Fair Isle
Fair Isle (/ˈfɛər ˌaɪl/; Old Norse: Friðarey; Scottish Gaelic: Fara) is an island in Shetland, in northern Scotland. It lies about halfway between mainland Shetland and Orkney. It is known for its bird observatory and a traditional style of knitting.
| Gaelic name | Fara |
|---|---|
| Norse name | Friðarøy[1]/Friðarey[2] |
| Meaning of name | "fair island" or possibly "far-off isle"[1] or "sheep isle".[3] The Norse form Friðarey means literally "calm/peaceful isle" or "island (ey) of tranquility (frið(u)r)".[4] |
Fair Isle viewed from the west. | |
| Location | |
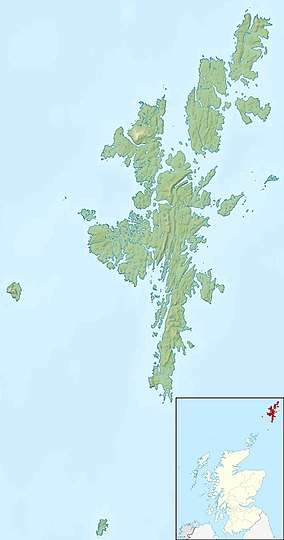 Fair Isle Fair Isle shown within Shetland | |
| OS grid reference | HZ209717 |
| Coordinates | 59.541°N 1.623°W |
| Physical geography | |
| Island group | Shetland |
| Area | 768 ha (1,900 acres) |
| Area rank | 61 [5] |
| Highest elevation | Ward Hill 217 m (712 ft) |
| Administration | |
| Sovereign state | United Kingdom |
| Country | Scotland |
| Council area | Shetland Islands Council |
| Demographics | |
| Population | 55[6] |
| Population rank | 51 [5] |
| Population density | 7.16/km2 (18.5/sq mi) |
| Largest settlement | Stonybreck |
| References | [1][7] |
 The view eastwards towards the Fair Isle North Lighthouse | |
| |
| Location | Fair Isle Shetland Scotland |
|---|---|
| Coordinates | 59.552142°N 1.609519°W |
| Year first constructed | 1892 |
| Automated | 1983 |
| Construction | masonry tower |
| Tower shape | cylindrical tower with balcony and lantern |
| Markings / pattern | white tower, black lantern, ochre trim |
| Tower height | 14 m (46 ft) |
| Focal height | 80 m (260 ft) |
| Light source | engine generator |
| Intensity | 204,000 cd |
| Range | 22 nmi (41 km) |
| Characteristic | Fl (2) W 30s. |
| Fog signal | 3 blasts every 45 s |
| Admiralty number | A3756 |
| NGA number | 3316 |
| ARLHS number | SCO-078 |
| Managing agent | Northern Lighthouse Board[8][9] |
| Heritage | category B listed building |
 Fair Isle South light | |
| |
| Location | Fair Isle Shetland Scotland |
|---|---|
| Coordinates | 59.513906°N 1.652611°W |
| Year first constructed | 1892 |
| Automated | 1998 |
| Construction | masonry tower |
| Tower shape | cylindrical tower with balcony and lantern |
| Markings / pattern | white tower, black lantern, ochre trim |
| Tower height | 26 m (85 ft) |
| Focal height | 32 m (105 ft) |
| Light source | wind power engine generator |
| Range | 22 nmi (41 km) |
| Characteristic | Fl(4) 30s, Fl(2) W 30s |
| Fog signal | 2 blasts every 60 s |
| Admiralty number | A3750 |
| NGA number | 3312 |
| ARLHS number | SCO-078 |
| Managing agent | Northern Lighthouse Board[8][10] |
| Heritage | category B listed building |
Geography

Fair Isle is the most remote inhabited island in the United Kingdom.[11] It is administratively part of the parish of Dunrossness, Shetland, and is roughly equidistant from Sumburgh Head, some 38 km (24 mi) to the northeast on the Mainland of Shetland[12][13] and North Ronaldsay, Orkney, some 43 km (27 mi) to the southwest.[7] Fair Isle is 4.8 km (3 mi) long and 2.4 km (1 1⁄2 mi) wide. It has an area of 3 sq mi (8 km2), making it the tenth largest of the Shetland Islands. It gives its name to one of the British Sea Areas.[14]
Most of the islanders live in the crofts on the southern half of the island, with the northern half consisting of rocky moorland. The western coast consists of cliffs of up to 200 m (660 ft) in height, with Ward Hill at 217 m (712 ft) being the highest point of the island and its only Marilyn. On the eastern coast the almost detached headland of Sheep Rock rises to 132 m (433 ft).[1]
History
Fair Isle has been occupied since Neolithic times, which is remarkable because of the lack of raw materials on the island, although it is surrounded by rich fishing waters. There are two known Iron Age sites: a promontory fort at Landberg and the foundations of a house underlying an early Christian settlement at Kirkigeo.
