Feldwebel
Feldwebel (Fw or F), literally "field usher", is a non-commissioned officer (NCO) rank in several countries. The rank originated in Germany, and is also used in Switzerland, Finland, Sweden, and Estonia. The rank has also been used in Russia, Austria-Hungary, and Bulgaria.
Feldwebel is a contraction of feld meaning "field" and weibel, an archaic word meaning "usher". Weibel comes from the Old High German weibôn, meaning to go back and forth.
There are variations on feldwebel, such as Oberstabsfeldwebel ("Superior Staff Field Usher"), which is the highest non-commissioned rank in the German army and air force.
Feldwebel in different languages
The rank is used in several countries: Swedish fältväbel, Russian фельдфебель (fel'dfebel'), Bulgarian фелдфебел (feldfebel), Finnish vääpeli and Estonian veebel.
In Swiss German the spelling Feldweibel is used.
Feldwebel in different countries and armed forces
The Landsknecht regiments first installed Feldwaibel to keep the men at line at the battlefield. The rank is used in the German Army and German Air Force.[1] It is grouped as OR6 in NATO, equivalent in the US Army to Staff Sergeant, or in British Army / RAF to Sergeant. In army/air force context NCOs of this rank were formally addressed as Herr Feldwebel.
Germany
19th century and Kaiserreich
Feldwebel gained its widest usage under the German military beginning from the early 19th century. The highest-ranking non-commissioned officer until 1918, the Feldwebel acted as Company Sergeant Major. By contrast with some other countries, the position and duty of Regimental Sergeant Major never existed in Germany.
From 1877 veteran NCOs could be promoted to the rank of Feldwebel-Leutnant. This Army Reserve officer ranked with the Commissioned Officers, but was always inferior to the lowest Leutnant.
From 1887 the Offizierstellvertreter (Deputy Officer) ranked as a kind of Warrant Officer (more NCO than officer) between Feldwebel and the commissioned officers.
There were three further NCO ranks: Vizefeldwebel (Vice Feldwebel, senior NCO), Sergeant (junior NCO) and Unteroffizier (Lance Sergeant or Corporal, junior NCO). The Gefreiter was not an NCO as he had no powers of authority, and was a higher grade of private soldier.
Reichswehr and Wehrmacht

After World War I, in the German Reichswehr and Wehrmacht, the Feldwebel rank group was divided into several grades:
- Feldwebel (deputy), in the meaning of platoon sergeant,
- Oberfeldwebel (platoon sergeant, possible appointment to Hauptfeldwebel (in the meaning of company sergeant major),
- Stabsfeldwebel (special rank reserved for 25-year volunteers only).
Feldwebel and above were Unteroffiziere mit Portepee (Senior NCOs); Unterfeldwebel and Unteroffiziere were Unteroffiziere ohne Portepee (Junior NCOs). In 1921, the rank of Sergeant was renamed Unterfeldwebel. Unterfeldwebels did duty as squad/section leaders.
The Stabsfeldwebel rank was reserved for those who had enlisted for 25 year terms of service in the pre-war German military and those who were enlisted for shorter terms were not eligible to hold this rank.
The appointment of Hauptfeldwebel (Company sergeant major/First sergeant) could be held by Stabsfeldwebels or Oberfeldwebels only. NCOs of a lower rank (Feldwebel, Unterfeldwebel, Unteroffizier) holding this position were titled Hauptfeldwebeldiensttuer (i.e. acting Hauptfeldwebel).

feldwebel

feldwebel
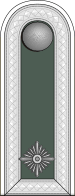
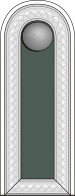
feldwebel
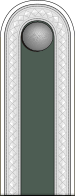
Not all Heer NCO's in this grade were called Unterfeldwebel, Feldwebel, Oberfeldwebel and Stabsfeldwebel which are ranks in the infantry tradition. In some other service branches, for example, the equivalent ranks were as follows.
- Cavalry and artillery
- Unterwachtmeister (equivalent to: Unterfeldwebel),
- Wachtmeister (Feldwebel),
- Oberwachtmeister (Oberfeldwebel), and
- Stabswachtmeister (Stabseldwebel).
- Waffen-SS
- SS-Scharführer (equivalent to: Unterfeldwebel),
- SS-Oberscharführer (Feldwebel),
- SS-Hauptscharführer (Oberfeldwebel), and
- SS-Sturmscharführer (Stabfeldwebel).
