveled the southern routes – the main caravan axes of Southeast Asia and Southern China – and include the former opium-producing countries of Thailand, Iran, and Pakistan.[41] After the 1990s, particularly after the Cold War ended, borders were opened and trading and customs agreements were signed so that the routes expanded to include China, Central Asia, and Russia.[41] There are, therefore, diversified drug trafficking routes available today, particularly in the heroin trade and these thrive due to the continuous development of new markets. A large amount of drugs are smuggled into Europe from Asia. The main sources of these drugs are Afghanistan, along with countries that constituted the so-called Golden Crescent. From these producers, drugs are smuggled into the West and Central Asia to its destinations in Europe and the United States.[42] Iran is now the route for smugglers, having been previously a primary trading route, due to its large-scale and costly war against drug trafficking.[41] The Border Police Chief of Iran said that his country "is a strong barrier against the trafficking of illegal drugs to Caucasus, especially the Republic of Azerbaijan."[43] The drugs produced by the Golden Triangle of Myanmar, Laos, and Thailand, on the other hand, pass through the southern routes to feed the Australian, U.S., and Asian markets.[44]
Profits

Statistics about profits from the drug trade are largely unknown due to its illicit nature. An online report published by the UK Home Office in 2007 estimated the illicit drug market in the UK at £4–6.6 billion a year[46]
In December 2009 United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime Executive Director Antonio Maria Costa claimed illegal drug money saved the banking industry from collapse. He claimed he had seen evidence that the proceeds of organized crime were "the only liquid investment capital" available to some banks on the brink of collapse during 2008. He said that a majority of the $352 billion (£216bn) of drug profits was absorbed into the economic system as a result:
"In many instances, the money from drugs was the only liquid investment capital. In the second half of 2008, liquidity was the banking system's main problem and hence liquid capital became an important factor...Inter-bank loans were funded by money that originated from the drugs trade and other illegal activities...there were signs that some banks were rescued that way".[47]
Costa declined to identify countries or banks that may have received any drug money, saying that would be inappropriate because his office is supposed to address the problem, not apportion blame.
Though street-level drug sales are widely viewed as lucrative, a study by Sudhir Venkatesh suggested that many low-level employees receive low wages. In a study he made in the 1990s working closely with members of the Black Gangster Disciple Nation in Chicago, he found that one gang (essentially a franchise) consisted of a leader (a college graduate named J.T.), three senior officers, and 25 to 75 street level salesmen ('foot soldiers') depending on season. Selling crack cocaine, they took in approximately $32,000 per month over a six-year period. This was spent as follows: $5,000 to the board of twenty directors of the Black Gangster Disciple Nation, who oversaw 100 such gangs for approximately $500,000 in monthly income. Another $5,000 monthly was paid for cocaine, and $4,000 for other non-wage expenses. J.T. took $8,500 monthly for his own salary. The remaining $9,500 monthly went to pay the employees a $7 per hour wage for officers and a $3.30 per hour wage for foot soldiers. Contrary to a popular image of drug sales as a lucrative profession, many of the employees were living with their mothers by necessity. Despite this, the gang had four times as many unpaid members who dreamed of becoming foot soldiers.[48]
Free trade link
There are several arguments on whether or not free trade has a correlation to an increased activity in the illicit drug trade. Currently, the structure and operation of the illicit drug industry is described mainly in terms of an international division of labor.[49] Free trade can open new markets to domestic producers who would otherwise resort to exporting illicit drugs. Additionally, extensive free trade among states increases cross-border drug enforcement and coordination between law enforcement agencies in different countries.[49] However, free trade also increases the sheer volume of legal cross-border trade and provides cover for drug smuggling—by providing ample opportunity to conceal illicit cargo in legal trade. While international free trade continues to expand the volume of legal trade, the ability to detect and interdict drug trafficking is severely diminished. Towards the late 1990s, the top ten seaports in the world processed 33.6 million containers.[49] Free trade has fostered integration of financial markets and has provided drug traffickers with more opportunities to launder money and invest in other activities. This strengthens the drug industry while weakening the efforts of law enforcement to monitor the flow of drug money into the legitimate economy. Cooperation among cartels expands their scope to distant markets and strengthens their abilities to evade detection by local law enforcement.[49] Additionally, criminal organizations work together to coordinate money-laundering activities by having separate organizations handle specific stages of laundering process.[49] One organization structures the process of how financial transactions will be laundered, while another criminal group provides the “dirty” money to be cleaned.[49] By fostering expansion of trade and global transportation networks, free trade encourages cooperation and formation of alliances among criminal organizations across different countries. The drug trade in Latin America emerged in the early 1930s.[50] It saw significant growth in the Andean countries, including Peru, Bolivia, Chile, Ecuador, Colombia and Venezuela.[50] The underground market in the early half of the 20th century mainly had ties to Europe. After World War II, the Andean countries saw an expansion of trade, specifically with cocaine.[50]
Drug trafficking by country
United States

Background
The effects of the illegal drug trade in the United States can be seen in a range of political, economic and social aspects. Increasing drug related violence can be tied to the racial tension that arose during the late 20th century along with the political upheaval prevalent throughout the 1960s and 70s. The second half of the 20th century was a period when increased wealth, and increased discretionary spending, increased the demand for illicit drugs in certain areas of the United States. Large-scale drug trafficking is one of the few capital crimes, and may result in a death sentence prescribed at the federal level.
Political impact
A large generation, the baby boomers, came of age in the 1960s. Their social tendency to confront the law on specific issues, including illegal drugs, overwhelmed the understaffed judicial system. The federal government attempted to enforce the law, but with meager effect.
