Kent County, Michigan
Kent County is a county in the U.S. state of Michigan. As of the 2010 census, the county had a population of 602,622.[2] Its county seat is Grand Rapids.[3] The county was set off in 1831, and organized in 1836.[1] It is named for New York jurist and legal scholar James Kent,[4] who represented the Michigan Territory in its dispute with Ohio over the Toledo Strip.
Kent County | |
|---|---|
 Kent County Courthouse | |
 Flag  Seal | |
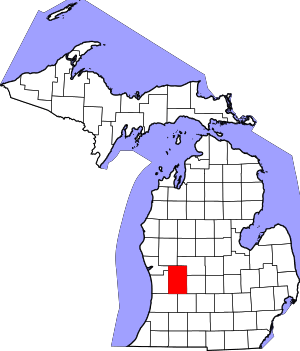 Location within the U.S. state of Michigan | |
 Michigan's location within the U.S. | |
| Coordinates: 43°02′N 85°33′W | |
| Country | |
| State | |
| Founded | March 2, 1831 (created) 1836 (organized)[1] |
| Named for | James Kent |
| Seat | Grand Rapids |
| Largest city | Grand Rapids |
| Area | |
| • Total | 872 sq mi (2,260 km2) |
| • Land | 847 sq mi (2,190 km2) |
| • Water | 25 sq mi (60 km2) 2.9%% |
| Population | |
| • Estimate (2019) | 656,955 |
| • Density | 766/sq mi (296/km2) |
| Time zone | UTC−5 (Eastern) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−4 (EDT) |
| Congressional districts | 2nd, 3rd |
| Website | www |
Kent County is part of the Grand Rapids–Kentwood Metropolitan Statistical Area and is West Michigan's economic and manufacturing center. It is home of the Frederik Meijer Gardens, a significant cultural landmark of the Midwest. The Gerald R. Ford International Airport is the county's primary location for regional and international airline traffic.
Traditionally a stronghold for the Republican Party, the Democratic Party has received increased support since the 2000s, with Grand Rapids and nearby suburbs supporting the Democratic Party while more rural areas support the Republican Party.[5][6] In 2008, Barack Obama became the first Democratic presidential candidate to carry the county since 1964.
History
The Grand River runs through the county. On its west bank are burial mounds, remnants of the Hopewell Indians who lived there.[7] The river valley was an important center for the fur trade in the early 19th century. After the War of 1812, Rix Robinson and Louis Campau were the earliest traders in the area.[8] In 1826, Campau established a trading post in what is today Grand Rapids. In 1831, he bought land and platted the town. Campau considered the town's "father".[9][10][11] One year later, government surveyor Lucius Lyon purchased land north of Campau's property. Campau surveyed and platted the village following Native American trails[10] and Lyon had platted his property in an English grid format, which meant there were two adjoining villages, with different platting formats.[10] Campau later merged the villages under the name of Grand Rapids.[10]
In 1831, it was set off from Kalamazoo County.[12] In 1838, Grand Rapids was incorporated[10] as the county's first village. By the end of the century, stimulated by the construction of several sawmills, the area was a significant center for agriculture, logging, and manufacturing furniture.
Geography
.jpeg)
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has an area of 872 square miles (2,260 km2), of which 847 square miles (2,190 km2) is land and 25 square miles (65 km2) (2.9%) is water.[13] Kent County's highest point is Fisk Knob Park,[14] in Solon Township, at 1048 feet.[15]
Rivers
The Grand River flows through the county from its eastern border to the west, and after passing through Ottawa County, empties into Lake Michigan at Grand Haven. It has three tributaries in Kent County, listed in order of convergence:
- Flat River, enters the county from the east, and joins the Grand from the north, in Lowell.
- Thornapple River, enters the county from the south, and joins the Grand in Ada.
- Rogue River, enters the county from the north, and joins the Grand in Belmont.
Trails
These hiking and biking trails run through the county:
- North Country Trail, runs north/south the length of the county, passing through Cedar Springs, Grattan and Lowell. Lowell is the trail's half-way point, and the national headquarters of the North Country Trail Association is located here.
