Northern Annamites rain forests
The Northern Annamites rain forests ecoregion (WWF ID:IM0136) covers the rugged and relatively unexplored northern Annamite Mountains of central Laos and Vietnam. There are high numbers of endemic plant species, and the relative remoteness and isolation of the area supports many rare and endangered animals. Rainfall is somewhat less than the lowland rainforest of the lower elevations in Vietnam, and the temperatures slightly cooler due to the higher altitude.[1][2] [3]
| Ecoregion: Northern Annamites rain forests | |
|---|---|
 | |
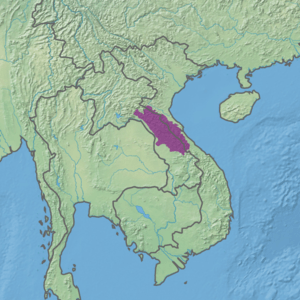 Ecoregion territory (in purple) | |
| Ecology | |
| Realm | Indomalayan |
| Biome | Tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests |
| Geography | |
| Area | 47,137 km2 (18,200 sq mi) |
| Country | Laos, Vietnam |
| Coordinates | 18°N 105°E |
Location and description
Most of the ecoregion is in central Laos, with a small portion on the eastern edge of the higher ridge of Annamite Range in Vietnam. The region is about 350 km long, and is at most about 150 km wide. Mean elevation is 453 metres (1,486 ft), with a highest point of 2,158 metres (7,080 ft).[3] Human density is relatively low due to the steep slopes and high elevations.[1]
Climate
The climate of the ecoregion is Dry-winter humid subtropical climate (Köppen climate classification (Cwa)). This climate is characterized as having no month averaging below 0 °C (32 °F), at least one month averaging above 22 °C (72 °F), and four months averaging over 10 °C (50 °F). Precipitation in the wet summer months is ten time or more the average of the winter months.[4][5] Precipitation in the ecoregion varies from 1,500-2,500 mm/year.[1]
Flora and fauna
About 75% of the region is forested (about 35,000 km2), most of which is closed forest, broadleaf evergreen.[3] From 800-1,500 meters elevation the dominant trees are myrtles (Myrtaceae), beeches and oaks (Fagaceae), Elaeocarpaceae (a woody tropical evergreen), and laurels (Lauraceae). Elevations of 1,200-1,800 meters, with a cool, moist character tends to be dominated by Fujian cypress (Fokienia hodginsii), the evergreen (Podocarpus), and Cunninghamia lanceolata, a type of cyprus. Where the forest canopy has been disturbed there are open areas of bamboo thickets.
Over 134 mammal species have been identified in the ecoregion, many endemic or vulnerable, including the endangered Douc langur (a type of monkey despite the name), the vulnerable Indian bison (Bos gaurus), and the vulnerable Sumatran serow (Capricornis sumatraensis). An estimated 525 species of bird are found in the ecoregion.[1]
Protected area
Officially protected areas in the ecoregion include:
- Pù Mát National Park, meaning "high slope", Pu Mat has exceptionally high biodiversity (2,461 identified plant species), and supports five mammals endemic to the Indochina. North central Vietnam. (911 km2)
- Nam Kading National Protected Area, a remote and rugged mountainous area with almost no human habitation. Central Laos. (1,690 km2)
- Phou Xang He National Protected Area, an mountainous area of mixed deciduous and dry dipterocarp forests, with many endemic and vulnerable mammal and bird species. Central Laos. (1,060 km2).
- Nakai–Nam Theun National Biodiversity Conservation Area (NBCA), one of the largest and last remaining wilderness areas in southeast Asia. Annamite Range and the adjacent Nakai Plateau. (3,445 km2).
- Phou Hin Poun National Biodiversity Conservation Area, a region of limestone mountains (karst topography in Laos. (1,801 km2)
References
- "Northern Annamites rain forests". World Wildlife Federation. Retrieved March 21, 2020.
- "Map of Ecoregions 2017". Resolve, using WWF data. Retrieved September 14, 2019.
- "Northern Annamites rain forests". Digital Observatory for Protected Areas. Retrieved August 1, 2020.
- Kottek, M., J. Grieser, C. Beck, B. Rudolf, and F. Rubel, 2006. "World Map of Koppen-Geiger Climate Classification Updated" (PDF). Gebrüder Borntraeger 2006. Retrieved September 14, 2019.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- "Dataset - Koppen climate classifications". World Bank. Retrieved September 14, 2019.