Marijuana was a popular drug seen through the Latin American trade route in the 1960s. Cocaine became a major drug product in the later decades.[51] Much of the cocaine is smuggled from Colombia and Mexico via Jamaica.[52] This led to several administrations combating the popularity of these drugs. Due to the influence of this development on the U.S. economy, the Reagan administration began "certifying" countries for their attempts at controlling drug trafficking.[51] This allowed the United States to intervene in activities related to illegal drug transport in Latin America. Continuing into the 1980s, the United States instated stricter policy pertaining to drug transit through sea. As a result, there was an influx in drug-trafficking across the Mexico–U.S. border. This increased the drug cartel activity in Mexico. By the early 1990s, so much as 50% of the cocaine available in the United States market originated from Mexico, and by the 2000s, over 90% of the cocaine in the United States was imported from Mexico.[51] In Colombia, however, there was a fall of the major drug cartels in the mid-1990s. Visible shifts occurred in the drug market in the United States. Between the 1996 and 2000, U.S. cocaine consumption dropped by 11%.[53]
In 2008, the U.S. government initiated another program, known as the Merida Initiative, to help combat drug trafficking in Mexico. This program increased U.S. security assistance to $1.4 billion over several years, which helped supply Mexican forces with "high-end equipment from helicopters to surveillance technology".[54] Despite U.S. aid, Mexican "narcogangs" continue to outnumber and outgun the Mexican Army, allowing for continued activities of drug cartels across the U.S.–Mexico border.[54]
Social impacts

Although narcotics are illegal in the US, they have become integrated into the nation's culture and are seen as a recreational activity by sections of the population.[55] Illicit drugs are considered to be a commodity with strong demand, as they are typically sold at a high value. This high price is caused by a combination of factors that include the potential legal ramifications that exist for suppliers of illicit drugs and their high demand.[56] Despite the constant effort by politicians to win the war on drugs, the US is still the world's largest importer of illegal drugs.[56]
Throughout the 20th century, narcotics other than cocaine also crossed the Mexican border, meeting the US demand for alcohol during the 1920s Prohibition, opiates in the 1940s, marijuana in the 1960s, and heroin in the 1970s.[57] Most of the U.S. imports of drugs come from Mexican drug cartels. In the United States, around 195 cities have been infiltrated by drug trafficking that originated in Mexico.[55] An estimated $10bn of the Mexican drug cartel's profits come from the United States, not only supplying the Mexican drug cartels with the profit necessary for survival, but also furthering America's economic dependence on drugs.[55]
Demographics
With a large wave of immigrants in the 1960s and onwards, the United States saw an increased heterogeneity in its public.[58] In the 1980s and 90s, drug related homicide was at a record high. This increase in drug violence became increasingly tied to these ethnic minorities. Though the rate of violence varied tremendously among cities in America, it was a common anxiety in communities across urban America. An example of this could be seen in Miami, a city with a host of ethnic enclaves.[58] Between 1985 and 1995, the homicide rate in Miami was one of the highest in the nation—four times the national homicide average. This crime rate was correlated with regions with low employment and was not entirely dependent on ethnicity.[58]
The baby boomer generation also felt the effects of the drug trade in their increased drug use from the 1960s to 80s.[59] Along with substance abuse, criminal involvement, suicide and murder were also on the rise. Due to the large amount of baby boomers, commercial marijuana use was on the rise. This increased the supply and demand for marijuana during this time period.[59]
Mexico
Political influences
Corruption in Mexico has contributed to the domination of Mexican cartels in the illicit drug trade. Since the beginning of the 20th century, Mexico's political environment allowed the growth of drug-related activity. The loose regulation over the transportation of illegal drugs and the failure to prosecute known drug traffickers and gangs increased the growth of the drug industry. Toleration of drug trafficking has undermined the authority of the Mexican government and has decreased the power of law enforcement officers in regulation over such activities. These policies of tolerance fostered the growing power of drug cartels in the Mexican economy and have made drug traders wealthier.[60] Many states in Mexico lack policies that establish stability in governance. There also is a lack of local stability, as mayors cannot be re-elected. This requires electing a new mayor each term. Drug gangs have manipulated this, using vacuums in local leadership to their own advantage.[51]
In 1929, the Institutional Revolutionary Party (PRI) was formed to resolve the chaos resulting from the Mexican Revolution. Over time, this party gained political influence and had a major impact on Mexico's social and economic policies.[51] The party created ties with various groups as a power play in order to gain influence, and as a result created more corruption in the government. One such power play was an alliance with drug traffickers. This political corruption obscured justice, making it difficult to identify violence when it related to drugs.[61] By the 1940s, the tie between the drug cartels and the PRI had solidified. This arrangement created immunity for the leaders of the drug cartels and allowed drug trafficking to grow under the protection of the government officials. During the 1990s, the PRI lost some elections to the new National Action Party(PAN). Chaos again emerged as elected government in Mexico changed drastically.[62] As the PAN party took control, drug cartel leaders took advantage of the ensuing confusion and used their existing influence to further gain power.[62] Instead of negotiating with the central government as was done with the PRI party, drug cartels utilized new ways to distribute their supply and continued operating through force and intimidation.[62] As Mexico became more democratized, the corruption fell from a centralized power to the local authorities.[62] Cartels began to bribe local authorities, thus eliminating the structure and rules placed by the government—giving cartels more freedom.[62] As a response, Mexico saw an increase in violence caused by drug trafficking.
