Architecture of Croatia
The architecture of Croatia has roots in a long history: the Croats have inhabited the area for fourteen centuries, but there are important remnants of earlier periods still preserved in the country.
.jpg)
Ancient heritage
Copper Age finds are from Vučedol culture (named after Vučedol near Vukovar). In Vučedol, people lived on hilltops with palisade walls. Houses were half buried, mostly square or circular (they were also combined in mushroom shape), with floors of burned clay and circular fireplaces.
The Bronze culture of the Illyrians, an ethnic group with distinct culture and art, started to organize itself in what is now Croatia. Numerous monumental sculptures are preserved, as well as walls of the citadel Nezakcij near Pula, one of numerous Istrian cities from the Iron Age.
Greek sailors and merchants reached almost every part of the Mediterranean including the shores of today's Croatia; there they have founded city-states in which they lived quite isolated. Trade cities on the Adriatic shores such as Tragurion (today Trogir), Salona (Solin near Split), Epetion (today Poreč), Issa (Vis), were geometrically shaped and had villas, harbors, public buildings, temples and theatres. While the Greek colonies were flourishing on the island, on the continent the Illyrians were organizing their centers. Their art was greatly influenced by Greek art, and they even copied some. In the Neretva Delta, there was an important influence of the Hellenistic Illyrian tribe of Daors.

Romans[1] subdued the Greek colonial cities in the 3rd century BC. They imposed an organization based on a military-economical system. Furthermore, the Romans subdued the Illyrians in the first century BC and organized the entire coastal territory by transforming the citadels into urban cities. After that the history of these parts is the history of Illyrian provinces of the Roman Empire. Numerous rustic villas, and new urban settlements (the most impressive are Verige in Brijuni, Pula and Trogir - formerly Tragurion) demonstrate the high level of Roman urbanization. There were at least thirty urban cities in Istria, Liburnia and Dalmatia with Roman citizenship (civitas). The best-preserved networks of Roman streets (decumanus/cardo) are those in Epetion (Poreč) and Jader (Zadar). The most perfectly preserved Roman monuments are in Pola (Pula); founded in the first century dedicated to Julius Caesar. It is full of classical Roman art such as: stone walls, two city gates, two temples on the Forum, and remains of two theaters, as well as the Arch from the year 30 AD, and the temple of Augustus built in the years 2 to 14 AD, and finally the Fluvian Amphitheater (so called – Arena) from the 2nd century. In the 3rd century AD, the city of Salona became the largest (it had 40,000 inhabitants) and most important city of Dalmatia. Near the city emperor Diocletian, born in Salona, built Diocletian's Palace around year the 300 AD,[2] which is the largest and most important monument of late antique architecture in the world. On its pathways, cellars, domes, mausoleums, arcades and courtyards we can trace numerous different art influences from the entire Empire. In the 4th century, Salona became the center of Christianity for the entire western Balkans. It had numerous basilicas and necropolises, and even two saints: Domnius (Duje) and Anastasius (Staš).
One of few preserved basilicas in western Europe (besides the ones in Ravenna) from the time of early Byzantium is Euphrasian Basilica in Poreč from the 6th century. The early Middle Ages brought the great migration of the Slavs and this period was perhaps a Dark Age in the cultural sense until the successful formation of the Slavic states which coexisted with Italic cities that remained on the coast, each of them modelled after Venice.
Early Middle Ages
.jpg)
In the 7th century, the Croats, with other Slavs and Avars, came from Northern Europe to the region where they live today. They were on the level of Iron Age nomadic culture, so they did not know how to enjoy the advantages of urban cities. This is why they first inhabited city boundaries on close by rivers (like Jadro near Roman Salona).[3]
The Croats were open to Roman art and culture, and first of all to Christianity. First churches were built as royal sanctuaries, and the influence of Roman art was strongest in Dalmatia where the urbanization was thickest and there were the largest number of monuments.[4] Gradually that influence was neglected and certain simplification, alteration of inherited forms, and even creation of original buildings appeared. All of them (a dozen large ones and hundreds of small ones) were built with roughly cut stone (natively called – lomljenac) bounded with thick layer of mortar from outside. Large churches are longitudinal with one or three naves like the St. Saviour at the source of the river Cetina, built in the 9th century. The church has strong semi-circular buttresses that give a feeling of fortification, emphasized by the mighty bell-tower positioned in front of entrance.
