Grand Quartier Général (1939–1940)
The Grand Quartier Général (abbreviated to GQG or Grand QG in spoken French) was the general headquarters of the French Army during the Second World War.[1] Originally established in 1911, GQG was re-established on the outbreak of war in 1939, the original GQG had functioned from 1914 to 1919 during the First World War. In the inter-war years, the plans for activation of GQG changed considerably, with the formation switching from an offensive-oriented position near the German border at Metz in the 1920s gradually westwards. By 1938 its planned base was at the Château de Vincennes in the suburbs of Paris, from where it was expected to conduct a defensive war.
| Grand Quartier Général | |
|---|---|
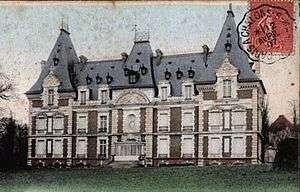 The chateau at Montry, home of the GQG staff from 18 January – 8 June 1940 | |
| Active | 3 September 1939–1 July 1940 |
| Country | France |
| Branch | French Army |
| Role | General Headquarters |
| Nickname(s) | GQG or Grand QG |
| Commanders | |
| 1939–1940 | Maurice Gamelin |
| 1940 | Maxime Weygand |
Activated in 1939 upon the mobilisation of the French Army, GQG struggled with an awkward distribution of staff between Vincennes and a number of more distant towns (including the staff of the important North-East army). The French chief of staff, General Maurice Gamelin, found this situation unworkable and instituted reforms in January 1940. The changes upset the North-East army commander General Alphonse Joseph Georges and were ill-received by the British army.
GQG responded slowly to the German attack into France when it eventually came in early May 1940. With the French and British armies in retreat, GQG was somewhat rejuvenated by the replacement of Gamelin with Maxime Weygand on 19 May. The boost was short lived and continued French reversals in the Battle of France forced the GQG staff to move south-west away from the advancing German forces. By the time of the signing of the Second Armistice at Compiègne on 22 June 1940, GQG was at Montauban, near Toulouse. GQG was disbanded on 1 July 1940, after the surrender to Germany.
Organisation

The GQG was established in 1911 as the wartime command structure of the French Army, the counterpart of the peacetime Conseil Supérieur de la Guerre (CSG).[2] The GQG was activated upon the general mobilisation of the army and remained active until stood down by the French parliament. GQG had been active during the First World War from mobilisation on 2 August 1914 until it was stood down on 20 October 1919.[3][4]
In the inter-war years there was much debate over how the French high command should be organised, including the role and location of GQG. In the years following the deactivation of the First World War's GQG it was planned that any new GQG would have control of only the metropolitan theatre of operations. The structure was to consist of a commander-in-chief, a major-général and three aide-majors. There were to be four bureaus with different areas of responsibility, much like the GQG of the First World War. The First Bureau dealt with organisation, the Second Bureau with information, the Third Bureau with military operations and the Fourth Bureau with logistics. There would also have been a Bureau of Personnel, a Courier Section, a group of Inspector-Generals and a group composed of units and services particular to GQG. A reorganisation proposal was submitted to Marshal Philippe Pétain (Vice-Chairman of the CSG) in 1928, which sought to reduce the sluggishness and inefficiency within the unit. In 1933 another proposed amendment sought to clarify the commander-in-chiefs powers. It was proposed that he would continue to have authority over just the metropolitan theatre but would act as an advisor to all other theatres and as a coordinator with any allied forces. However no reforms were implemented.[5]
The GQG was finally reorganised upon the appointment of General Maurice Gamelin as Chief of the General Staff for National Defence and General Alphonse Joseph Georges as head of the north-east army in 1938. On 28 September 1938 the new responsibilities of GQG were set out in a memorandum.[5] The structure changes only slightly, introducing another aide-major and making changes to the role of the inspector-generals. The function of the GQG was, however, radically altered. The new GQG is expected to act both as commander of the metropolitan theatre (also responsible for the north-east army), as before, and as overall commander of all French ground forces. Gamelin, as commander-in-chief, decided to form his own staff, separate from the GQG organisation, and to establish a separate command post away from GQG. This structure was the form brought into operation as the wartime GQG in 1939.[5]
Location of GQG