The corruption cartels created resulted in distrust of government by the Mexican public.[62] This distrust became more prominent after the collapse of the PRI party.[62] In response, the presidents of Mexico, in the late twentieth century and early twenty-first century, implemented several different programs relating to law enforcement and regulation. In 1993, President Salinas created the National Institute for the Combat of Drugs in Mexico. From 1995–1998, President Zedillo established policies regarding increased punishment of organized crime, allowing "[wire taps], protected witnesses, covert agents and seizures of goods", and increasing the quality of law enforcement at the federal level. From 2001–2005, President Vicente Fox created the Federal Agency of Investigation.[60] These policies resulted in the arrests of major drug-trafficking bosses:
| Year | Person | Cartel |
|---|---|---|
| 1989 | Miguel Angel Felix Gallardo | Guadalajara Cartel |
| 1993 | Joaquín Guzmán Loera | Sinaloa Cartel |
| 1995 | Héctor Luis Palma | Sinaloa Cartel |
| 1996 | Juan Garcia Abrego | Gulf Cartel |
| 2002 | Ismael Higuera Guerrero[60] | Tijuana Cartel |
| Jesus Labra | Tijuana Cartel | |
| Adan Amezcua | Colima Cartel | |
| Benjamin Arellano Felix | Tijuana Cartel | |
| 2003 | Osiel Cardenas[60] | Gulf Cartel |
Mexico's economy
Over the past few decades drug cartels have become integrated into Mexico's economy. Approximately 500 cities are directly engaged in drug trafficking and nearly 450,000 people are employed by drug cartels.[62] Additionally, the livelihood of 3.2 million people is dependent on the drug cartels.[62] Between local and international sales, such as to Europe and the United States, drug cartels in Mexico see a $25–30bn yearly profit, a great deal of which circulates through international banks such as HSBC.[62] Drug cartels are fundamental in local economics. A percentage of the profits seen from the trade are invested in the local community.[62] Such profits contribute to the education and healthcare of the community.[62] While these cartels bring violence and hazards into communities, they create jobs and provide income for its many members.[62]
Culture of drug cartels
Major cartels saw growth due to a prominent set culture of Mexican society that created the means for drug capital. One of the sites of origin for drug trafficking within Mexico, was the state of Michoacán. In the past, Michoacán was mainly an agricultural society. This provided an initial growth of trade. Industrialization of rural areas of Mexico facilitated a greater distribution of drugs, expanding the drug market into different provinces.[61] Once towns became industrialized, cartels such as the Sinaloa Cartel started to form and expand. The proliferation of drug cartel culture largely stemmed from the ranchero culture seen in Michoacán. Ranchero culture values the individual as opposed to the society as a whole.[61] This culture fostered the drug culture of valuing the family that is formed within the cartel. This ideal allowed for greater organization within the cartels. Gangs play a major role in the activity of drug cartels. MS-13 and the 18th Street gang are notorious for their contributions and influence over drug trafficking throughout Latin America. MS-13 has controlled much of the activity in the drug trade spanning from Mexico to Panama[63] Female involvement is present in the Mexican drug culture. Although females are not treated as equals to males, they typically hold more power than their culture allows and acquire some independence. The increase in power has attracted females from higher social classes.[64] Financial gain has also prompted women to become involved in the illegal drug market. Many women in the lower levels of major drug cartels belong to a low economic class. Drug trafficking offers women an accessible way to earn income.[64] Females from all social classes have become involved in the trade due to outside pressure from their social and economic environments.
Colombia
.jpg)
Political ties
It was common for smugglers in Colombia to import liquor, alcohol, cigarettes and textiles, while exporting cocaine.[50] Personnel with knowledge of the terrain were able to supply the local market while also exporting a large amount of product.[50] The established trade that began in the 1960s involved Peru, Bolivia, Colombia, Venezuela and Cuba. Peasant farmers produced coca paste in Peru and Bolivia, while Colombian smugglers would process the coca paste into cocaine in Colombia, and trafficked product through Cuba.[50] This trade route established ties between Cuban and Colombian organized crime. From Cuba, cocaine would be transported to Miami, Florida; and Union City, New Jersey. Quantities of the drug were then smuggled throughout the US.[50] The international drug trade created political ties between the involved countries, encouraging the governments of the countries involved to collaborate and instate common policies to eradicate drug cartels. Cuba stopped being a center for transport of cocaine following the establishment of a communist government in 1959. As a result, Miami and Union City became the sole locations for trafficking.[50] The relations between Cuban and Colombian organized crime remained strong until the 1970s, when Colombian cartels began to vie for power. In the 1980s and 90s, Colombia emerged as a key contributor of the drug trade industry in the Western Hemisphere. While the smuggling of drugs such as marijuana, poppy, opium and heroin became more ubiquitous during this time period, the activity of cocaine cartels drove the development of the Latin American drug trade. The trade emerged as a multinational effort as supplies (i.e. coca plant substances) were imported from countries such as Bolivia and Peru, were refined in Colombian cocaine labs and smuggled through Colombia, and exported to countries such as the US.[65]
Colombia's economy
Colombia has had a significant role in the illegal drug trade in Latin America. While active in the drug trade since the 1930s, Colombia's role in the drug trade did not truly become dominant until the 1970s.[65] When Mexico eradicated marijuana plantations, demand stayed the same. Colombia met much of the demand by growing more marijuana. Grown in the strategic northeast region of Colombia, marijuana soon became the leading cash crop in Colombia.[50] This success was short-lived due to anti-marijuana campaigns that were enforced by the US military throughout the Caribbean.[50] Instead, drug traffickers in Colombia continued their focus on the exportation of cocaine.[50] Having been an export of Colombia since the early 1950s, cocaine remained popular for a host of reasons. Colombia's location facilitated its transportation from South America into Central America, and then to its destination of North America. This continued into the 1990s, when Colombia remained the chief exporter of cocaine.