Most of the place names date from after the 9th century Norse settlement of the Northern Isles. By that time the croft lands had clearly been in use for centuries.
Between the 9th and 15th centuries, Fair Isle was a Norwegian possession. In 1469, Shetland, along with Orkney, was part of the dowry of the King of Denmark's daughter, Margaret, on her marriage to James III of Scotland.[15]
On 20 August 1588 the flagship of the Spanish Armada, El Gran Grifón, was shipwrecked in the cove of Stroms Hellier, forcing its 300 sailors to spend six weeks living with the islanders.[16] The wreck was discovered in 1970. The large Canadian sailing ship Black Watch was wrecked on Fair Isle in 1877.

Fair Isle was bought by the National Trust for Scotland in 1954 from George Waterston, the founder of the bird observatory.[17][18]
The population has decreased steadily from about 400 in 1900. There are currently around 55 permanent residents on the island,[6] the majority of whom are crofters. The island has 14 scheduled monuments, ranging from the earliest signs of human activity to the remains of a Second World War radar station. The two automated lighthouses are protected as listed buildings.
The island houses a series of high-technology relay stations carrying vital TV, radio, telephone and military communication links between Shetland, Orkney and the Scottish mainland.[19] In this respect it continues its historic role as a signal station, linking the mainland and the more remote island groups. In 1976, when television relay equipment was updated to permit colour broadcasts to Shetland, the new equipment was housed in former World War Two radar station buildings on Fair Isle.[20] Many television signals are relayed from Orkney to Shetland (rather than from the Scottish mainland) via Orkney's Keelylang Hill transmitter station.
Wartime military role
During the Second World War, the Royal Air Force built a radar station on top of Ward Hill (712 ft or 217 m) during the Battle of the Atlantic. The ruined buildings and nissen huts are still present. A cable-operated narrow gauge railway lies disused, though it was once used to send supplies up to the summit of Ward Hill.
On 17 January 1941, a German Heinkel He 111 bomber, modified as a meteorological aircraft, crashed on the island; wreckage remains on the crash-site to the present day.[21] The aircraft had been flying on a routine weather reconnaissance flight from its base at Oldenburg in Germany. It was intercepted by RAF Hawker Hurricane fighters from 3 Squadron, based at RAF Sumburgh; both of the aircraft's engines were damaged and several of the five crew were wounded. The pilot managed to make a crash-landing on Fair Isle to avoid ditching his crippled aircraft in the sea. Two crew died and three survived. The dead crew were buried in the island's churchyard; the survivors were detained by the islanders and remained for several days until weather conditions allowed them to be taken off the island by means of the Shetland Lifeboat.[21]
Economy
Over the centuries the island has changed hands many times. Trading links with Northern Europe are reflected in Fair Isle Haa, a traditional Hanseatic trading booth located not far from the South Harbour, traditionally used by residents of the southern part of the island. Rent was usually paid to absentee landlords (who rarely visited) in butter, cloth and fish oil.
Fishing has always been an important industry for the island. In 1702, the Dutch, who were interested in Shetland's herring fisheries, fought a naval battle against French warships just off the island.
Fair Isle is also noted for its woollen jumpers, with knitting forming an important source of income for the women of the islands. The principal activity for the male islanders is crofting.
In January 2004, Fair Isle was granted Fairtrade Island status.
Bird life
Many rare species of bird have been found on the island, with at least 27 species found on the island that were the first British records, and is probably[22] the best place in western Europe to see skulking Siberian passerines such as Pechora pipit, lanceolated warbler and Pallas's grasshopper warbler. For example, in 2015, rare birds discovered on the island included pallid harrier, arctic warbler, Moltoni's warbler, booted warbler, paddyfield warbler, siberian thrush and thrush nightingale.[23]
The island is also home to an endemic subspecies of Eurasian wren, the Fair Isle wren Troglodytes troglodytes fridariensis.