- Thornapple Trail, begins in Kentwood and runs southeast through Dutton and Caledonia.
- White Pine Trail begins in Comstock Park and runs northeast through Belmont, Rockford, Cedar Springs, and Sand Lake.
- Kent Trails (which is singular in spite of the 's') runs north/south from John Ball Park in Grand Rapids to 84th Street in Byron Township, with an extension that runs east/west along 76th Street and north/south from 76th Street to Douglas Walker Park on 84th street.
- The Frederik Meijer Trail, which, as of November, 2008, was incomplete, runs east/west mostly along the M-6 freeway and will connect the Kent Trails and the Thornapple Trail when completed.
- Cannon Township Trail runs through Cannon Township in the eastern part of the county from Cannon Township Center on M-44. It runs along M-44 then south near Sunfish Lake Road, turning east through the Cannonsburg Cemetery, and ends at Warren Townsend Park near Cannonsburg.
Adjacent counties
.jpeg)
- Newaygo County - north
- Montcalm County - northeast
- Muskegon County - northwest
- Ionia County - east
- Ottawa County - west
- Allegan County, - southwest
- Barry County - southeast
Demographics
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1840 | 2,587 | — | |
| 1850 | 12,016 | 364.5% | |
| 1860 | 30,716 | 155.6% | |
| 1870 | 50,403 | 64.1% | |
| 1880 | 73,253 | 45.3% | |
| 1890 | 109,922 | 50.1% | |
| 1900 | 129,714 | 18.0% | |
| 1910 | 159,145 | 22.7% | |
| 1920 | 183,041 | 15.0% | |
| 1930 | 240,511 | 31.4% | |
| 1940 | 246,338 | 2.4% | |
| 1950 | 288,292 | 17.0% | |
| 1960 | 363,187 | 26.0% | |
| 1970 | 411,044 | 13.2% | |
| 1980 | 444,506 | 8.1% | |
| 1990 | 500,631 | 12.6% | |
| 2000 | 574,335 | 14.7% | |
| 2010 | 602,622 | 4.9% | |
| Est. 2019 | 656,955 | [16] | 9.0% |
| U.S. Decennial Census[17] 1790-1960[18] 1900-1990[19] 1990-2000[20] 2010-2019[2] | |||
As of the 2010 United States Census,[21] there were 602,622 people living in the county. 76.1% were non-Hispanic White, 10.2% Black or African American, 2.4% Asian, 0.7% Native American, 4.5% of some other race and 2.6% of two or more races. 9.7% were Hispanic or Latino (of any race).

As of the census[22] of 2000, there were 574,335 people, 212,890 households, and 144,126 families living in the county. The current estimated population is 604,323. The population density was 671 people per square mile (259/km²). There were 224,000 housing units at an average density of 262 per square mile (101/km²). The racial makeup of the county was 83.13% White, 8.93% Black or African American, 0.52% Native American, 1.86% Asian, 0.06% Pacific Islander, 3.34% from other races, and 2.16% from two or more races. 7.00% of the population were Hispanic or Latino of any race.
19.6% reported being of Dutch ancestry; 14.9% German, 13.1% English, 7.4% Irish, 7.1% Polish and 5.5% American ancestry according to the 2010 American Community Survey.[23] 90.0% spoke only English at home, while 6.0% spoke Spanish.
There were 212,890 households out of which 35.80% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 52.30% were married couples living together, 11.60% had a female householder with no husband present, and 32.30% were non-families. 25.60% of all households were made up of individuals and 8.00% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.64 and the average family size was 3.20.
The age distribution of the county was as follows: 28.30% were under the age of 18, 10.50% from 18 to 24, 31.20% from 25 to 44, 19.70% from 45 to 64, and 10.40% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 32 years. For every 100 females, there were 96.90 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 93.70 males.
The median income for a household in the county was $45,980, and the median income for a family was $54,770. Males had a median income of $39,878 versus $27,364 for females. The per capita income for the county was $21,629. 8.90% of the population and 6.30% of families were below the poverty line. 10.20% of the population under the age of 18 and 7.50% of those 65 or older were living in poverty.