[53] The business of drug trafficking can be seen in several stages in Colombia towards the latter half of the 20th century. Colombia served as the dominant force in the distribution and sale of cocaine by the 1980s. As drug producers gained more power, they became more centralized and organized into what became drug cartels.[53] Cartels controlled the major aspects of each stage in the traffic of their product. Their organization allowed cocaine to be distributed in great amounts throughout the United States. By the late 1980s, intra-industry strife arose within the cartels.[53] This stage was marked by increased violence as different cartels fought for control of export markets. Despite this strife, this power struggle led to then having multiple producers of coca leaf farms. This in turn caused an improvement in quality control and reduction of police interdiction in the distribution of cocaine.[53] This also led to cartels attempting to repatriate their earnings which would eventually make up 5.5% of Colombia's GDP.[53] This drive to repatriate earnings led to the pressure of legitimizing their wealth, causing an increase in violence throughout Colombia.[53]

Throughout the 1980s, estimates of illegal drug value in Colombia ranged from $2bn to $4bn.[65] This made up about 7–10% of the $36bn estimated GNP of Colombia during this decade. In the 1990s, the estimates of the illegal drug value remained roughly within the same range (~$2.5bn).[65] As the Colombian GNP rose throughout the 1990s ($68.5bn in 1994 and $96.3bn in 1997),[65] illegal drug values began to comprise a decreasing fraction of the national economy.[65] By the early 1990s, although Colombia led in the exportation of cocaine, it found increasing confrontations within its state. These confrontations were primarily between cartels and government institutions. This led to a decrease in the drug trade's contribution to the GDP of Colombia; dropping from 5.5% to 2.6%.[53] Though a contributor of wealth, the distribution of cocaine has had negative effects on the socio-political situation of Colombia and has weakened its economy as well.[53]
Social impacts
By the 1980s, Colombian cartels became the dominant cocaine distributors in the US.[50] This led to the spread of increased violence throughout both Latin America and Miami.[50] In the 1980s, two major drug cartels emerged in Colombia: the Medellin and Cali groups. Throughout the 1990s however, several factors led to the decline of these major cartels and to the rise of smaller Colombian cartels.[65] The U.S. demand for cocaine dropped while Colombian production rose, pressuring traffickers to find new drugs and markets. In this time period, there was an increase in activity of Caribbean cartels that led to the rise of an alternate route of smuggling through Mexico. This led to the increased collaboration between major Colombian and Mexican drug traffickers. Such drastic changes in the execution of drug trade in Colombia paired with the political instabilities and rise of drug wars in Medellin and Cali, gave way for the rise of the smaller Colombian drug trafficking organizations (and the rise of heroin trade).[65] As the drug trade's influence over the economy increased, drug lords and their networks grew in their power and influence in society. The occurrences in drug-related violence increased during this time period as drug lords fought to maintain their control in the economy.[65] Typically a drug cartel had support networks that consisted of a number of individuals. These people individuals ranged from those directly involved in the trade (such as suppliers, chemists, transporters, smugglers, etc.) as well as those involved indirectly in the trade (such as politicians, bankers, police, etc.). As these smaller Colombian drug cartels grew in prevalence, several notable aspects of the Colombian society gave way for further development of the Colombian drug industry. For example, until the late 1980s, the long-term effects of the drug industry were not realized by much of society. Additionally, there was a lack of regulation in prisons where captured traffickers were sent. These prisons were under-regulated, under-funded, and under-staffed, which allowed for the formation of prison gangs, for the smuggling of arms/weapons/etc., for feasible escapes, and even for captured drug lords to continue running their businesses from prison.[65]
Trade in specific drugs
Cannabis
While the recreational use of (and consequently the distribution of) cannabis is illegal in most countries throughout the world, recreational distribution is legal in some countries, such as Canada, and medical distribution is permitted in some places, such as 10 of the 50 US states (although importation and distribution is still federally prohibited).[66] Beginning in 2014, Uruguay became the first country to legalize cultivation, sale, and consumption of cannabis for recreational use for adult residents.[67] In 2018, Canada became the second country to legalize use, sale and cultivation of cannabis. The first few weeks were met with extremely high demand, most shops being out of stock after operating for only four days.
Cannabis use is tolerated in some areas, most notably the Netherlands which has legalized the possession and licensed sale (but not cultivation) of the drug. Many nations have decriminalized the possession of small amounts of marijuana. Due to the hardy nature of the cannabis plant, marijuana is grown all across the world and is today the world's most popular illegal drug with the highest level of availability.[68] Cannabis is grown legally in many countries for industrial, non-drug use (known as hemp) as well. Cannabis-hemp may also be planted for other non-drug domestic purposes, such as seasoning that occurs in Aceh.[69]
The demand for cannabis around the world, coupled with the drug's relative ease of cultivation, makes the illicit cannabis trade one of the primary ways in which organized criminal groups finance many of their activities. In Mexico, for example, the illicit trafficking of cannabis is thought to constitute the majority of many of the cartels' earnings,[70] and the main way in which the cartels finance many other illegal activities; including the purchase of other illegal drugs for trafficking, and for acquiring weapons that are ultimately used to commit murders (causing a burgeoning in the homicide rates of many areas of the world, but particularly Latin America).[71][72]
Some studies show that the increased legalization of cannabis in the United States (beginning in 2012 with Washington Initiative 502 and Colorado Amendment 64) has led Mexican cartels to smuggle less cannabis in exchange for more heroin.[73][74][75]
Alcohol
Alcohol, in the context of alcoholic beverages rather than denatured alcohol, is illegal in a number of Muslim countries, such as Saudi Arabia, and this has resulted in a thriving illegal trade in alcohol.[76] The manufacture, sale, transportation, importation and exportation of alcoholic beverage were illegal in the United States during the time known as the Prohibition in the 1920s and early 1930s.