Bird observatory
A permanent bird observatory was founded on Fair Isle by George Waterston in 1948. Because of its importance as a bird migration watchpoint, it provided most of the accommodation on the island.[24] The first director of the observatory was Kenneth Williamson.[25] It was unusual amongst bird observatories in providing catered, rather than hostel-style, accommodation.
In 2010, a new observatory was built: a wooden lodge of two storeys, which cost £4 million and accommodated around 30 guests.[26] The 2010 observatory building was destroyed by fire on 10 March 2019; the observatory's records had been digitised and were not affected.[26][27][28]
Infrastructure

Other than the restaurant of the Bird Observatory, and its little evening-only bar, there are no pubs or restaurants on the island. There is one shop, and one school (see below). There is a community hall available for meetings and social events.
Electricity supply
Fair Isle is not connected to the National Grid and electricity is provided by the Fair Isle Electricity Company. From the 1980s,[29] power was generated by two diesel generators and two wind turbines. Diesel generators were automatically switched off if wind turbines provided sufficient power. Excess capacity was distributed through a separate network for home heating, with remote frequency-sensitive programmable relays controlling water heaters and storage heaters in the buildings of the community.[30] Since October 2018, the island has a 24-hour electricity supply; following the installation of three wind turbines, combined with solar panels and batteries, in a £3.5 million scheme.[29]
Communication
Fair Isle is home to two GSM 900 MHz base stations operated by Vodafone and O2.[31] On 16 April 2019, an EE 4G antenna was turned on by Openreach.[32]
Emergency services
Fair Isle has a fire station equipped with a single fire appliance, and staffed by a retained fire crew of local volunteers. It was originally part of the Highlands and Islands Fire and Rescue Service, which was absorbed into the national Scottish Fire and Rescue Service on 1 April 2013. A locally organised volunteer fire brigade was formed in 1996 by island residents. This was later absorbed into the statutory fire service, with professional training provided, and the local service designated a retained fire crew. The first purpose-built fire engine was stationed to the island in 2002.[33]
In October 2011 a contract for the construction of a £140,000 purpose-built fire station was awarded to Shetland company Ness Engineering,[34] who completed the construction and equipping of the fire station, including its connection to the island power and water supplies, and the installation of a rainwater harvesting system within the building.[35] The new fire station was officially opened on 14 March 2013.[36]
There is a small Coastguard cliff-rescue team on the island. Like the fire service, the Coastguard is a retained (volunteer) emergency service.[37] The Fair Isle Coastguard cliff rescue team were the first British Coastguard unit to be equipped with a quad ATV.[38] The quad is painted in H M Coastguard livery, with reflective Battenburg markings and has an optional equipment trailer.
There are no emergency medical services on Fair Isle. Routine medical care is provided by a community nurse. In the event of accident and emergency the community nurse provides first aid until casualties can be removed to Shetland Mainland, usually by fixed-wing air ambulance. In severe weather conditions the Coastguard helicopter can sometimes undertake medical evacuations when the air ambulance is grounded.[39]
Transport
Air

Fair Isle Airport serves the island with flights to Tingwall Airport near Lerwick, and weekly to Sumburgh Airport, both on Shetland Mainland. Flights to Kirkwall on Orkney were scheduled to begin in September 2017, provided by Loganair.[40] Private aircraft use the facility and scheduled flights arrive twice daily, three days a week. There is a small terminal building, but facilities are otherwise very limited. Fire cover is provided by the island fire service.
There is also a helipad at the South Fair Isle lighthouse, for official use by the Northern Lighthouse Board and Coastguard helicopters, and a second one at the North Fair Isle lighthouse.
Sea
There are two main harbours (north harbour and south harbour), both formed naturally, being sheltered by the headland of Bu Ness. They are separated by a narrow isthmus of gravel. The north harbour is the main route for goods, provisions, and Royal Mail postal services arriving at and departing from the island. The ferry Good Shepherd IV plies between Fair Isle north harbour and Grutness on Shetland Mainland.
Road
A road connects the populated areas of the island, along its full length.