German Bundeswehr
| Feldwebel | |
|---|---|
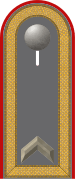 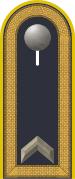 Heer and Luftwaffe shoulder insignia | |
| Country | |
| Service branch | |
| Abbreviation | Fw |
| Rank | Unteroffiziere mit Portepee grade[2] |
| NATO rank | OR-6b |
| Non-NATO rank | E-6 |
| Formation | 1957 |
| Next higher rank | Oberfeldwebel |
| Next lower rank | Stabsunteroffizier |
| Equivalent ranks | Bootsmann |
.jpg)
In the modern German Bundeswehr, Feldwebel is considered a Senior NCO, due in part to the large number of Corporal positions which exist as junior grades.
The modern Bundeswehr NCO grades are as follows:
- Junior NCOs (de: Unteroffiziere ohne Portepee) – Unteroffizier, Stabsunteroffizier (NATO-Rank Code OR 5a, 5c)
- Fähnrich ranks: Fahnenjunker (OR-5b), Fähnrich (OR-6b) and Oberfähnrich (OR-7) are ranks only held by Officer aspirants (OA) (en: Officer candidate or Officer Designate)
- Portepeeunteroffizier (Senior NCOs)
The sequence of ranks (top-down approach) in that particular group (NCOs with portepee or Senior NCOs with portepee) is as follows:
- OR-9: Oberstabsfeldwebel / Oberstabsbootsmann
- OR-8: Stabsfeldwebel / Stabsbootsmann
- OR-7: Hauptfeldwebel / Hauptbootsmann
- OR-6a: Oberfeldwebel / Oberbootsmann
- OR-6b: Feldwebel / Bootsmann
- OR-5a: Stabsunteroffizier / Obermaat
- OR-5b: Unteroffizier / Maat
- Remark
The abbreviation "OR" stands for "Other Ranks / fr: sous-officiers et militaires du rang / ru:другие ранги, кроме офицеров"!
| junior Rank Stabsunteroffizier |
(German NCO rank) |
senior Rank Oberfeldwebel |
Austria
Feldwebel was a typical infantry rank of the k.u.k. Austro-Hungarian Army (1867–1918). It might have been comparable to NCO-rank OR8.[3]/ Company Sergeant-major ranks in the British Army.
In the k.u.k. Austro-Hungarian Army Feldwebel was equivalent to:
- Beschlagmeister I. Klasse (Master-Blacksmith 1st class) cavalry,
- Feuerwerker (literal: Fire worker; en: Master-Sergeant) artillery,
- Oberjaeger (en: Master-Sergeant) of the mountain troops and rifles,
- Rechnungs-Unteroffizier I. Klasse (en: Fiscal sergeant 1st class),
- Regimentshornist (en: Regimental bugler),
- Regimentstambour (en: Regimental drummer),
- Wachtmeister (en: Master-Sergeant) cavalry,
- Waffenmeister I. Klasse (en: Weapon master 1st class) artillery and weapon arsenal,
- Einjährig-Freiwilliger-Feldwebel (en: Master-Sergeant - volunteer serving one year), and
- Kadett-Feldwebel (en: Cadet-Master-Sergeant).
| Junior rank Zugsführer (Sergeant) |
(Austro-Hungarian armed forces rank) Feldwebel |
Senior rank Stabsfeldwebel (Regimental Sergeant-major) |
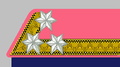
Then rank insignia was a gorget patch on the stand-up collar of the so-called Waffenrock (en: Tunic), and consisted of three white stars on 13 mm ragged yellow silk galloon. The gorget patch and the stand-up collar showed the particular Waffenfarbe (en: corps colour).
- Examples (selection)
| Designation | Non-commissioned officers OR8/ Feldwebel ranks | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 | ||
| Rank insignia | |||||
| Rank description | Feuerwerker | Wachtmeister | Oberjäger | Feldwebel | |
| Branch | Artillery | Cavalry | Mountain infantry | Infantry | Militärwachkorps |
| (English) | (Artillery Master-Sergeant) | (Cavalry LMaster-Sergeant) | (Rifles Master-Sergeant) | (Master-Sergeant) | (Master-Sergeant mil. guards) |
- Feldwebel of the k.u.k. Army

InfRgt Nr.5
(more than 9 years in service)
InfRgt Nr. 13 
InfRgt Nr. 15
(German style uniform / more than 6 years in service)
InfRgt Nr. 35 
InfRgt Nr. 44 
InfRgt Nr. 63 
InfRgt Nr. 74
(German style uniform)
InfRgt Nr. 79
(Hungarian style uniform)
InfRgt Nr. 98 
InfRgt Nr. 100
(German style uniform)
- See also
Bulgaria
In the Bulgarian army, фелдфебел (pronounced "feldfebel") existed from the late 19th century to the late 1940s, when the German-type military organization was phased out in favor of a new doctrine, identical to the Soviet one.
