A. B. Dobrowolski Polar Station
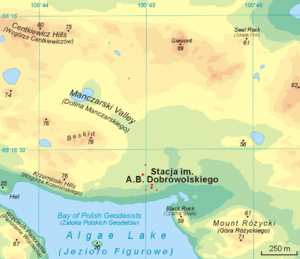
A.B. Dobrowolski Polar Station (Polish: Stacja im. A.B. Dobrowolskiego) is an inactive Polish polar research station in Antarctica. It is located at the edge of the Algae Lake, Bunger Hills region in the Wilkes Land and was originally constructed by the Soviet Union. It is one of the two Polish stations in Antarctica, the other being the Henryk Arctowski Polish Antarctic Station.
Dobrowolski Station | |
|---|---|
| A. B. Dobrowolski | |
 Buildings of the Dobrowolski Station (Bunger Hills, Antarctica) in 1979 (Photo: Zbigniew Battke). | |
 Dobrowolski Station Location of Dobrowolski Station in Antarctica | |
| Coordinates: 66°16′28″S 100°45′00″E | |
| Country | |
| Location in Antarctica | Algae Lake Bunger Hills Wilkes Land |
| Administered by | Institute of Geophysics, Polish Academy of Sciences |
| Established | 1959 |
| Inactive since | 1998 |
| Named for | Antoni Bolesław Dobrowolski |
The station is named after Polish geophysicist, meteorologist and explorer Antoni Bolesław Dobrowolski.[1]
Oasis Station
The research station was built by the Soviet Antarctic Expedition in 1956 and named Oazis (Оазис, English: Oasis). The station was handed over by the Soviet Academy of Sciences to the Polish Academy of Sciences in January 1959.[1] It was manned briefly by the Polish expedition, which carried out a number of studies, primarily in the fields of gravimetry and geomorphology.[2] The station has not been used regularly since, due to the lack of funds and the high costs of air transport,[2] and there are no plans to reopen the station as a permanent institution.[3] The station has been visited periodically by Polish and other research teams.[4][5] The last Polish team was reported to have visited the station in the 1960s or 1970s (sources vary).[6][7][8] A 1998 Polish statistical yearbook described the base as "periodically active".[9] Official classification of the station is "inactive".[8] The station is only occasionally visited by tourists, such as those who documented their visit in 2010.[5]
Historic monuments
The magnetic observatory building, along with a plaque commemorating the establishment of Oasis Station in 1956, has been designated a Historic Site or Monument (HSM 10) following a proposal by Russia to the Antarctic Treaty Consultative Meeting (ATCM). The concrete pillar erected by the Polish expedition to measure acceleration due to gravity has similarly been designated a Historic Site or Monument (HSM 49) following a proposal by Poland to the ATCM.[10]
See also
References
- "Dobrowolski Station (A.B.)". Scientific Committee on Antarctic Research. SCAR Gazetteer Ref. No 3714. Archived from the original on 2014-04-07 – via the Composite Gazetteer of Antarctica.
- Geographical journal. 1973. p. 204. Retrieved 3 September 2013.
- Geographical journal. 1973. p. 206. Retrieved 3 September 2013.
- "Waly lodowo-morenowe Antarktydy". Polish Geographical Review. Institute of Geography and Spatial Organization PAS. 56: 101. 1984. ISSN 0033-2143.
- Chandler, Jo (2010-01-06). "Cold War relics frozen in Antarctic". The Age. Archived from the original on 2018-03-08. Retrieved 2013-09-03.
- http://portalwiedzy.onet.pl/24617,,,,antarktyka,haslo.html
- "Polacy w Antarktyce « Młody Technik". Mt.com.pl. 2013-01-24. Archived from the original on 2013-10-29. Retrieved 2013-09-03.
- "Z wyprawami radzieckimi". Arctowski.pl. Retrieved 2013-09-03.
- Mały rocznik Statystyczny. Nakładem Głównego Urzędu Statystycznego. 1998. p. 28. Retrieved 3 September 2013.
- "List of Historic Sites and Monuments approved by the ATCM (2012)" (PDF). Antarctic Treaty Secretariat. 2012. Retrieved 2013-10-26.
.svg.png)