Education
Fair Isle has one primary school, with two classrooms. There is a full-time head teacher, and a part-time assistant teacher.[41] The number of pupils varies over time, but is generally between 5 and 10, with 5 pupils in 2014/2015. Islanders of secondary school age are generally educated off-island, on Shetland Mainland, where they board in halls of residence, returning to the island during holiday periods.
Religion
Christianity is the only formally organised religion on Fair Isle. There are two churches, one Methodist, and one Church of Scotland (Presbyterian). The Methodist Church has a resident non-stipendiary minister, who reports to a full-time minister on Shetland Mainland.[42] The Methodist Church was constructed in 1886.[43]
The Church of Scotland church was built in 1892. The Church of Scotland parish which contains Fair Isle is Dunrossness, which is linked with Sandwick, Cunningsburgh and Quarff parish. The congregation's minister is the Reverend Charles H Greig.
Climate
Fair Isle experiences an oceanic climate (Köppen Cfb, bordering on a subpolar oceanic climate (Cfc), with cool summers and mild winters. This is especially pronounced due to its location far from any sizeable landmass; Fair Isle has the smallest overall temperature range (least continental) of any weather station in the British Isles: an absolute maximum of 20.2 °C (68.4 °F) and an absolute minimum of −5.6 °C (21.9 °F) since 1951. This 60+ year temperature span is actually smaller than many places in inland southern England will record within a given three-month period. To further illustrate how extreme the maritime moderation at Fair Isle is, a rural location near the coastline in Northern Stockholm County on a similar latitude in Sweden broke Fair Isle's all-time records in both directions within a 48-hour period between 26 and 28 April 2014.[44]
The lowest temperature recorded in recent years was −4.6 °C (23.7 °F) in February 2010.[45] Rainfall, at under 1,000 mm (39 in), is lower than one might expect for somewhere often in the main path of Atlantic depressions. This is explained by a lack of heavy convective rainfall during spring and summer months due to the absence of warm surface conditions.
Fair Isle's ocean moderation is so strong that areas on the same latitudes in the Scandinavian inland less than 1000 kilometres to the east have average summer highs 2–3 °C (4–5 °F) higher than Fair Isle's all-time record temperature, for example the Norwegian capital of Oslo and the Swedish capital of Stockholm. The −5 °C (23 °F) all-time low is uniquely mild for European locations on the 59th parallel north. The winter daily means are comparable to many areas as far south in the British Isles as south-central England, due to the extreme maritime moderation.
| Climate data for Fair Isle 57 m asl, 1981–2010, Extremes 1951– | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 11.1 (52.0) |
10.5 (50.9) |
13.9 (57.0) |
12.2 (54.0) |
17.7 (63.9) |
18.0 (64.4) |
20.1 (68.2) |
20.2 (68.4) |
18.0 (64.4) |
15.5 (59.9) |
13.1 (55.6) |
11.5 (52.7) |
20.2 (68.4) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 6.7 (44.1) |
6.1 (43.0) |
6.7 (44.1) |
7.9 (46.2) |
9.9 (49.8) |
11.9 (53.4) |
13.7 (56.7) |
14.1 (57.4) |
12.8 (55.0) |
10.7 (51.3) |
8.7 (47.7) |
7.2 (45.0) |
9.7 (49.5) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 4.9 (40.8) |
4.4 (39.9) |
4.9 (40.8) |
6.1 (43.0) |
8.0 (46.4) |
10.0 (50.0) |
11.9 (53.4) |
12.4 (54.3) |
11.1 (52.0) |
9.1 (48.4) |
7.0 (44.6) |
5.4 (41.7) |
7.9 (46.2) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 3.1 (37.6) |
2.6 (36.7) |
3.0 (37.4) |
4.2 (39.6) |
6.0 (42.8) |
8.1 (46.6) |
10.1 (50.2) |
10.6 (51.1) |
9.4 (48.9) |
7.5 (45.5) |
5.2 (41.4) |
3.6 (38.5) |
6.1 (43.0) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −4.5 (23.9) |
−5.6 (21.9) |
−5.0 (23.0) |
−4.0 (24.8) |
−1.6 (29.1) |
1.5 (34.7) |
4.2 (39.6) |
4.4 (39.9) |
1.4 (34.5) |