Much thought was given to the physical location of GQG headquarters. In its First World War incarnation GQG had established its headquarters fairly close to the front and it had been forced to move with the armies during the Retreat from Mons, eventually establishing itself near Paris at Chantilly where it remained for most of the war.[4] Army planners considered many different factors such as accessibility, telephone provision, security, protection from aerial attack and the need to be close to political leaders.[5]
For the first part of the 1920s GQG was to be established at the army headquarters of the Metz region, sited in accordance with the contemporary French plans in case of war with Germany. French war plans at the time called for a quick offensive strike to occupy the Rhineland for which Metz was well suited. The site was changed to Chalons-sur-Marne in the later 1920s, reflecting a change in French war plans from the offensive to the defensive. This however, proved susceptible to aerial attack and GQG was switched to Vertus, 20 miles (32 km) west of Chalons. Virtus' small towns provided the potential to disperse GQG in different locations and the extensive wine cellars could be transformed into air raid shelters. However the site was still considered insufficient in regards to defence against aerial attack and so in March 1935 the site of La Ferté-sous-Jouarre was chosen. The site proved unsuited to dispersal of GQG elements and so the plan was later altered to allow the rear echelon bureaus to be established at Meaux, 20 kilometres (12 mi) away.[5]
The appointment of Gamelin led to a further change of location, as he sought to reconcile his roles as theatre commander (demanding close proximity to the field armies) and as commander-in-chief (which required working alongside the Paris-based Minister of National Defence). Gamelin established his own command post, separate from the GQG structure, at the Château de Vincennes in the eastern suburbs of Paris, a site originally earmarked for the command post of the French Navy. By doing so he avoided direct pressure from the political body and involvement with the day-to-day affairs of the GQG, still sited at La Ferté-sous-Jouarre and Meaux.[5]
GQG at war
Activation
Upon the outbreak of war GQG was activated and its constituent departments dispatched to their posts. Gamelin and his staff to Vicennes; Georges and his north-east army staff, General Henri-Marie-Auguste Bineau (the major-général), the First, Second, Third and Fourth Bureaus, the postal, personnel, security, rail and wireless departments to La Ferté-sous-Jouarre and the service branches and inspector-generals to Meaux. Gamelin and his staff were housed in "T" bunker, a three-level underground facility built in 1832. Georges and his staff were housed at Chateau Bondons, an eighteenth-century house in a 5 hectares (12 acres) park beside the Marne with no fewer than 70 other properties utilised in or around the town to better disperse the staff in case of aerial attack. At Meaux 24 different properties were utilised, including at nearby Lizy-sur-Ourcq, Esbly and Condé-Sainte-Libiaire. This considerable fragmentation of the staff prevented effective communication between departments and generated unnecessary paperwork.[5] Gamelin and the GQG staff hosted the Duke of Windsor to dinner on 14 October 1939.[6]
January 1940 reform

Gamelin had been considering reform of GQG since November, owing to the complexity of its organisation and friction between him and Georges over their individual responsibilities. A new structure was implemented on 6 January 1940, despite the protests of Georges. Georges ceased to be involved with the GQG and a new headquarters staff was drawn up with officers taken from the bureaus supplemented by some seconded from the field armies. The Northeast Army was recognised as the most important in the field and to ensure its logistics were handled effectively the 4th bureau took over direct responsibility for its rear supply lines. To facilitate this the officers of the fourth bureau and the inspector-generals, whilst remaining under the nominal command of the major-général, received their orders direct from Georges.[5]
From 18 January much of the new GQG was established at the 19th-century castle of the Rothschild family at Montry, Seine-et-Marne. The second bureau and the postal staff were provided new quarters nearby Esbly and Saint-Germain-sur-Morin while the inspector-generals and a few other staff remained at Meaux. General Bineau, having reached the age limit for retirement, was replaced by General Aimé Doumenc.[5] Doumenc's aide-major-général was Louis-Marie Koeltz.[7]
Gamelin's reforms were not well received. The focus of GQG on the Northeast Army led to difficulties in carrying out duties for the other field armies, the restructuring increased tensions between Gamelin and Georges and presented difficulties to the individual army staffs and the British Army who did not know whom to report to.[5]
With the ongoing Phoney War life at GQG was dull and monotonous, occasionally broken by social and leisure events, and some officers requested a transfer to the combat units in the hope of getting more exciting work. Security was tight with all comings and goings from the buildings monitored and a 9pm curfew implemented for all enlisted personnel. Visitors noted a marked difference between the two sections of GQG with Gamelin's staff described as unfriendly and cold and Georges as more welcoming and cheerful. A climate of mutual distrust existed between the two sections.[5] This has been compared to a cold war between Gamelin and Georges.[8] Georges said of Gamelin's reforms that "he takes the GQG and leaves me with [the responsibility]". The reorganisation was also ill-received by the British staff with General John Swayne, attached to Georges' headquarters, saying "however illogical the original organisation may have been it had settled down and it was generally felt that it was not the time to break up the organisation and create difficulties of working".[9]
German invasion
After the German offensive into France began on 10 May 1940 GQG was found to be too unwieldy to respond quickly. Some changes were made, with Doumenc and the head of the fourth bureau moving from Montry to Georges' headquarters at Ferte-sous-Jouarre to better liaise with the Northeast Army.[5]