Heroin


Up until around 2004 the majority of the world's heroin was produced in an area known as the Golden Triangle.[77] However, by 2007, 93% of the opiates on the world market originated in Afghanistan.[78] This amounted to an export value of about US$64 billion, with a quarter being earned by opium farmers and the rest going to district officials, insurgents, warlords and drug traffickers.[79] Another significant area where poppy fields are grown for the manufacture of heroin is Mexico.
According to the United States Drug Enforcement Administration, the price of heroin is typically valued 8 to 10 times that of cocaine on American streets, making it a high-profit substance for smugglers and dealers.[80] In Europe (except the transit countries Portugal and the Netherlands), for example, a purported gram of street heroin, usually consisting of 700–800 mg of a light to dark brown powder containing 5–10% heroin base, costs €30–70, making the effective value per gram of pure heroin €300–700. Heroin is generally a preferred product for smuggling and distribution—over unrefined opium due to the cost-effectiveness and increased efficacy of heroin.
Because of the high cost per volume, heroin is easily smuggled. A US quarter-sized (2.5 cm) cylindrical vial can contain hundreds of doses. From the 1930s to the early 1970s, the so-called French Connection supplied the majority of US demand. Allegedly, during the Vietnam War, drug lords such as Ike Atkinson used to smuggle hundreds of kilograms of heroin to the US in coffins of dead American soldiers (see Cadaver Connection). Since that time it has become more difficult for drugs to be imported into the US than it had been in previous decades, but that does not stop the heroin smugglers from getting their product across US borders. Purity levels vary greatly by region with Northeastern cities having the most pure heroin in the United States. On 17 October 2018 police in Genoa Italy, discovered 270 kg of heroin hidden in a ship coming from the Iranian southern port of Bandar Abbas. The ship had already passed and stopped at Hamburg in Germany and Valencia in Spain.[81]
Penalties for smuggling heroin or morphine are often harsh in most countries. Some countries will readily hand down a death sentence (e.g. Singapore) or life in prison for the illegal smuggling of heroin or morphine, which are both internationally Schedule I drugs under the Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs.
Methamphetamine
.jpg)
Methamphetamine is another popular drug among distributors. Three common street names are or "meth", "crank", and "ice".[82]
According to the Community Epidemiology Work Group, the number of clandestine methamphetamine laboratory incidents reported to the National Clandestine Laboratory Database decreased from 1999 to 2009. During this period, methamphetamine lab incidents increased in mid-western States (Illinois, Michigan, Missouri, and Ohio), and in Pennsylvania. In 2004, more lab incidents were reported in Missouri (2,788) and Illinois (1,058) than in California (764). In 2003, methamphetamine lab incidents reached new highs in Georgia (250), Minnesota (309), and Texas (677). There were only seven methamphetamine lab incidents reported in Hawaii in 2004, though nearly 59 percent of substance abuse treatment admissions (excluding alcohol) were for primary methamphetamine abuse during the first six months of 2004. As of 2007, Missouri leads the United States in drug-lab seizures, with 1,268 incidents reported.[83] Often canine units are used for detecting rolling meth labs which can be concealed on large vehicles, or transported on something as small as a motorcycle. These labs are more difficult to detect than stationary ones, and can often be obscured among legal cargo in big trucks.[84]
Methamphetamine is sometimes used intraveneously, placing users and their partners at risk for transmission of HIV and hepatitis C.[85] "Meth" can also be inhaled, most commonly vaporized on aluminum foil or in a glass pipe. This method is reported to give "an unnatural high" and a "brief intense rush".[86]
In South Africa methamphetamine is called "tik" or "tik-tik"."Known locally as "tik," the drug was virtually unknown as late as 2003. Now, it is the country's main drug of abuse, even when alcohol is included. "[87] Children as young as eight are abusing the substance, smoking it in crude glass vials made from light bulbs. Since methamphetamine is easy to produce, the substance is manufactured locally in staggering quantities.
The government of North Korea currently operates methamphetamine production facilities. There, the drug is used as medicine because no alternatives are available; it also is smuggled across the Chinese border.[88]
The Australian Crime Commission's illicit drug data report for 2011–2012 stated that the average strength of crystal methamphetamine doubled in most Australian jurisdictions within a 12-month period, and the majority of domestic laboratory closures involved small "addict-based" operations.[89]
Temazepam
Temazepam, a strong hypnotic benzodiazepine, is illicitly manufactured in clandestine laboratories (called jellie labs) to supply the increasingly high demand for the drug internationally.[90] Many clandestine temazepam labs are in Eastern Europe. The labs manufacture temazepam by chemically altering diazepam, oxazepam or lorazepam.[91] "Jellie labs" have been identified and shut down in Russia, the Ukraine, Czech Republic, Latvia and Belarus.[92]
Surveys in many countries show that temazepam, MDMA, nimetazepam, and methamphetamine rank among the top illegal drugs most frequently abused.[93][94][95][96][97][98][99][100][101][102][103]
Cocaine
Cocaine is a highly prominent drug among many drug dealers and manufacturers. The cocaine black market distribution industry is worth more than 85 billion dollars. It has been a heavily fought over and massively produced. Around 1.1 million kilograms of cocaine were made in 2009 and it is believed to have been consumed by around 17 million people worldwide. This drug's mass trade is believed to have been possible by notorious drug dealing kingpin Joaquín "El Chapo" Guzmán who ran the Sinaloa Cartel.[104]
See also
- Allegations of CIA drug trafficking
- Arguments for and against drug prohibition
- Counterfeit medications
- Corruption
- Drug Cartel
- Drug trafficking organizations
- Drug liberalization
- Illegal drug trade in popular culture
- Legal drug trade
- Narco-capitalism
- Operation Show Me How
- War on Drugs
International coordination
References
- Sandeep Chawla, Anja Korenblik, Suzanne Kunnen, Thibault Le Pichon, Aruna Nathwani, Thomas Pietschmann, Wolfgang Rhomberg, Ali Saadeddin, Johny Thomas, Melissa Tullis (2005). World Drug Report 2005: Volume 1: Analysis (Report). United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime. p. 127. ISBN 92-1-148200-3. Retrieved 24 May 2017.CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link)
- "History of the Opium Trade in China". Druglibrary.org. Retrieved 8 October 2017.