Transportation
Air service
Commercial air service to Grand Rapids is provided by Gerald R. Ford International Airport (GRR). Previously named Kent County International Airport, it holds Grand Rapids' mark in modern history with the United States' first regularly scheduled airline service, beginning July 31, 1926, between Grand Rapids and Detroit.
Bus service
Public bus transportation is provided by the Interurban Transit Partnership, which brands itself as "The Rapid." Transportation is also provided by the DASH buses: the "Downtown Area Shuttle." These provide transportation to and from the parking lots in the city of Grand Rapids to various designated loading and unloading spots around the city.
Railroad
Amtrak provides direct train service to Chicago from the passenger station via the Pere Marquette line. Freight service is provided by CN, CSX Transportation, and by a local short-line railroad, the Grand Rapids Eastern Railroad.
Highways
County-designated highways


Economy
These corporations are headquartered in Kent County, in the following communities:
- Amway, Ada
- American Seating, Grand Rapids
- Bissell Homecare, Walker
- Gordon Food Service, Wyoming
- Meijer, Walker
- Old Orchard, Sparta
- Spartan Stores, Byron Township
- Steelcase, Grand Rapids
- Universal Forest Products, Northview
- Wolverine Worldwide, Rockford
- X-Rite, Kentwood
- Zondervan, Cascade Township
Government
The county government operates the jail, maintains rural roads, operates the major local courts, keeps files of deeds and mortgages, maintains vital records, administers public health regulations, and participates with the state in the provision of welfare and other social services. The county board of commissioners controls the budget but has only limited authority to make laws or ordinances. In Michigan, most local government functions—police and fire, building and zoning, tax assessment, street maintenance, etc.—are the responsibility of individual cities and townships.
Elected officials
- Prosecuting Attorney: Chris Becker (Republican)
- Sheriff: Michelle LaJoye-Young (Republican)
- County Clerk/Register of Deeds: Lisa Posthumus Lyons (Republican)
- County Treasurer: Kenneth Parrish (Republican)
- Drain Commissioner: Ken Yonker (Republican)
- County Commission or Board of Commissioners: 19 members, elected from districts (11 Republicans, 8 Democrats), Mandy Bolter (Republican) serves as board chair.[24]
- Circuit Court: 10 judges (non-partisan)
- Probate Court: 3 judges (non-partisan)
(information as of post-2018 election)
Politics
| Year | Republican | Democratic | Third Parties |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | 47.7% 148,180 | 44.6% 138,683 | 7.7% 24,031 |
| 2012 | 53.0% 155,925 | 45.4% 133,408 | 1.7% 4,873 |
| 2008 | 48.8% 148,336 | 49.3% 149,909 | 1.8% 5,554 |
| 2004 | 58.9% 171,201 | 40.2% 116,909 | 1.0% 2,781 |
| 2000 | 59.4% 148,602 | 38.1% 95,442 | 2.5% 6,274 |
| 1996 | 54.3% 121,335 | 38.5% 85,912 | 7.2% 16,132 |
| 1992 | 47.5% 115,285 | 33.9% 82,305 | 18.5% 44,963 |
| 1988 | 63.8% 131,910 | 35.5% 73,467 | 0.7% 1,465 |
| 1984 | 67.0% 137,417 | 32.3% 66,238 | 0.7% 1,365 |
| 1980 | 54.6% 112,604 | 35.3% 72,790 | 10.1% 20,896 |
| 1976 | 67.2% 126,805 | 31.3% 59,000 | 1.5% 2,828 |
| 1972 | 59.3% 104,041 | 38.5% 67,587 | 2.2% 3,833 |
| 1968 | 53.7% 85,810 | 38.7% 61,891 | 7.6% 12,149 |