Smaller churches often have several apses. The largest and most complicated central based church from the 9th century is the church of St. Donatus in Zadar. Around its circular centre – with dome above – is a nave in the shape of a ring with three apses directed to the east; that shape is followed on the second floor forming a gallery. For that period, with its size and beauty, St. Donatus is comparable only with the chapel of Charlemagne in Aachen.
The altar fences and windows of those churches were highly decorated with transparent shallow string-like ornament that is called pleter (meaning to weave) because the strings were threaded and rethreaded through itself. Motifs of those reliefs were taken from Roman art (waves, three-string interlace, pentagrams, net of rhomboids etc.), but while in Roman art they only made the frame of a sculpture, in the Dark Ages it fills the entire surface. Sometimes figures from Bible appeared alongside this decoration, like Relief in Holy Nedjeljica in Zadar, and then they were dominated by their pattern. This also happened to engravings in early Croatian script – Glagolitic. Soon, the Glagolitic writings were replaced with Latin on altar fences and architraves of old-Croatian churches. Those inscriptions usually mention to whom the church was dedicated, who built it and when it was built, as well who produced the building. That was the way that "barbarian newcomers" could fit amongst the Romanised natives.
By joining the Hungarian state in the twelfth century, Croatia lost its independence, but it did not lose its ties with the south and the west, and instead this ensured the beginning of a new era of Central European cultural influence.
Romanesque
In the 11th century, monumental cities were built along the entire Dalmatian coast. Houses were constructed from stone. On the ground floor there were shops or taverns (natively – konoba), seen today in cities such as Poreč, Rab, Zadar, Trogir and Split. In those cities the most important buildings were churches. They were commonly stone-built basilicas with three naves, three apses, columns, arches, arcades and wooden roofs, and were erected near the monasteries of Benedictine monks who came out of Italy. St. Peter in Supetarska Draga on the island of Rab (11th century) is the best-preserved church of that type in Croatia. On the same island is the Cathedral of Rab (12th century) that has a high-Romanesque bell tower, the largest in Dalmatia. It is specific with its openings, which multiply with each level of floor (Latin: mono-fore, bi-fore, tri-fore, quadro-fore). This is typical for Romanesque architecture, but also architecturally innovative, as each floor is slightly lighter than the one below.
The Cathedral of St. Anastasia, Zadar (natively - St. Stošija) in Zadar (13th century) is marked outside by a string of blind arch-niches on both sides and on the frontal side where it also has two rose windows with radial columns and three portals. In is reminiscent of the cathedral in Pisa. Inside, it has three naves, slim columns that support a gallery, and flat figurative reliefs.
In Croatian Romanesque sculpture we see a transformation of decorative interlace relief (natively – pleter) to figurative, which is found on stone ceilings. At the end of the Romanesque period, in Istria there were workshops of monumental figures. They had geometrical and naturalistic features reminiscent of Gothic. The best examples of Romanesque sculpture are the wooden doors of Split Cathedral done by artisan Andrija Buvina (c.1220) and the stone portal of the Trogir Cathedral done by artisan Radovan (c. 1240).
- Romanesque Architecture in Croatia
 The famous bell tower of the Split Cathedral.
The famous bell tower of the Split Cathedral. Cathedral of St Stošija in Zadar, 13th century
Cathedral of St Stošija in Zadar, 13th century Church of St. Mary in Zadar, mid 11th century
Church of St. Mary in Zadar, mid 11th century St Peters Basilica in Supetarska Draga, Rab
St Peters Basilica in Supetarska Draga, Rab
Gothic
The Gothic art in the 14th century was supported by the culture of city councils, preaching orders (like the Franciscans), and knightly culture. It was the golden age of free Dalmatian cities that traded with Croatian feudal nobility in the continent. Urban organization and the evolution of Dalmatian cities can be followed through the development and expansion of Rab and Trogir, the regulation of streets in Dubrovnik, and the integration of Split. It was also a time of paving the streets with stone, sewage canals, and communalities.
The largest urban project of this period was the complete building of two new towns – Mali Ston and Ston, and about a kilometre of wall with guard towers between them (14th century). After Hadrian's wall, this was and is the longest wall in Europe. Thanks to the wall, all of Pelješac peninsula was surrounded and protected from land shore with the aim to protect the most valuable possession of the Republic of Ragusa – salt from Ston.