−0.9 (30.4) |
−3.4 (25.9) |
−4.5 (23.9) |
−5.6 (21.9) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 101.9 (4.01) |
81.7 (3.22) |
85.6 (3.37) |
51.0 (2.01) |
41.7 (1.64) |
45.9 (1.81) |
54.9 (2.16) |
70.3 (2.77) |
83.6 (3.29) |
116.0 (4.57) |
113.5 (4.47) |
100.6 (3.96) |
946.7 (37.27) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 1.0 mm) | 19.5 | 15.9 | 17.3 | 12.1 | 9.2 | 8.3 | 10.4 | 12.2 | 14.9 | 18.8 | 19.3 | 18.9 | 176.8 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 29.4 | 60.5 | 105.8 | 149.7 | 210.6 | 173.3 | 144.7 | 151.1 | 115.6 | 76.9 | 38.0 | 20.6 | 1,276.3 |
| Source 1: Met Office[46] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: Tutiempo[47] | |||||||||||||
Conservation designations
Most of the island has been designated by Scottish Natural Heritage (SNH) as both a Site of Special Scientific Interest (SSSI) and a Special Area of Conservation (SCA).[48][49] The island and its surrounding seas are also designated by SNH as a Special Protection Area (SPA) due to the important bird species present.[50]
In 2016 the seas around Fair Isle were designated as a Marine Protected Area (MPA).[51] As of 2019 it is the only MPA in Scotland to be designated specifically as a "Demonstration and Research" MPA.[52] The aims of this MPA designation are defined as being:
To demonstrate and research the use of an ecosystem approach, which includes the following -
a) the environmental monitoring of seabirds and of other mobile marine species;
b) the environmental monitoring of the factors which influence the populations of seabirds and of other mobile species;
c) the development and implementation of a local sustainable shellfish fishery;
d) the development of a research programme into local fisheries which includes research on species composition, size, distribution and temporal and spatial changes in fish stocks;e) based upon the research undertaken under sub-paragraph (d), the development of a sustainable-use management programme for local fisheries.
— Scottish Government[53]
Notable people
- Ewen Thomson (born 1971 in Fair Isle), a Scottish luthier, specialising in violins, violas and cellos
- Inge Thomson (born 1974 in Fair Isle), a singer and multi instrumentalist
- Chris Stout (born 1976), a Scottish fiddle/violin player from Shetland; grew up in Fair Isle
Gallery
 Good Shepherd IV at Fair Isle
Good Shepherd IV at Fair Isle North Haven, Fair Isle, 1974
North Haven, Fair Isle, 1974 Da Sherriff
Da Sherriff 100 kW Aerogenerator, Fair Isle
100 kW Aerogenerator, Fair Isle Fair isle station
Fair isle station Fair Isle Kirk interior
Fair Isle Kirk interior Fair Isle - Croft houses
Fair Isle - Croft houses
See also
Footnotes
- Haswell-Smith, Hamish (2004). The Scottish Islands. Edinburgh: Canongate. ISBN 978-1-84195-454-7.
- Anderson, Joseph (ed.) (1873) The Orkneyinga Saga. Translated by Jón A. Hjaltalin & Gilbert Goudie. Edinburgh. Edmonston and Douglas. The Internet Archive. Retrieved 26 August 2013.
- Mac an Tàilleir, Iain (2003) Ainmean-àite/Placenames. (pdf) Pàrlamaid na h-Alba. Retrieved 26 August 2012.
- The form friðar is the genitive singular.
- Area and population ranks: there are c. 300 islands over 20 ha in extent and 93 permanently inhabited islands were listed in the 2011 census.
- "Bid to boost Fair Isle population launched". BBC News Online. Retrieved 1 July 2015.
- Ordnance Survey: Landranger map sheet 4 Shetland (South Mainland) (Map). Ordnance Survey. 2014. ISBN 9780319228104.
- "Lighthouses of Scotland: Shetland". The Lighthouse Directory. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. Retrieved 14 July 2016.
- Fair Isle North Northern Lighthouse Board. Retrieved 28 May 2016
- "Fair Isle South". Northern Lighthouse Board. Retrieved 14 July 2016.
- Crane, Nicholas (18 February 2016). "Britain's 10 best islands". Daily Telegraph. Retrieved 14 July 2016.
- "Unknown: Atlantic" Canmore. Retrieved 7 January 2012.