- "Illegal Drugs in America: A Modern History". Deamuseum.org. Archived from the original on 2004-12-04. Retrieved 2011-11-26.
- "The 1912 Hague International Opium Convention". Druglibrary.org. Retrieved 2011-11-26.
- "History of Legislative Control Over Opium, Cocaine, and Their Derivatives". Druglibrary.org. Retrieved 2011-11-26.
- Hanes, William Travis; Sanello, Frank (2004). The Opium Wars: The Addiction of One Empire and the Corruption of Another. Sourcebooks, Inc. p. 34. ISBN 978-1-4022-0149-3.
- Berridge, Virginia; Edwards, Griffith (1981). Opium and the People, Opiate Use in Nineteenth-Century England. Archived from the original on 2013-12-25.
- Organized Crime – American Mafia, Law Library – American Law and Legal Information
- Report on the Enforcement of the Prohibition Laws of the United States. National Commission on Law Observance and Enforcement. Dated January 7th 1931
- "Narconomics". The Economist. 25 June 2014. Retrieved 18 May 2016.
- "Of bongs and bureaucrats". The Economist. 17 January 2014. Retrieved 18 May 2016.
- Laura Smith-Spark and Hada Messia; CNN (11 February 2014). "Gambino, Bonanno family members held in joint US-Italy anti-mafia raid - CNN.com". CNN. Retrieved 18 May 2016.
- "Asia-Pacific | Australian executed in Singapore". BBC News. 2005-12-02. Retrieved 2013-06-09.
- "Two Friends Sent To The Gallows For Drug Trafficking". Bernama.com. Retrieved 2011-11-26.
- Los Angeles Times (18 January 2015). "Outcry after Indonesia executes 6 for drug trafficking". latimes.com. Retrieved 18 May 2016.
- "Organized Crime: The World's Largest Social Network". WIRED. 19 (2). 31 January 2011. Retrieved 18 May 2016.
- "How the Wildlife Trade Relates to Other Illicit Trades". One Green Planet. 2014-08-20. Retrieved 18 May 2016.
- Bill McCollum (April 2002). Threat Posed by the Convergence of Organized Crime, Drug Trafficking, and Terrorism: Congressional Hearing. DIANE Publishing. pp. 39–. ISBN 978-0-7567-2082-7.
- Linda Helfrich. "Refugees in Ecuador". Archived from the original on 2010-06-04. Retrieved 2010-05-31.
- "Estados Unidos denuncia que el 79 porciento de cocaína pasa por Honduras – Radio HRN". Radio HRN. Archived from the original on 11 June 2016. Retrieved 18 May 2016.
- "Honduras Has World's Highest Murder Rate: UN". International Business Times. 2011-11-23. Retrieved 18 May 2016.
- International Crisis Group. "The Tunisian Exception: Success and Limits of Consensus Archived 2014-08-08 at the Wayback Machine". CrisisGroup.org. 5 June 2014. Retrieved 31 July 2014.
- "Drug-Related Crime – Fact sheet – Drug Facts". Whitehousedrugpolicy.gov. Retrieved 2008-10-19.
- "Out of control". The Economist. 2013-03-09. Retrieved 18 May 2016.
- Holmes, Jennifer S.; Piñeres, Sheila Amin Gutiérrez De; Curtin, Kevin M. (2007-04-01). "A Subnational Study of Insurgency: FARC Violence in the 1990s". Studies in Conflict & Terrorism. 30 (3): 249–265. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.553.6185. doi:10.1080/10576100601148456. ISSN 1057-610X.
- Traci Carl (November 3, 2009). "Progress in Mexico drug war is drenched in blood". Associated Press. Retrieved May 4, 2010.
- "Transform". TDPF. Archived from the original on 2011-11-07. Retrieved 2011-11-26.
- El Universal, 24 February 2008, Aumenta narcotráfico por Venezuela
- Neuman, William (26 July 2012). "In Venezuela, Remote Areas Provide a Drug Trafficking Hub « Previous". The New York Times. Retrieved 5 June 2015.
- al-Ameri, Alaa (31 March 2014). "Venezuela's Drug-Running Generals May Be Who Finally Ousts Maduro". Vice News. Retrieved 26 May 2014.
- United Nations, World Drug Report 2010 Statistical Annex: Drug seizures
- "Drug seizures Report From Year: 2009 Until Year: 2012 Drug Group: Cocaine-type". United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime. Retrieved 29 May 2015.
- Raymond, Nate (19 November 2016). "Venezuelan first lady's nephews convicted in U.S. drug trial". Reuters. Retrieved 19 November 2016.
- "Ex-MLB players implicated in major drug trafficking organization, Dominican officials say". CNN. Retrieved 21 August 2019.
- Janus Initiative
- "West Africa and Drug Trafficking". africaecon.org. Africa Economic Institute. Retrieved 14 October 2013.
- "GIABA". GIABA. Retrieved 2013-06-09.