We can recognize Gothic fortifications with their high towers in the shape of a square prism from simple Romanesque ones, or round Renaissance one. The best-preserved ones in Croatia are in Istria (Hum, Bale, Motovun, Labin etc.) and those on north (Medvedgrad above Zagreb from year 1260) or on the south Sokolac in Lika (14th century).
The Franciscan church in Pula (1285) is the most representative example of Early Gothic. This simple one nave building with a wooden rib-vault ceiling, a square apse, and high stained glass windows was built from 13th to the 15th century.
Mongols destroyed the Romanesque cathedral in Zagreb during their scourge in 1242, but right after their departure Zagreb got the title of a free city from Hungarian King Béla IV. Soon after, bishop Timotej began to rebuild the cathedral in the new Gothic style. This was a building with three naves, polygonal apses, and rib-vault and it had Romanesque round towers. The naves were built in the 14th century, and the vault was finished in 15th. With the arrival of Turks in the 16th century, high walls and towers surrounded it. Only one tower was finished in the 17th century, while in the 18th the Baroque roof became the landmark of the entire city. An earthquake in 1880 severely damaged the cathedral. With the restoration in the 19th century in the Neo-gothic style, it lost its former harmony.
During the 14th century, the Split cathedral of St Duje and the cloister of the Franciscan monastery in Dubrovnik were also built.
In Dubrovnik after the fire in 1435, two of the most important buildings, the Rector's Palace and the Sponza Palace, were restored in style of Venetian Gothic by an artisan from Naples, Onofrio della Cava.
 Cathedral of St Stephen in capital of Croatia, Zagreb, interior from 14th century
Cathedral of St Stephen in capital of Croatia, Zagreb, interior from 14th century The Rector's Palace and behind it the Sponza Palace in Dubrovnik
The Rector's Palace and behind it the Sponza Palace in Dubrovnik
Renaissance

In the 15th century, Croatia was divided between three states – northern Croatia was a part of Austrian Empire, Dalmatia was under the rule of Venetian Republic (with exception of Dubrovnik), and Slavonia was under Ottoman occupation. Dalmatia was on the periphery of several influences, equidistant from Italy, Ottoman Bosnia, and Austria, so it drew influence from all. In those circumstances in Dalmatia flourished religious and public architecture with clear influences of the Italian Renaissance, but still original.
Only in this kind of environment, free of dogmas and self-governed - far from major governing centers - could it be possible for the artisan known as Giorgio da Sebenico (Juraj Dalmatinac) to build a church entirely as his own project – the Cathedral of St.James in Šibenik, constructed in 1441. Besides mixing of the Gothic and Renaissance styles it was also original in its unity of stone building and montage construction (big stone blocks, pilasters and ribs were bounded with joints and slots on them - without concrete) in the way that was usual in wooden constructions. This was a unique building with so-called three-leaves frontal and half-barrel vaults, the first in Europe. The cathedral and its original stone dome was finished by Nikola Firentinac following the original plans of Juraj.
In the entire area of the Republic of Ragusa there were numerous villas of nobility, unique by their functionality and spatial organization, a combination of Renaissance villa and government building. Sorkočević's villa in 'Lapad' near Dubrovnik in 1521 is original by the order of its building parts in asymmetrical, dynamic balance.
In northwestern Croatia, the beginning of the wars with the Ottoman Empire caused many problems but in the long term it both reinforced the northern influence by establishing the Austrians as the rulers of a large part of Croatia. With permanent danger from the Ottomans in the east, there was only a modest influence of the Renaissance, while fortifications thrived. The plan for the fortified city of Karlovac in 1579 was the first entirely new urban city to be built by Renaissance plans (so called "ideal city" plan) in Europe. It was built in radial plan, later common in Baroque city design. The Renaissance fort of the Ratkay family in Veliki Tabor from the 16th century has mixed features of Gothic architecture (high roofs) and Renaissance (cluster and round towers) making it an example of Mannerism.
Baroque and Rococo
In the 17th and 18th century, Croatia was reunited with the parts of country that were occupied by Venetian Republic and Ottoman Empire. The unity attributed to the sudden flourishing of art in every segment. In northern Croatia and Slavonia numerous and worthy works of Baroque art sprung out, from urban plans and large forts to churches, palaces, public buildings, and monuments.
Large fortifications with radial plan, ditches, and numerous towers were built because of constant Ottoman threat. The two largest ones were Osijek and Slavonski Brod. Later they become large cities. They were fortified with water and earth – earth mounds with cannons and canals filled with water that was supposed to slow down the approaching enemies. The fort of Slavonski Brod was the largest in all Croatia, and one of the largest in all Europe because it was the bounty fort of Europe facing the Ottoman Empire.
