Globulin
The globulins are a family of globular proteins that have higher molecular weights than albumins and are insoluble in pure water but dissolve in dilute salt solutions. Some globulins are produced in the liver, while others are made by the immune system. Globulins, albumins, and fibrinogen are the major blood proteins. The normal concentration of globulins in human blood is about 2.6-3.5 g/dL.
The term "globulin" is sometimes used synonymously with "globular protein". However, albumins are also globular proteins, but are not globulins. All other serum globular proteins are globulins.
Types of globulins
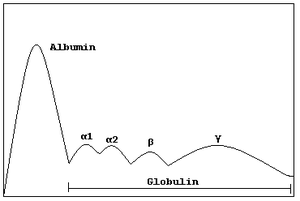
All globulins fall into one of the following four categories :
- Alpha 1 globulins
- Alpha 2 globulins
- Beta globulins
- Gamma globulins (one group of gamma globulins is the immunoglobulins, which are also known as "antibodies")
Globulins can be distinguished from one another using serum protein electrophoresis.
Globulins exert oncotic pressure. Their deficiency results in loss of carrier functions of globulins, oedema due to decreased oncotic pressure, and susceptibility to infections due to decreased gamma-globulins (immuno-globulins) leading to decreased production of antibodies.
Sizes ~ weights
Globulins exist in various sizes. The lightest globulins are the alpha globulins, which typically have molecular weights of around 93 kDa, while the heaviest class of globulins are the gamma globulins, which typically weigh about 1193 kDa. Being the heaviest, the gamma globulins are among the slowest to segregate in gel electrophoresis.
The immunologically active gamma globulins are also called "immunoglobulins" or "antibodies".
Human blood plasma levels
The normal concentration of globulins in human blood is about 2.6-4.6 g/dL.
Nonhuman globulins
Globulin proteins exist not only in other animal species, but also in plants. Vicilin and legumin, from peas and other legumes, function as protein storage within seeds. These proteins can cause allergic reactions if they bind with human IgE antibodies.[1]
Pseudoglobulins and euglobulins
Pseudoglobulins are a class of globulins that are more soluble in ammonium sulfate than euglobulins. Pseudoglobulins are also soluble in pure water, while euglobulins are not.[2]
References
- SanchMonge, R.; Lopez-Torrejón, G.; Pascual, C. Y.; Varela, J.; Martin-Esteban, M.; Salcedo, G. (12 November 2004). "Vicilin and convicilin are potential major allergens from pea". Clinical & Experimental Allergy. 34 (11): 1747–1753. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2222.2004.02085.x. PMID 15544600.
- Harris, T; Eagle (1935). "THE IMMUNOLOGICAL SPECIFICITY OF THE EUGLOBULIN AND PSEUDOGLOBULIN FRACTIONS OF HORSE AND HUMAN SERUM". J Gen Physiol. 19 (2): 383–396. doi:10.1085/jgp.19.2.383. PMC 2141424. PMID 19872935.