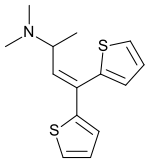
Dimethylthiambutene
Dimethylthiambutene (N,N-Dimethyl-1-methyl-3,3-di-2-thienylallylamine, DMTB, trade names Ohton, Aminobutene, Dimethibutin, Kobaton, Takaton, Dimethibutin) is an opioid analgesic drug, most often used in veterinary medicine in Japan and to a lesser extent in other countries in the region and around the world. It is the most prominent and widely used of the thiambutenes, a series of open-chain opioids structurally related to methadone which are also called the thienyl derivative opioids which also includes diethylthiambutene and ethylmethylthiambutene, as well as the non-opioid cough suppressant tipepidine.
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C14H17NS2 |
| Molar mass | 263.42 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 169 to 170 °C (336 to 338 °F) |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Dimethylthiambutene was developed in the United Kingdom in the late 1940s[1] and introduced to the market by Burroughs-Wellcome in 1951. Dimethylthiambutene is now under international control under the UN Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs 1961, the laws governing habit-forming substances in virtually all countries and Schedule I of the US Controlled Substances Act of 1970 due to high abuse potential and never being introduced clinically in the United States; other countries regulate it much as morphine or diamorphine. Its DEA ACSCN is 9619 and it had a zero manufacturing quota in 2013.