Baroque urban planning is felt in numerous new towns like Karlovac, Bjelovar, Koprivnica, Virovitica etc. that had large straight streets, rectangular squares in the middle surrounded with buildings as government and military ones as well as representative church.

The cities of Dalmatia also had Baroque towers and bastions incorporated in their old walls, like the ones in Pula, Šibenik, and Hvar. But the biggest Baroque undertaking happened in Dubrovnik in the 17th century after a catastrophic earthquake in 1667 when almost the entire city was destroyed. In the Baroque style were rebuilt the church of St Vlaho on the main square (1715), Main Cathedral and Jesuit house with church of St Ignatius. Paolo Passalaqua united several of those baroque masterpieces with his Jesuit Stairway. This beautiful wide stone stairway with series of convexities and concavities and a strong balustrade (reminiscent of the famous Spanish Steps in Rome) actually connected two separate Baroque parts of the city - the Jesuit church above and Ivan Gundulić Square below.
During the Baroque period, numerous churches of enchanting size and form were built in of all Croatia, thus becoming a crown in every town or city. The monastery churches often had an enclosing wall with inner porches lavishly decorated, like in the Franciscan monastery in Slavonski Brod where the columns are as thick as baroque abundance. The most beautiful one is probably the church in Selima near Sisak. It has an oval shape with elliptic dome and concave and convex front with two according towers.
Wall painting flourished in all parts of Croatia, from illusionist frescoes in the church of Holy Mary in Samobor, St Catherine in Zagreb to the Jesuit church in Dubrovnik. The best preserved examples are the Rococo frescoes in Miljana mansion where allegorical seasons and natural elements were depicted through human nature and its reflection on art.
19th century

In Austrian countries on the beginning of the 19th century (to which Croatia belonged than) building in Classicistic Manner prevailed. In Croatia most prominent architect was Bartol Felbinger who also build City Hall in Samobor (1826) and Januševac Castle near Zagreb.
The Romantic movement in Croatia was sentimental, gentle and subtle a reflection of the bourgeoisie's humble and modest virtues. In architecture there were simple decorations made of shallow arch-like niches around windows.
Historicism is marked with building three large churches: the neo-Romanesque cathedral in Đakovo (K. Roesner and F. Schmidt, 1882), monumental parish church of St Peter and Paul in Osijek (1898) and neo-gothic rebuilding of Zagreb cathedral with glazed roof tiles and 105 m tall towers (Herman Bolle, 1880–1902). At the end of 19th century Herman Bolle undertook one of the largest projects of European historicism, a half-kilometer long neo-Renaissance arcade with twenty domes on Zagreb cemetery Mirogoj. At the same time the cities in Croatia got important urban makeovers: Karlovac transformed its Renaissance bastions into a parkway that surrounds the entire old town (just like Vienna's Ringstraẞe), while the coastal cities (Trogir, Zadar, Pula, Pag and Šibenik) took down their walls and opened to the sea. The size and importance the urban regulation of Downtown Zagreb (largely the work of Milan Lenuzzio, 1860–1880) was revolutionary. Between Zagreb's longest street – Ilica, and the new railway the new geometrical city was built with large public and social buildings like the neo-Renaissance building of the Croatian Academy of Science and Art (HAZU, F. Scmidt, 1884), the neo-Baroque Croatian National Theater (HNK, H. Helmer and F. Fellner, 1895), and to that date very modern Art Pavilion (1898) with montage construction of steel and glass – Croatia's "Crystal Palace", and finally the masterpiece of Art Nouveau – The National Library (Lubinski, finished in 1912). This urban plan is bounded with a series of parks and parkways decorated with numerous fountains, sculptures, avenues and gardens (known as "Green Horseshoe") making Zagreb one of the first cities build according to new European art theory of "city as a work of art".
A pseudo building that emphasizes all three visual arts is the former building of the Ministry of Prayer and Education in Zagreb (H. Bolle, 1895). Alongside rooms in Pompeii style and Renaissance cabinet, the large neo-Baroque "Golden Hall" was painted with historic compositions. "The Golden Hall" became a unified monument of its age, one of few in Europe.
