Eastern Highlands moist deciduous forests
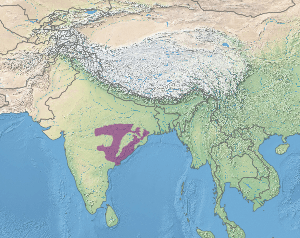
The Eastern Highlands moist deciduous forests, or East Deccan moist deciduous forests, is a tropical moist deciduous forest ecoregion of east-central India. The ecoregion covers an area of 341,100 square kilometers (131,700 sq mi), extending across portions of Andhra Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Odisha, and Telangana states.
| Eastern Highlands moist deciduous forests | |
|---|---|
 Tropical moist diciduous forest habitat (Kambalakonda Wildlife Sanctuary, Andhra Pradesh) | |
 | |
| Ecology | |
| Biome | Tropical moist deciduous forests |
| Borders | List
|
| Bird species | 313 |
| Geography | |
| Area | 341,100 km2 (131,700 sq mi) |
| Country | India |
| Coordinates | 19°12′N 80°30′E |
| Conservation | |
| Conservation status | Critical/Endangered |
| Protected | 3.97% |
Setting
The Eastern Highlands moist deciduous forests extend from the Bay of Bengal coast in northern Andhra Pradesh and southern Orissa, across the northern portion of the Eastern Ghats range and the northeastern Deccan Plateau, to the eastern Satpura Range and the upper Narmada River valley.
The forests of the ecoregion are sustained by the moisture-bearing monsoon winds from the Bay of Bengal, which lies to the southeast. The ecoregion is bounded on the north and west by tropical dry deciduous forest ecoregions, including the Central Deccan Plateau dry deciduous forests to the southwest and west, the Narmada valley dry deciduous forests to the northwest, and the Chota Nagpur dry deciduous forests to the north and northeast. The drier Northern dry deciduous forests ecoregion, lying west of the Eastern Ghats range, is completely surrounded by the Eastern Highlands moist deciduous forests, in the rain shadow of the Ghats, which partially block the moisture-laden monsoon winds off the Bay of Bengal. The humid Orissa semi-evergreen forests ecoregion lies to the northeast in the coastal lowlands of Orissa.
Flora
The ecoregion's forests are dominated by Sal (Shorea robusta), in association with Terminalia, Adina, Toona, Syzygium, Buchanania, Cleisanthus, and Anogeissus, according to soil variations. The flora of the ecoregion shares many species with the moist forests of the Western Ghats and the Eastern Himalayas.
From the Western Ghats this includes plants like Jackfruit and several lianas such as Schefflera Vine (schefflera venulosa), Joint Fir (gnetum ula), and common rattan.
From the Eastern Himalayas this includes the peculiar Indian pepper tree and several shrubs, herbs and flowers such as Yellow Himalayan raspberry, False nettle (Boehmeria macrophylla), and Whipcord cobra lily among others.
Several globally threatened plant species are found in this ecoregion, including the two endemic plants Leucas mukerjiana and Phlebophyllum jeyporensis.
 Inside a tropical moist deciduous forest
Inside a tropical moist deciduous forest- Sal trees are common in these forests
 Characteristic yellow-white sal-flowers in winter coincides with leaffall
Characteristic yellow-white sal-flowers in winter coincides with leaffall- Terminalia, and especially asna trees (Indian laurel), are also common.
- Bamboo, especially calcutta bamboo, is prominent in many parts of this ecoregion
 Plants in common with the Western Ghats includes several types of lianas (Joint Fir).
Plants in common with the Western Ghats includes several types of lianas (Joint Fir). Plants in common with the Eastern Himalayas spans a wide range of species (Indian pepper tree)
Plants in common with the Eastern Himalayas spans a wide range of species (Indian pepper tree)
Fauna

The ecoregion still harbours large intact areas of tropical moist deciduous forests and is therefore considered an important refuge and safe haven for healthy populations of most of the original large vertebrates associated with this habitat. Among the mammals, this includes the predators Indian tigers, wolves, dhole and sloth bear, and herbivores gaur, chousingha, blackbuck, and chinkara. The Asian elephants that once lived here, though, has been extirpated long ago.
