Conversion between Julian and Gregorian calendars
The tables below list equivalent dates in the Julian and Gregorian calendars. Years are given in astronomical year numbering.
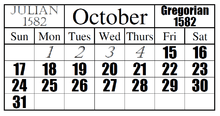
Conventions
- Within these tables, January 1 is always the first day of the year.
- The Gregorian calendar did not exist before October 15, 1582. Gregorian dates before that are proleptic, that is, using the Gregorian rules to reckon backward from October 15, 1582.
- Years are given in astronomical year numbering.
- Augustus corrected errors in the observance of leap years by omitting leap days until AD 8. Julian calendar dates before March AD 4 are proleptic, and do not necessarily match the dates actually observed in the Roman Empire. (Nautical almanac offices of the United Kingdom and United States, 1961, p. 411)
Conversion table
This table is taken from the book by the Nautical almanac offices of the United Kingdom and United States originally published in 1961.[1]
| Year | Julian date | Gregorian date | Difference |
|---|---|---|---|
| −500 | March 5 | February 28 | |
| −500 | March 6 | March 1 | −5 |
| −300 | March 3 | February 27 | −5 |
| −300 | March 4 | February 28 | |
| −300 | March 5 | March 1 | −4 |
| −200 | March 2 | February 27 | −4 |
| −200 | March 3 | February 28 | |
| −200 | March 4 | March 1 | −3 |
| −100 | March 1 | February 27 | −3 |
| −100 | March 2 | February 28 | |
| −100 | March 3 | March 1 | −2 |
| 100 | February 29 | February 27 | −2 |
| 100 | March 1 | February 28 | |
| 100 | March 2 | March 1 | −1 |
| 200 | February 28 | February 27 | −1 |
| 200 | February 29 | February 28 | |
| 200 | March 1 | March 1 | 0 |
| 300 | February 28 | February 28 | 0 |
| 300 | February 29 | March 1 | |
| 300 | March 1 | March 2 | 1 |
| Year | Julian date | Gregorian date | Difference |
| 500 | February 28 | March 1 | 1 |
| 500 | February 29 | March 2 | |
| 500 | March 1 | March 3 | 2 |
| 600 | February 28 | March 2 | 2 |
| 600 | February 29 | March 3 | |
| 600 | March 1 | March 4 | 3 |
| 700 | February 28 | March 3 | 3 |
| 700 | February 29 | March 4 | |
| 700 | March 1 | March 5 | 4 |
| 900 | February 28 | March 4 | 4 |
| 900 | February 29 | March 5 | |
| 900 | March 1 | March 6 | 5 |
| Year | Julian date | Gregorian date | Difference |
| 1000 | February 28 | March 5 | 5 |
| 1000 | February 29 | March 6 | |
| 1000 | March 1 | March 7 | 6 |
| 1100 | February 28 | March 6 | 6 |
| 1100 | February 29 | March 7 | |
| 1100 | March 1 | March 8 | 7 |
| 1300 | February 28 | March 7 | 7 |
| 1300 | February 29 | March 8 | |
| 1300 | March 1 | March 9 | 8 |
| 1400 | February 28 | March 8 | 8 |
| 1400 | February 29 | March 9 | |
| 1400 | March 1 | March 10 | 9 |
| 1500 | February 28 | March 9 | 9 |
| 1500 | February 29 | March 10 | |
| 1500 | March 1 | March 11 | 10 |
| Year | Julian date | Gregorian date | Difference |
| 1582 | October 4 | October 14 | 10 |
| 1582 | October 5 | October 15 | 10 |
| 1582 | October 6 | October 16 | 10 |
| 1700 | February 18 | February 28 | 10 |
| 1700 | February 19 | March 1 | 11 |
| 1700 | February 28 | March 10 | 11 |
| 1700 | February 29 | March 11 | 11 |
| 1700 | March 1 | March 12 | 11 |
| 1800 | February 17 | February 28 | 11 |
| 1800 | February 18 | March 1 | 12 |
| 1800 | February 28 | March 11 | 12 |
| 1800 | February 29 | March 12 | 12 |
| 1800 | March 1 | March 13 | 12 |
| 1900 | February 16 | February 28 | 12 |
| 1900 | February 17 | March 1 | 13 |
| 1900 | February 28 | March 12 | 13 |
| 1900 | February 29 | March 13 | 13 |
| 1900 | March 1 | March 14 | 13 |
| 2100 | February 15 | February 28 | 13 |
| 2100 | February 16 | March 1 | 14 |
| 2100 | February 28 | March 13 | 14 |
| 2100 | February 29 | March 14 | 14 |
Using the tables
Dates near leap days that are observed in the Julian calendar but not in the Gregorian are listed in the table. Dates near the adoption date in some countries are also listed. For dates not listed, see below.
The usual rules of algebraic addition and subtraction apply; adding a negative number is the same as subtracting the absolute value, and subtracting a negative number is the same as adding the absolute value.
If conversion takes you past a February 29 that exists only in the Julian calendar, then February 29 is counted in the difference. Years affected are those which divide by 100 without remainder but do not divide by 400 without remainder (e.g., 1900 and 2100 but not 2000).
No guidance is provided about conversion of dates before March 5, -500, or after February 29, 2100 (both being Julian dates).
For unlisted dates, find the date in the table closest to, but earlier than, the date to be converted. Be sure to use the correct column. If converting from Julian to Gregorian, add the number from the "Difference" column. If converting from Gregorian to Julian, subtract.
- H M Nautical Almanac Office (1974). Explanatory Supplement to the Astronomical Ephemeris. London. pp. 416-18.
See also
References
- Nautical almanac offices of the United Kingdom and United States. (1961). Explanatory Supplement to the Astronomical Ephemeris and the American Ephemeris and Nautical Almanac (pp. 410–18 ). London: H. M. Stationery Office. Available from http://archive.org/details/astronomicalalmanac1961/page/n1/mode/2up