20th century
Vienna Secession
Till the end of World War I several art movements and styles coexisted in Croatia, but all avant-garde movements were absent. That is why the greatest artworks of that period were done in the spirit of 19th-century art, including the most important examples of Vienna Secession style: the Ethnographic Museum, Zagreb in 1901, Kallina House in 1903, the National Library in 1912 were built in Zagreb, while Sulphurous Bath in 1903, and the Croatian National Theatre in 1908, were built in Split.

 Kallina House by Vjekoslav Bastl, 1903
Kallina House by Vjekoslav Bastl, 1903- National Library , 1912
Interwar modernism and the "Zagreb school"

Yugoslav architecture emerged in the first decades of the 20th century before the establishment of the state; during this period a number of South Slavic creatives, enthused by the possibility of statehood, organized a series of art exhibitions in Serbia in the name of a shared Slavic identity. Following governmental centralization after the 1918 creation of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia, this initial bottom-up enthusiasm began to fade. Yugoslav architecture became more and more dictated by an increasingly concentrated national authority which sought to establish a unified state identity.[5] Beginning the 1920s, Yugoslav architects began to advocate for architectural modernism, viewing the style as the logical extension of progressive national narratives. Despite these shifts, differing relationships to the west made the adoption of modernism inconsistent in Yugoslavia WWII; Croatia and Slovenia were familiar with Western influence and the most eager to adopt modernism.[6][7]
Modern Croatian architecture appeared in Croatia with Viktor Kovačić, who was the first to speak against historicism and represented the idea that architecture must be individual and modern, but also practical and comfortable. His projects are marked with subtle purity of reduced elements of historicism, like in the monumental Palace of Burze in Zagreb, 1924.
Drago Ibler published a manifest of the group "Earth" in which he wrote: "We should live in the spirit of our age and create accordingly; … The modern life is full of social ideas and questions considering everybody and an artist can’t stand outside that collective because art and life are one." Between 1925 and 1935, he established the so-called "Zagreb school of architecture" with fellow architects Drago Galić, Mladen Kauzlarić, Stjepan Planić and others. From the thirties the works of "Zagreb school" of architecture can stand alongside with the best world architecture. They often merge two opposite directions in the architecture of those days – functionalistic and organic.
Stjepan Planić, also a member of group "Earth", with his numerous buildings made a makeover of Zagreb and earned a place in the Anthology of Modern Architecture. Every project of his is marked with some new idea: Villa in Kozarčeva street from 1931 is gradually accommodated to the hillside, "Tomislav Home" in Sljeme from 1935, made out of wood and stone, has a unique plane in the shape of letter Y, while circular villa on the Prekrižje, also from 1935, has radial inner walls. He fought for the architectural freedom to plan the buildings accordingly with climatic conditions, the sun, the wind and the sightings, and for the affirmation of new social and human ideas in habitat culture.
 Modernist school designed by Ivan Zemljak in 1930 in Zagreb
Modernist school designed by Ivan Zemljak in 1930 in Zagreb The Meštrović Pavilion in Zagreb was designed by Ivan Meštrović as an art gallery in 1933
The Meštrović Pavilion in Zagreb was designed by Ivan Meštrović as an art gallery in 1933 Secondary school in Zagreb designed by Egon Steinmann and completed in 1933
Secondary school in Zagreb designed by Egon Steinmann and completed in 1933
Socialist realism
Immediately following the Second World War, Yugoslavia's brief association with the Eastern Bloc ushered in a short period of socialist realism. Centralization within the communist model led to the abolishment of private architectural practices and the state control of the profession. During this period, the governing Communist Party condemned modernism as "bourgeois formalism," a move that caused friction among the nation's pre-war modernist architectural elite.[8]
Socialist modernism