- "Fair Isle" Northlink Ferries. Retrieved 7 January 2012. Archived 8 August 2012 at the Wayback Machine
- "Fair Isle". fairisle.org.uk. Archived from the original on 8 March 2008. Retrieved 9 February 2008.
- Krauskopf, Sharma (2003). Scotland's Northern Lights: Sharma Krauskopf. p. 7.
- William Boyd, Calendar State Papers Scotland, vol. 9 (Edinburgh, 1915), p. 635.
- "Case Study: Wind Power on Fair Isle". National Trust for Scotland. Archived from the original on 20 April 2008. Retrieved 7 May 2008.
- Nicolson, James R (1972). Shetland. Newton Abbot: David & Charles. p. 27.
- See reference at Fairisle.org.uk Archived 24 September 2015 at the Wayback Machine.
- See "Bringing Colour to the Shetland Isles", by Gerry L Sanderson, 1976, page 48, available on-line here.
- "Deutsche Luftwaffe Heinkel He111 H-2 / T5+EU". Air Crash Sites Scotland. Retrieved 10 April 2013.
- Archer, Mike; Grantham, Mark; Howlett, Peter; Stansfield, Steven (2010). Bird Observatories of the British Isles. London: T & AD Poyser. p. 163. ISBN 978-1-4081-1040-9.
- "Report on rare birds in Great Britain in 2015" (PDF). British Birds. 109. October 2016. Retrieved 22 June 2020.
- Okill, David; Shaw, Deryk (2010). "Fair Isle". In Archer, Mike; Grantham, Mark; Howlett, Peter; Stansfield, Steven (eds.). Bird Observatories of Britain and Ireland (PDF). T & A D Poyser. Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 March 2012.
- "The History of Fair Isle Bird Observatory". fairislebirdobs.co.uk. Archived from the original on 13 May 2008. Retrieved 1 August 2008.
- "Fair Isle fire family 'humbled' by kindness". BBC. 15 March 2019. Retrieved 15 March 2019.
- "Fire damages Shetland's Fair Isle Bird Observatory roof". BBC. 10 March 2019. Retrieved 10 March 2019.
- "Vow to rebuild fire-hit Fair Isle Bird Observatory in Shetland". BBC. 11 March 2019. Retrieved 12 March 2019.
- Johnston, John (12 October 2018). "The glory of 24-hour power finally reaches Fair Isle". BBC News. Retrieved 12 October 2018.
- "Fair Isle Renewed". Network Control. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016.
- "Sitefinder.ofcom.org.uk reference 6840 and 6983". Archived from the original on 7 December 2009. Retrieved 5 December 2009.
- 4G arrives in Fair Isle
- History of the service and the appliance recorded in The Scotsman newspaper.
- Contract award and value recorded in The Shetland Times newspaper.
- Construction and design outlined by Ness Engineering.
- Link to photographs of the opening ceremony.
- Photographs of Fair Isle Coastguard team members receiving long-service awards.
- The quad is reported, with photographs, here.
- An example of such a medical evacuation.
- Dalton, Alastair (23 March 2017). "New Fair Isle flights from Orkney launched by Loganair". The Scotsman. Retrieved 9 June 2017.
- School website.
- Details of ministers on the Shetland Methodist website
- Date referenced at Undiscovered Scotland.
- "Öppna data för Svanberga A" (in Swedish). Swedish Meteorological and Hydrological Institute. Retrieved 7 September 2019.
- "2010 temperature". Tutiempo.
- "Fair Isle climate 1981–2010". Met Office. Retrieved 4 September 2013.
- "Fair Isle climate 1981–". TuTiempo. Retrieved 8 November 2011.
- "Fair Isle SSSI". Scottish Natural Heritage. Retrieved 2 September 2019.
- "Fair Isle SAC". Scottish Natural Heritage. Retrieved 2 September 2019.
- "Fair Isle SPA". Scottish Natural Heritage. Retrieved 2 September 2019.
- "Fair Isle MPA(DR)". Scottish Natural Heritage. Retrieved 2 September 2019.
- "Scottish MPA network – Parliamentary Report" (PDF). Scottish Government. December 2018. p. 28. Retrieved 2 September 2019.
- "Scottish MPA network – Parliamentary Report" (PDF). Scottish Government. December 2018. p. 45. Retrieved 2 September 2019.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Fair Isle. |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Fair Isle. |