- Kijk magazine, February 2012
- Alexandre Schmidt, UNODC, Amadou Ndiaye, Mu'azu Umaru, GIABA
- "Africa is heroin's new highway to the West". The Economist. 31 January 2019.
- Chouvy, Pierre-Arnaud (2010). Opium: Uncovering the Politics of the Poppy. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press. p. 63. ISBN 9780674051348.
- Bowman, Marion Eugene (2007). Transnational Threats: Smuggling and Trafficking in Arms, Drugs, and Human Life. Westport, CT: Praeger Security International. p. 97. ISBN 9780275994044.
- "Iran is a firm barrier against drug trafficking to Caucasus". Young Journalists Club. yjc.ir. September 18, 2013. Retrieved September 18, 2013.
- McPhedran, Ian (2017). The Smack Track. Sydney: HarperCollins Australia. ISBN 9781460707555.
- Bartlett, Jamie (5 October 2014). "Dark net markets: the eBay of drug dealing". Retrieved 17 May 2015.
- The illicit drug trade in the United Kingdom Archived 2011-02-18 at the UK Government Web Archive Home Office Online Report 20/07
- Syal, Rajeev (2009-12-13). "Drug money saved banks in global crisis, claims UN advisor". The Guardian. London.
- "Why Drug Dealers Live With Their Moms". Los Angeles Times. 2005-04-24.
- Bartilow, Horace; Kihong Eom (Summer 2009). "Free Trader and Drug Smugglers: The Effects of Trade Openness of States' Ability to Combat Drug Trafficking". Latin American Politics and Society. 51 (2): 117–145. doi:10.1111/j.1548-2456.2009.00050.x.
- Lopez Restrepo, Andres; Alvaro Camacho Guizado (2003). "From Smugglers to Warlords: Twentieth Century Colombian Drug Traffickers". Canadian Journal of Latin American and Caribbean Studies. 28 (55/56): 249–275. JSTOR 41800191.
- O'Neil, Shannon (July–August 2009). "The Real War in Mexico: How Democracy Can Defeat the Drug Cartels". Foreign Affairs. 88 (4): 63–77. JSTOR 20699622.
- "Drug Trafficking in the United States". Policy Almanac. Archived from the original on 29 May 2016. Retrieved 18 May 2016.
- Rocha Garcia, Ricardo (2003). "Drug Trafficking and Its Impact on Colombia: An Economic Overview". Canadian Journal of Latin American and Caribbean Studies. 28 (55/56): 277–30. doi:10.1080/08263663.2003.10816844. JSTOR 41800192.
- Quinones, Sam (March–April 2009). "State of War". Foreign Policy. 171 (171): 76–80. JSTOR 20684853.
- Epstein, RJ (18 November 1989). "Drug Wars in the United States". British Medical Journal. 299 (6710): 1275–1276. doi:10.1136/bmj.299.6710.1275. JSTOR 29706058. PMC 1838155. PMID 2513908.
- Naim, Moises (May–June 2009). "The American Prohibition on Thinking Smart in the Drug War". Foreign Policy. 172 (172): 167–168. JSTOR 20684881.
- Gootenberg, Paul (2012). "Cocaine's Long March North, 1900–2010". Latin American Politics. 54 (1): 159–180. doi:10.1111/j.1548-2456.2012.00146.x.
- Martinez Jr., Ramiro; Matthew T. Lee; Amie L. Nielsen (Spring 2004). "Segmented Assimilation, Local Context and Determinants of Drug Violence in Miami and San Diego: Does Ethnicity and Immigration Matter?". International Migration Review. 38 (1): 131–157. doi:10.1111/j.1747-7379.2004.tb00191.x. JSTOR 27645360.
- Jacobson, Mireille (Nov 2004). "Baby Booms and Drug Busts: Trends in Youth Drug Use in the United States, 1975–2000". The Quarterly Journal of Economics. 119 (4): 1481–1512. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.525.5505. doi:10.1162/0033553042476125. JSTOR 25098723.
- Chabat, Jorge (December 2010). "Combatting Drugs in Mexico under Calderon: The Inevitable War" (PDF). CIDE. 205: 1–14. Retrieved 5 November 2013.
- Salvador Maldonado, Aranda (April 2013). "Stories of Drug Trafficking in Rural Mexico: Territories, Drugs and Cartels in Michoacan". European Review of Latin American and Caribbean Studies. 94 (94): 43–66. JSTOR 23408421.
- Morris, Stephen D. (2012-09-07). "Project MUSE". Latin American Research Review. 47 (2): 216–223. doi:10.1353/lar.2012.0011.
- Morris, Stephen. "Drugs, Violence, and Life in Mexico" (PDF): 216–223. Archived from the original (PDF) on 3 December 2013. Retrieved 5 November 2013. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - Campbell, Howard (Winter 2008). "Female Drug Smugglers on the U.S. Mexico Border: Gender, Crime, and Empowerment". Anthropological Quarterly. 81 (1): 233–267. doi:10.1353/anq.2008.0004.
- Thoumi, Francisco (Jul 2002). "Illegal Drugs in Colombia: From Illegal Economic Boom to Social Crisis". The Annals of the American Academy of Political and Social Science. 582 (2): 102–116. doi:10.1177/0002716202058002008. JSTOR 1049737.
- "Marijuana Law and Legal Definition". definitions.uslegal.com.
- Malena Castaldi; Felipe Llambias (11 December 2013). "Uruguay becomes first country to legalize marijuana trade". Reuters.
- "GDS: the world's biggest drug survey". globaldrugsurvey.com.
- "The usage of Marijuana as food ingredients". nutritionfortheworld.wikifoundry.com.
- Greg Campbell (13 July 2012). "Blunt Trauma – Marijuana, the new blood diamonds". The New Republic.
