Conalbumin
Ovotransferrin (conalbumin) is a glycoprotein of egg white albumen.[1] Egg white albumen is composed of multiple proteins, of which ovotransferrin is the most heat reliable. It has a molecular weight of 76,000 daltons and contains about 700 amino acids.[2] Ovotransferrin makes up approximately 13% of egg albumen (in contrast to ovalbumin, which comprises 54%).[3] As a member of the transferrin and metalloproteinase family, ovotransferrin has been found to produce heat shock proteins.[4] When these heat shock proteins are induced in the skin, they provide protection against cold stress and other environmental stresses.
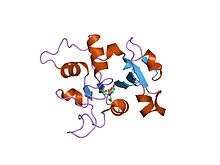
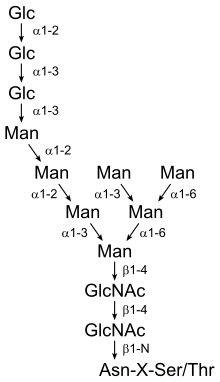
Structure
Ovotransferrin is folded in a way that forms two lobes (N- and C- terminals) and each lobe consists of a binding site. Each lobe is then divided into two domains of 160 amino acid residues. Its structure also consists of fifteen disulfide crosslinks and no free sulfhydryl groups. Disulfide groups stabilize the tertiary structures of proteins. Transferrins are iron binding proteins and acute phase reactants of animal serum.[2] It has a binding log of 15 at a pH of 7 or above, meaning that the iron binding capacity of ovotransferrin rapidly decreased at a pH that is less than 6. This family is also known for their role in cell maturation by transporting essential nutrients to developing embryos.[4] Ovotransferrin functions as an antimicrobial agent and transports iron to the developing embryo. Because they bind to iron, this makes it difficult for harmful bacteria to be nutritionally satisfied with them so it acts as an antimicrobial.
The primary sequence of ovotransferrin is similar to that of many serum transferrins found in other species. Recently, scientists have discovered a blood serum transferrin in humans, that binds iron like ovotransferrin and which shows 50% homology to ovotransferrin, i.e., they have similar amino acid composition and carbohydrate content. At the C- lobe, human serum has two N-glycans while the hen ovotransferrin has a single N-glycan.[4] Consequently, structurally this protein differs from its serum counterpart because of its glycosylation pattern. These proteins are said to be glycosylated because they have carbohydrates attached to them. Glycosylation is the most common covalent modification (formation of chemical bonds) that occurs in living organisms. This process is determined by the structure of the protein backbone and the carbohydrate attachment site.
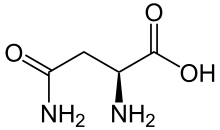
In addition, ovotransferrin is glycosylated by the N-linkage to the amino acid known as asparagine, meaning that the glycan, the carbohydrate chain, is attached to the nitrogen on the amino acid. Asparagine, found abundantly in asparagus (hence, its name), is one of twenty of the most common amino acids and was the first amino acid to be isolated. While ovotransferrin identifies with its family, there are two types of ovotransferrin proteins: apo and holo. Apo-Ovotransferrin is deprived of iron and holo-Ovotransferrin is saturated with iron.[4] Because the apo-ovotransferrin is iron-deprived, it is easily destroyed by physical and chemical treatments.
Biologically, conalbumin isolates and sequesters metallic contaminants in the egg white.[5]
See also
References
- "Fordras S.A. Nutraceutical Ingredients, Functional Food, Pharmaceutical API And Culture Media : Ovotransferrin". www.fordras.com. Archived from the original on 2017-07-26. Retrieved 2017-07-19.
- "Ovotransferrin". Archived from the original on 2013-06-28. Retrieved 2017-07-19.
- Wu, Jianping; Acero-Lopez, Alexandra (2012). "Ovotransferrin: Structure, bioactivities, and preparation". Food Research International. 46 (2): 480–487. doi:10.1016/j.foodres.2011.07.012.
- "Fordras S.A. Nutraceutical Ingredients, Functional Food, Pharmaceutical API And Culture Media : Ovotransferrin". www.fordras.com. Archived from the original on 2017-07-26.
- "Conalbumin". steadyhealth. Archived from the original on 2011-07-16.
External links
- Conalbumin at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)