| 1964 | 43.4% 66,830 | 56.4% 86,860 | 0.2% 269 |
| 1960 | 60.7% 95,477 | 39.0% 61,313 | 0.3% 506 |
| 1956 | 65.7% 94,969 | 33.8% 48,871 | 0.4% 642 |
| 1952 | 62.1% 79,647 | 36.8% 47,221 | 1.1% 1,447 |
| 1948 | 54.3% 53,669 | 43.7% 43,205 | 1.9% 1,902 |
| 1944 | 54.7% 54,163 | 44.1% 43,679 | 1.3% 1,274 |
| 1940 | 52.1% 53,131 | 47.2% 48,196 | 0.7% 749 |
| 1936 | 42.9% 36,633 | 52.6% 44,823 | 4.5% 3,848 |
| 1932 | 48.6% 42,186 | 48.0% 41,601 | 3.4% 2,936 |
| 1928 | 75.1% 56,573 | 24.2% 18,229 | 0.7% 508 |
| 1924 | 76.6% 45,207 | 13.5% 7,982 | 9.9% 5,819 |
| 1920 | 70.1% 40,802 | 25.4% 14,763 | 4.5% 2,610 |
| 1916 | 42.5% 16,095 | 53.7% 20,364 | 3.8% 1,444 |
| 1912 | 20.4% 6,498 | 29.5% 9,412 | 50.2% 16,016 |
| 1908 | 55.4% 16,576 | 38.3% 11,445 | 6.3% 1,880 |
| 1904 | 71.6% 20,254 | 22.7% 6,430 | 5.6% 1,593 |
| 1900 | 54.8% 17,861 | 42.3% 13,775 | 3.0% 962 |
| 1896 | 54.3% 17,053 | 43.3% 13,582 | 2.4% 749 |
| 1892 | 46.3% 12,388 | 43.1% 11,533 | 10.6% 2,829 |
| 1888 | 49.4% 12,811 | 45.8% 11,864 | 4.8% 1,254 |
| 1884 | 45.7% 9,007 | 49.0% 9,639 | 5.3% 1,045 |
Historically, Kent County has been rather conservative for an urban county. It supported the Republican Party in all but three elections from 1884 to 2004.
Since the 2000s, Grand Rapids, the county's largest city, and its inner-ring suburbs have favored the Democratic Party, while outer suburbs of Grand Rapids have remained mostly Republican.[5][6] Grand Rapids also normally sends Democrats to the state legislature, who are usually the only elected Democrats above the county level.
In 2008, Democratic presidential candidate Barack Obama narrowly carried the county, receiving 49.34% of its votes to Republican John McCain's 48.83%.[26] It was the first time the county had supported a Democrat for president since 1964, and only the fourth time since 1884. By comparison, George W. Bush had taken almost 59 percent of the county's vote in 2004.
In 2012, the county returned to the Republican camp as Mitt Romney won 53.0% of the vote to Obama's 45.35%.[27] Four years later, Republican Donald Trump won the county with 47.66% of the vote, to 44.61% for his Democratic rival, Hillary Clinton, while Gary Johnson of the Libertarian Party received 4.58%.[28]
Communities
Cities
- Cedar Springs
- East Grand Rapids
- Grand Rapids (county seat)
- Grandville
- Kentwood
- Lowell
- Rockford
- Walker
- Wyoming
Census-designated places
Other unincorporated communities
- Ada
- Alaska
- Alto
- Belmont
- Cannonsburg
- Cascade
- Dutton
- Englishville
Townships
- Ada Township
- Algoma Township
- Alpine Township
- Bowne Township
- Byron Township
- Caledonia Township*
- Cannon Township
- Cascade Township*
- Courtland Township
- Gaines Township*
- Grand Rapids Township*
- Grattan Township
- Lowell Township*
- Nelson Township
- Oakfield Township
- Plainfield Township*
- Solon Township
- Sparta Township
- Spencer Township
- Tyrone Township
- Vergennes Township
(* denotes Charter status)
See also
- Kent District Library
- List of Michigan State Historic Sites in Kent County, Michigan
- National Register of Historic Places listings in Kent County, Michigan
References
- Clarke Historical Library. "Bibliography on Kent County". Central Michigan University. Retrieved January 19, 2013.
- "State & County QuickFacts". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on July 6, 2011. Retrieved August 28, 2013.