- "Laura Carlsen: How Legalizing Marijuana Would Weaken Mexican Drug Cartels". HuffPost. Retrieved 2013-06-09.
- "Cash From Marijuana Fuels Mexico's Drug War". NPR. 19 May 2010.
- "Measuring America's changing drug habits, on the border". The Washington Post.
- Ioan Grillo. "U.S. Legalization of Marijuana Has Hit Mexican Cartels' Cross-Border Trade". Time.
- Mary Emily O’Hara (8 May 2014). "Legal Pot in the US Is Crippling Mexican Cartels". VICE News.
- "Violent anti-Western extremism is nothing new to Saudi Arabia, but several bombings in the past two years raise fresh questions". Sptimes.com. Retrieved 2013-06-09.
- See McCoy, A; The Politics of Heroin, Lawrence Hill, 2003
- United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime. "Afghanistan Opium Survey 2007" (PDF). Retrieved 2008-01-27. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - "Opium Amounts to Half of Afghanistan's GDP in 2007, Reports UNODC" (Press release). UNODC. 2008-11-16. Archived from the original on 2007-12-02. Retrieved 2007-01-27.
- "News from DEA, Congressional Testimony, 11/09/05". Dea.gov. Archived from the original on 2008-05-16. Retrieved 2008-10-17.
- I talian Police Make Major Heroin Haul On Ship From Iran
- Street Terms: Methamphetamine Office of National Drug Control Policy
- DEA (2008). "Maps of Methamphetamine Lab Incidents". Archived from the original on 2009-09-09.
- Bootie Cosgrove-Mather."Rolling Meth Labs In Vogue – Methamphetamine Makers Turn Vehicles Into Rolling Drug Labs." CBS News. Published July 17, 2002. Retrieved on 2009-02-14.
- NIDA (2008). "NIDA InfoFacts: Methamphetamine".
- Sommerfeld, Julia (February 2001). "Beating an addiction to meth". Meth's Deadly Buzz. NBC News. Retrieved 2008-06-29.
- ""Tik": Crystal meth in Cape Town". Unodc.org. Retrieved 8 October 2017.
- Huang, Jende (2012-02-07). "Spreading Meth across the Chinese-North Korean Border". Retrieved 7 June 2012.
- MARK SCHLIEBS (20 May 2013). "Purity on the rise as ice tops the drugs wave". The Australian. Retrieved 20 May 2013.
- Alex Robertson (2003-10-10). "Deadly 'jellies' flood city from Eastern Europe; Police chiefs fear drug-fueled crime surge as home-made tablets hit streets again". Evening Times.
- European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction (EMCDDA), 2006. Annual Report 2006: The State of the Drugs Problem in Europe, EMCDDA, Luxembourg.
- UNODC Office for Russia and Belarus, Illicit drug trends in the Russian Federation 2005. Moscow: UNODC, 2006
- Niaz, K (1998). Drug Abuse Monitoring System in Rawalpindiislamabad. Report of the Asian Multicity Epidemiology Workgroup. Eds. Navaratnam V and Bakar A.A., 151-l 60.
- Morrison V (April 1989). "Psychoactive substance use and related behaviours of 135 regular illicit drug users in Scotland". Drug Alcohol Depend. 23 (2): 95–101. doi:10.1016/0376-8716(89)90013-6. PMID 2702930.
- Sakol MS, Stark C, Sykes R (April 1989). "Buprenorphine and temazepam abuse by drug takers in Glasgow--an increase". Br J Addict. 84 (4): 439–41. doi:10.1111/j.1360-0443.1989.tb00589.x. PMID 2566343.
- Lavelle TL, Hammersley R, Forsyth A (1991). "The use of buprenorphine and temazepam by drug injectors". J Addict Dis. 10 (3): 5–14. doi:10.1300/J069v10n03_02. PMID 1932153.
- Hammersley R, Lavelle T, Forsyth A (February 1990). "Buprenorphine and temazepam--abuse". Br J Addict. 85 (2): 301–3. doi:10.1111/j.1360-0443.1990.tb03088.x. PMID 1969295.
- Hammersley R, Cassidy MT, Oliver J (July 1995). "Drugs associated with drug-related deaths in Edinburgh and Glasgow, November 1990 to October 1992". Addiction. 90 (7): 959–65. doi:10.1046/j.1360-0443.1995.9079598.x. PMID 7663317.
- Forsyth AJ, Farquhar D, Gemmell M, Shewan D, Davies JB (May 1993). "The dual use of opioids and temazepam by drug injectors in Glasgow (Scotland)". Drug Alcohol Depend. 32 (3): 277–80. doi:10.1016/0376-8716(93)90092-5. PMID 8348877.
- Chowclhury, S. & R&ma& A. (1998). Pattern and trends of drug abuse in Dh&a, Bangladesh. Report of the Asian Multicity Epidemiology Workgroup. Eds. Navamtnam V. and B&a-, A. A.. 144-50.
- Baumevieille M, Haramburu F, Bégaud B (1997). "Abuse of prescription medicines in southwestern France". Ann Pharmacother. 31 (7–8): 847–50. doi:10.1177/106002809703100706. PMID 9220042.
- Chapleo, C-B.; Reisinger, M.; Rindom, H. (1997). "European update". Research & Clinical Forums. 19: 33–38.
- Chatterjee A, Uprety L, Chapagain M, Kafle K (1996). "Drug abuse in Nepal: a rapid assessment study". Bull Narc. 48 (1–2): 11–33. PMID 9839033.
- Crowley, Julian (2011-11-08). "BUSINESS 10 Largest Illegal Drug Trades on Earth". Business Pundit. Retrieved 30 March 2019.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Illegal drug trade. |