The only endemic species found in the ecoregion is the cave-dwelling Khajuria's leaf-nosed bat.
 Sloth bears are here
Sloth bears are here_MH_India.jpg) Indian bison (gaur) is present in parts of this ecoregion
Indian bison (gaur) is present in parts of this ecoregion Several kinds of antilope and deer species live in this ecoregion (Chousingha)
Several kinds of antilope and deer species live in this ecoregion (Chousingha)- Pallas's fish-eagle, a globally threatened species, is living here
 Green avadavat, a globally threatened species, has found a refuge in this ecoregion
Green avadavat, a globally threatened species, has found a refuge in this ecoregion
Conservation


Approximately 25% of the original habitat remains, much of it in blocks of 5000 km² or larger. 31 protected areas, totaling 13,540 km², preserve about 4% of the ecoregion's intact habitat. The largest protected area in the ecoregion is Simlipal National Park in Odisha state.[1]
- Achanakmar Wildlife Sanctuary, Chhattisgarh (550 km²)
- Badalkhol Wildlife Sanctuary, Chhattisgarh (120 km²)
- Baisipalli Wildlife Sanctuary, Odisha (170 km²)
- Balimela Wildlife Sanctuary, Odisha (130 km²)
- Barnawapara Wildlife Sanctuary, Chhattisgarh (240 km²)
- Bhairamgarh Wildlife Sanctuary, Bijapur district, Chhattisgarh (160 km²)
- Bori Wildlife Sanctuary, Hoshangabad district, Madhya Pradesh (460 km²)
- Eturnagaram Wildlife Sanctuary, Warangal district, Telangana (120 km²)
- Hadgarh Wildlife Sanctuary, Odisha (140 km²)
- Indravati National Park, Bijapur district, Chhattisgarh (1,150 km²)
- Kambalakonda Wildlife Sanctuary, Visakhapatnam, Andhra Pradesh (70 km²)
- Kanha National Park, Mandla and Balaghat districts, Madhya Pradesh (900 km²)
- Karlapat Wildlife Sanctuary, Odisha (150 km²)
- Kawal Wildlife Sanctuary, Adilabad district, Telangana (1,080 km²)
- Kinnerasani Wildlife Sanctuary, Khammam district, Telangana (290 km²)
- Kolleru Wildlife Sanctuary (480 km², partially in the Central Deccan Plateau dry deciduous forests ecoregion).
- Kondakameru Wildlife Sanctuary, Odisha (400 km²)
- Kotgarh Wildlife Sanctuary, Odisha (400 km²)
- Lakhari Valley Wildlife Sanctuary, Ganjam district, Odisha (180 km²)
- Lanjamadugu Wildlife Sanctuary, Karimnagar district, Telangana (80 km²)
- Mahuadaur Wildlife Sanctuary, Jharkhand (60 km²)
- Pachmarhi Wildlife Sanctuary, Madhya Pradesh (500 km²)
- Pakhal Wildlife Sanctuary, Warangal district, Telangana (120 km²)
- Pamed Wildlife Sanctuary, Chhattisgarh (60 km²)
- Papikonda Wildlife Sanctuary, East and West Godavari districts, Andhra Pradesh (530 km²)
- Phen Wildlife Sanctuary, Mandla district, Madhya Pradesh (100 km²)
- Pranahita Wildlife Sanctuary, Adilabad district, Telanagana (130 km²)
- Satkosia Gorge Wildlife Sanctuary, Odisha (790 km²)
- Satpura National Park, Madhya Pradesh (490 km²)
- Simlipal National Park, Mayurbhanj district, Odisha (2,550 km²))
- Sitanadi Wildlife Sanctuary, Chhattisgarh (670 km²)
- Udanti Wildlife Sanctuary, Chhattisgarh (340 km²)
References
- Wikramanayake, Eric; Eric Dinerstein; Colby J. Loucks; et al. (2002). Terrestrial Ecoregions of the Indo-Pacific: a Conservation Assessment. Island Press; Washington, DC. pp. 306-308
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Eastern Highlands moist deciduous forests. |
- "Eastern highlands moist deciduous forests". Terrestrial Ecoregions. World Wildlife Fund.
- "Ecoregions 2017". Resolve.
Geographical ecoregion maps and basic info.