- "Find a County". National Association of Counties. Archived from the original on May 31, 2011. Retrieved June 7, 2011.
- Gannett, Henry (1905). The Origin of Certain Place Names in the United States. Washington, DC: Government Printing Office. pp. 173.
- Tavernise, Sabrina; Gebeloff, Robert; Lee, Christopher (October 25, 2019). "Are the Suburbs Turning Democratic?". The New York Times. Retrieved January 23, 2020.
- Burnett, Sara; Eggert, David (March 28, 2019). "Trump's return to west Michigan comes amid Democratic gains". Associated Press. Retrieved January 23, 2020.
- Beld, Gordon G. (2012). Grand Times in Grand Rapids: Pieces of Furniture City History. The History Press. pp. 17–19. ISBN 9781609496296 – via Google Books.
- Fuller, George Newman (1916). Economic and Social Beginnings of Michigan. Wynkoop Hallenbeck Crawford. p. 423 – via Internet Archive.
- History and Directory of Kent County, Michigan, Containing a History of Each Township, and the City of Grand Rapids; the Name, Location and Postoffice Address of All Residents Outside of the City: A List of Postoffices in the County; a Schedule of Population; and Other Valuable Statistics. Grand Rapids, MI: Daily Eagle Steam Printing House. November 21, 1870. pp. 114–136.
- Ellison, Garret (May 22, 2014). "How a feud between the city's founding fathers shaped Monroe Center and downtown Grand Rapids". MLive.
- Garret Ellison (August 11, 2013). "History in bronze: Influential figures immortalized at 12 sites so far in Grand Rapids". MLive.
- Purkey, Thomas H. (1986). Soil Survey of Kent County, Michigan. United States Department of Agriculture Soil Conservation Service. p. 2 – via Google Books.
- "2010 Census Gazetteer Files". United States Census Bureau. August 22, 2012. Archived from the original on November 13, 2013. Retrieved September 26, 2014.
- "Fisk Knob". Kent County Parks. Grand Valley State University. Archived from the original on November 5, 2016.
- Google. "Highest Point in Kent County" (Map). Google Maps. Google.
- "Population and Housing Unit Estimates". Retrieved March 26, 2020.
- "U.S. Decennial Census". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved September 26, 2014.
- "Historical Census Browser". University of Virginia Library. Retrieved September 26, 2014.
- "Population of Counties by Decennial Census: 1900 to 1990". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved September 26, 2014.
- "Census 2000 PHC-T-4. Ranking Tables for Counties: 1990 and 2000" (PDF). United States Census Bureau. Retrieved September 26, 2014.
- "U.S. Census website". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved May 24, 2016.
- "U.S. Census website". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved January 31, 2008.
- "2010 Data Release – Data & Documentation – American Community Survey – U.S. Census Bureau". Archived from the original on October 27, 2015.
- "Kent County Commissioners elect Mandy Bolter as new board chair". mlive.com. January 3, 2019. Retrieved January 3, 2019.
- Leip, David. "Dave Leip's Atlas of U.S. Presidential Elections". uselectionatlas.org. Retrieved April 2, 2018.
- "State Data". Dave Leip's Atlas of U.S. Presidential Elections.
- http://uselectionatlas.org/RESULTS/statesub.php?year=2012&fips=26081&off=0&elect=0&f=0
- http://uselectionatlas.org/RESULTS/statesub.php?year=2016&fips=26081&off=0&elect=0&f=0
Further reading
- Romig, Walter (1986) [1973]. Michigan Place Names: The History of the Founding and the Naming of More than Five Thousand Past and Present Michigan Communities. Great Lakes Books. Detroit: Wayne State University Press. ISBN 978-0814318386.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Kent County, Michigan. |
- Official Website of Kent County, Michigan
- Official GIS Map of Kent County, Michigan
- History and Genealogy of Kent County, Michigan
- Kent County Open Government Project - A non-partisan resource for comparing tax rates, school districts, and local government transparency across Kent County
- "Bibliography on Kent County". Clarke Historical Library, Central Michigan University. Retrieved January 19, 2013.