Initially optimistic about the state of their defences the staff at GQG became more nervous after the fall of Sedan on 14 May. Struggling to find reserves to stem the German advance the GQG officers worked longer and longer hours and relations with other units became fraught. On 19 May Gamelin, who had been under pressure from president of the CSG Paul Reynaud to resign since before the offensive, was replaced by General Maxime Weygand. Weygand's arrival restored some energy to GQG and improved relations with Georges but worsening results in the field and the unfolding collapse of the French army soon shook their confidence.[5]
The speed of the German advance threatened the security of the GQG headquarters itself and it was soon forced to pull back from the front lines. GQG established its point of retreat to be Briare in Loiret on 17 May to be close to Tours, the place designated as a fallback location for the French government ministries in Paris. The move was ordered at 14.30 on 8 June, having been delayed by Weygand in an attempt to preserve the morale of French armies in the field. The move was carried out from midnight that night and through the next day by rail and road to in stages to preserve continuity of command. The last elements of GQG withdrew from Montry at 10.00 on 9 June, with German forces just a few miles away. General Georges joined Weygand at Briare, uniting their commands for the first time.[5]

At Briare GQG took up residence in nearby Vaugereau, Weygand and Doumenc at the Mugeut Chateau and Georges in the Beauvoir Castle in Briare itself. The reduced distances between the various units led to greater efficiency for GQG, but the French retreat soon forced them to move again.[5] At 17.00 on 15 June GQG moved south to Vichy, on 17 June to Ussel, 19 June to La Bourboule and 20 June to Montauban.[5][7] These movements had little fore-planning and GQG was forced to occupy whatever spaces were available, including hotels, spas and schools. The staff officers of GQG, spending much of their time on the road, grew despondent and frustrated at not being able to fight the enemy directly. The eventual signing of the armistice was greeted with a sense of acceptance and relief. GQG moved one last time to Clermont-Ferrand at the end of June prior to its disbandment on 1 July 1940.[5]
See also
References
- Edmonds, J. E. (1991) [1948]. Military Operations France and Belgium 1917: 7 June – 10 November. Messines and Third Ypres (Passchendaele). History of the Great War Based on Official Documents by Direction of the Historical Section of the Committee of Imperial Defence. II (Imperial War Museum & Battery Press ed.). London: HMSO. ISBN 0-89839-166-0.
- King, Jere Clemens (1951). Generals & Politicians: Conflict Between France's High Command, Parliament, and Government, 1914-1918. Berkeley & Los Angeles, USA: University of California Press. p. 13.
- King, Jere Clemens (1951). Generals & Politicians: Conflict Between France's High Command, Parliament, and Government, 1914-1918. Berkeley & Los Angeles, USA: University of California Press. p. 15.
- LaGarde, Lieutenant Benoit. "Grand Quartier Général 1914-1918" (PDF). Sous-Serie GR 16 NN — Répertoire Numérique Detailleé (in French). Service Historique de Défense. Retrieved 18 January 2013.
- Garçon, Ségolène (2007). "Travailler au Grand Quartier général des Forces Terrestres en 1939-1940" [Work at the General Headquarters of French Land Forces in 1939-1940]. Revue historique des armées (in French). 248: 71–81. ISSN 1965-0779.
- Bloch, Michael (1982). The Duke of Windsor's War. London: Hachette.
- Chapman, Guy (2011). Why France Collapsed. Bloomsbury. p. Appendix A.
- Blatt, Joel (1998). The French Defeat of 1940: Reassessments. New York: Berghahn. p. 276. ISBN 1-57181-109-5.
- Blatt, Joel (1998). The French Defeat of 1940: Reassessments. New York: Berghahn. p. 277. ISBN 1-57181-109-5.