Socialist realist architecture in Yugoslavia came to an abrupt end with Josip Broz Tito's 1948 split with Stalin. In the following years the nation turned increasingly to the West, returning to the modernism that had characterized pre-war Yugoslav architecture.[7] During this era, modernist architecture came to symbolize the nation's break from the USSR (a notion that later diminished with growing acceptability of modernism in the Eastern Bloc).[8][9] The nation's postwar return to modernism is perhaps best exemplified in Vjenceslav Richter's widely acclaimed 1958 Yugoslavia Pavilion at Expo 58, the open and light nature of which contrasted the much heavier architecture of the Soviet Union.[10]
 Vjesnik building
Vjesnik building FER building C, 1956
FER building C, 1956 Ilički neboder, 1957-58
Ilički neboder, 1957-58 Zagrepčanka, 1971-76
Zagrepčanka, 1971-76 Cibona Tower, by Marijan Hržić 1983
Cibona Tower, by Marijan Hržić 1983
Spomeniks
During this period, the Yugoslav break from Soviet socialist realism combined with efforts to commemorate World War II, which together led to the creation of an immense quantity of abstract sculptural war memorials, known today as spomenik [11]
Brutalism
In the late 1950s and early 1960s Brutalism began to garner a following within Yugoslavia, particularly among younger architects, a trend possibly influenced by the 1959 disbandment of the Congrès Internationaux d'Architecture Moderne.[12]
Decentralization
With 1950s decentralization and liberalization policies in SFR Yugoslavia, architecture became increasingly fractured along ethnic lines. Architects increasingly focused on building with reference to the architectural heritage of their individual socialist republics in the form of critical regionalism.[13]
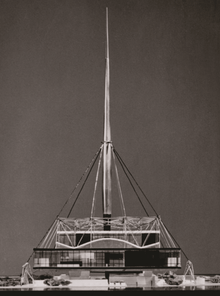 Vjenceslav Richter: Original project for the Yugoslav Pavilion at Expo 58, Bruxelles
Vjenceslav Richter: Original project for the Yugoslav Pavilion at Expo 58, Bruxelles
 Mamutica in East Novi Zagreb city district (Travno local committee area), an apartment complex built in 1974 as the Croatian version of the plattenbau, largest building (by volume) in Zagreb and in Croatia
Mamutica in East Novi Zagreb city district (Travno local committee area), an apartment complex built in 1974 as the Croatian version of the plattenbau, largest building (by volume) in Zagreb and in Croatia
Post-Yugoslav architecture
- ...

- Sky Office Tower, Zagreb
 New terminal of the Zagreb International Airport
New terminal of the Zagreb International Airport- Mosque of Rijeka, completed in 2013
 Strojarska Business Center, Zagreb 2015
Strojarska Business Center, Zagreb 2015 Dalmatia Tower, Split 2020
Dalmatia Tower, Split 2020
See also
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Architecture of Croatia. |
- Art of Croatia
- Hollow Church
- Church of Holy Trinity, Split
- Architecture of Yugoslavia
Sources
- "Roman Art". Artchive.com. Retrieved 2012-07-26.
- The Megalithic Portal and Megalith Map. "C.Michael Hogan, "Diocletian's Palace", The Megalithic Portal, A. Burnham ed, Oct 6, 2007". Megalithic.co.uk. Retrieved 2012-07-26.
- "Barbarians and Romans | Thematic Essay | Heilbrunn Timeline of Art History | The Metropolitan Museum of Art". Metmuseum.org. Retrieved 2012-07-26.
- "The First Croatian State". culturenet.hr. Retrieved 2 December 2012.
- Deane, Darren (2016). Nationalism and Architecture. Taylor & Francis. ISBN 9781351915793.
- Đorđević, Zorana (2016). "Identity of 20th Century Architecture in Yugoslavia: The Contribution of Milan Zloković". Култура/Culture. 6.
- Babic, Maja (2013). "Modernism and Politics in the Architecture of Socialist Yugoslavia, 1945-1965" (PDF). University of Washington.
- Vladimir., Kulić (2012). Modernism in-between : the mediatory architectures of socialist Yugoslavia. Jovis Verlag. ISBN 9783868591477. OCLC 814446048.
- Alfirević, Đorđe; Simonović Alfirević, Sanja (2015). "Urban housing experiments in Yugoslavia 1948-1970" (PDF). Spatium (34): 1–9.
- Kulić, Vladimir (2012). "An Avant-Garde Architecture for an Avant-Garde Socialism: Yugoslavia at EXPO '58". Journal of Contemporary History. 47 (1): 161–184. doi:10.1177/0022009411422367. ISSN 0022-0094. JSTOR 23248986.
- Kulić, Vladmir. "Edvard Ravnikar's Liquid Modernism: Architectural Identity in a Network of Shifting References" (PDF). New Constellations New Ecologies.
- di Radmila Simonovic, Ricerca (2014). "New Belgrade, Between Utopia and Pragmatism" (PDF). Sapienza Università di Roma.
- Entertainment, The only biannual Magazine for Architectural. "YUGOTOPIA: The Glory Days of Yugoslav Architecture On Display". pinupmagazine.org. Retrieved 2019-02-05.
.jpg)