Estonia
The Estonian rank of "veebel" is derived from the name of the German rank "Feldwebel".
| Senior NCOs | [4][5][6] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Estonian: Auastmed | Ülemveebel | Staabiveebel | Vanemveebel | Veebel | Nooremveebel | |
| English: Ranks | Command Sergeant Major | Sergeant Major | Master Sergeant | Sergeant First Class | Staff Sergeant | |
| Estonian: Auastmed | Ülemveebel | Staabiveebel | Vanemveebel | Veebel | Nooremveebel | |
| English: Ranks | Master Chief Petty Officer of the Navy | Master Chief Petty Officer | Senior Chief Petty Officer | Chief Petty Officer 1st Class | Chief Petty Officer 2nd Class | |
| Estonian: Auastmed | Ülemveebel | Staabiveebel | Vanemveebel | Veebel | Nooremveebel | |
| English: Ranks | Chief Master Sergeant of the Air Force | Chief Master Sergeant | Senior Master Sergeant | Master Sergeant | Technical Sergeant | |
Finland
- Rank insignia
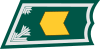
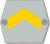
The military rank of vääpeli was previously used by salaried NCOs. Responsibility was given for training and maintenance.
The rank of vääpeli is a rank of wartime formation and can be given to soldier of "ylikersantti". In peacetime, the term yksikköupseeri, literally "officer of the unit", is used, and this position is held by a salaried officer, typically senior lieutenant. The responsibility is for the provisioning, maintenance, human resources management and generally well-being of the unit (company).
Russia
In the Imperial Russian Army a Feldfebel (Russian: фельдфебель; today comparable to NATO OR6[3]) held the highest Unteroffizier (унтер-офицер/ unter-ofitser; NCO) rank from 1722 (its introduction into Peter the Great's Table of Ranks until 1826 (the introduction of the still-higher Unteroffizier ranks Podpraporshchik (подпрапорщик; literally: Junior praporschschik) OR-7 and later Zauryad-praporshchik (зауряд-прапорщик; Praporshchik deputy) OR-8 in 1884). Feldwebels, even after the introduction of these senior ranks, were usually the most senior Unteroffiziers in a unit and held the positions of the unit's CO senior assistant or Starshina (старшина; Sergeant Major). When they were promoted to Zauryad-praporshchik OR-8 or Podpraporshchik OR-7 ranks, but still held the Feldfebel OR-6 positions, they were authorized to still wear the Feldvebel's bands on their shoulder boards. The cavalry equivalent of this rank was the vakhtmistr or vakhmistr (вахмистр - derived from German Wachtmeister), also OR-6.
| junior rank: Starshy unterofitser |
Feldvebel (Wakhtmistr) |
senior rank: Podpraporshchik |
- Rank insignia
| designation | Rank insignia as to the years 1904-1917 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| shoulder board epaulette |
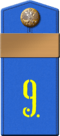 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 | ||
| military rank |
Feldvebel (1904) |
Feldvebel (1907) |
Wakhtmistr (1904) |
Wakhtmistr (1908) |
Wakhtmistr longer serving (1911) |
Podpraporshchik on assignment Feldvebel (1914) | ||
| NATO rank | OR-6 | OR-7 | ||||||
Switzerland
Feldweibel is the lowest rank of "Higher Non-Commissioned Officers" in the Swiss Army. Until the "Reform XXI" agenda, there were two branches of Feldweibels: technical and company level.
The Feldweibel oversees unit-level military service and operations. In 2004, the rank of Hauptfeldweibel was introduced. Since then, only technical specialists have remained in the rank of Feldweibel.
On international missions they are referred to as "Sergeant Major" (NATO Code: OR-7).
See also
- History of Russian military ranks
- Ranks and insignia of NATO Armies Enlisted (Army)
- Ranks and insignia of NATO
References
- BROCKHAUS, The encyclopedia in 24 volumes (1796–2001), Volume 7: 3-7653-3676-9, page 185
- https://www.gesetze-im-internet.de/slv_2002/__18.html
- The abbreviation "OR" stands for "Other Ranks / fr: sous-officiers et militaires du rang / ru:другие ранги, кроме офицероф"
- "Maaväe auastmed" (in Estonian). Estonian Defence Forces. Retrieved 14 June 2014.
- "Land Forces Insignia". Estonian Defence Forces. Retrieved 14 June 2014.
- "Military Service Act – Riigi Teataja". www.riigiteataja.ee. Retrieved 2019-11-17.
Sources
- BROCKHAUS, Die Enzyklopädie in 24 Bänden (1796–2001), Band 5: 3-7653-3665-3, S. 487, Feldwebel