Eng (letter)
Eng or engma (capital: Ŋ, lowercase: ŋ) is a letter of the Latin alphabet, used to represent a velar nasal (as in English singing) in the written form of some languages and in the International Phonetic Alphabet.
| Ŋ | |
|---|---|
| Ŋ ŋ | |
| (See below) | |
.svg.png) | |
| Usage | |
| Writing system | Latin script |
| Type | Alphabetic and Logographic |
| Language of origin | Latin language |
| Phonetic usage | [ŋ] [ŋ̊] /ˈɛŋ/ |
| Unicode value | U+014A, U+014B |
| History | |
| Development | |
| Time period | 1619 to present |
| Descendants | None |
| Sisters | Ꞑ ꞑ |
| Transliteration equivalents | ng |
| Variations | (See below) |
| Other | |
| Other letters commonly used with | n(x), ng |

In Washo, lower-case ⟨ŋ⟩ represents a typical [ŋ] sound, while upper-case ⟨Ŋ⟩ represents a voiceless [ŋ̊] sound. This convention comes from Americanist phonetic notation.
History
The First Grammatical Treatise, a 12th-century work on the phonology of the Old Icelandic language, uses a single grapheme for the eng sound, shaped like a g with a stroke ⟨ǥ⟩. Alexander Gill the Elder uses an uppercase G with a hooked tail and a lowercase n with the hooked tail of a script g ⟨ŋ⟩ for the same sound in Logonomia Anglica in 1619.[1] William Holder uses the letter in Elements of speech: An essay of inquiry into the natural production of letters, published in 1669, but it was not printed as intended; he indicates in his errata that “there was intended a character for Ng, viz., n with a tail like that of g, which must be understood where the Printer has imitated it by n or y”.[2] It was later used in Benjamin Franklin's phonetic alphabet, with its current phonetic value.
Appearance
Lowercase eng is derived from n, with the addition of a hook to the right leg, somewhat like that of j. The uppercase has two variants: it can be based on the usual uppercase N, with a hook added (or "N-form"); or it can be an enlarged version of the lowercase (or "n-form"). The former is preferred in Sami languages that use it, the latter in African languages,[3] such as in Shona from 1931–1955, and several in west and central Africa currently.
Early printers, lacking a specific glyph for eng, sometimes approximated it by rotating a capital G, or by substituting a Greek letter η (eta) before modified to present form ŋ for it (encoded in Unicode as the Latin letter n with long leg: Ƞ ƞ).
 An 1856 text in Gamilaraay, using a rotated capital G as a substitute for ŋ.
An 1856 text in Gamilaraay, using a rotated capital G as a substitute for ŋ..svg.png) Italic ŋ based on double-storey g as used in Horatio Hale's Ethnography and Philology (1846).
Italic ŋ based on double-storey g as used in Horatio Hale's Ethnography and Philology (1846).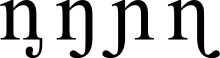
Pronunciation of words containing eng sound
In most languages eng is absent in the Latin alphabet but its sound can be present in the letter n in words. In English it is heard in the potential digraphs nc (hard c), ng (hard g), nk, nq and nx, often at the end of words. For the pronunciation of ng with eng, it can either be /ŋ/ in words such as singer, hanged and when it is final, or /ŋg/ in words such as finger and angle.
In British English, n is pronounced eng in the prefixes en- and in- when they are followed by c, g and q, as in encroachment, engagement, enquiry, incursion, ingredient, inquiry et al. In all other English this is neglected as the n is rather pronounced /n/. Also in many British dialects the ng in strength and length is simply pronounced /n/, making the g a silent letter, the ng is otherwise pronounced /ŋ/ in those words.
Usage
Technical transcription
- Americanist phonetic notation, where it may also represent a uvular nasal.
- Sometimes for the transcription of Australian Aboriginal languages
- International Phonetic Alphabet
- Uralic Phonetic Alphabet including U+1D51 ᵑ MODIFIER LETTER SMALL ENG[4]
- Teuthonista phonetic transcription system uses U+AB3C ꬼ LATIN SMALL LETTER ENG WITH CROSSED-TAIL[5]
- Rheinische Dokumenta, a phonetic alphabet for many West Central German dialects, Low Rhenish, and few related languages.
Vernacular orthographies
 |
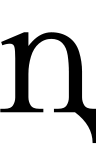 |
| Janalif variant of eng is represented as N with descender. An equivalent version is used in the Cyrillic alphabet. | |
Languages marked † no longer use eng, but formerly did.
- African languages
- American languages
- Inupiat
- Lakota
- O'odham
- Austroasiatic languages
- Australian Aboriginal languages
- Bandjalang
- Yolngu
- Languages of China
- Zhuang† (replaced by the digraph ng in 1986)
- Sami languages
- Inari Sami
- Lule Sami
- Northern Sami
- Skolt Sami
- Kildin Sami (during Latinisation in the 1930s)
- Turkic languages during Latinisation in the 1930s used Ꞑ ꞑ, sometimes considered a variant of eng.
- Kazakh language (2019 revision of the Latin alphabet)
- Mapuche language (Wirizüŋun script)
- Kalam languages
Computer encoding
Eng is encoded in Unicode as U+014A LATIN CAPITAL LETTER ENG and U+014B LATIN SMALL LETTER ENG, part of the Latin Extended-A range. In ISO 8859-4 (Latin-4) it's located at BD (uppercase) and BF (lowercase).
In African languages such as Bemba, ng' (with an apostrophe) is widely used as a substitute in media where eng is hard to reproduce.
See also
- Ng (digraph)
- Nh (digraph)
- Eta (Greek letter)
Similar Latin letters:
Similar Cyrillic letters:
References
- David Crystal (2003). The Cambridge Encyclopedia of the English Language
- Robert W. Albright (1958). The International Phonetic Alphabet: Its Backgrounds and Development, Indiana University. p. 11
- "Essay Archives and Poetry". Retrieved 10 June 2004.
- Everson, Michael; et al. (2002-03-20). "L2/02-141: Uralic Phonetic Alphabet characters for the UCS" (PDF).
- Everson, Michael; Dicklberger, Alois; Pentzlin, Karl; Wandl-Vogt, Eveline (2011-06-02). "L2/11-202: Revised proposal to encode "Teuthonista" phonetic characters in the UCS" (PDF).
- Majnep, Ian Saem; Bulmer, Ralph (1977). Birds of my Kalam Country [Mn̄mon Yad Kalam Yakt]. illustrations by Christopher Healey. New Zealand: Aukland University Press. pp. 17–18. ISBN 9780196479538. OCLC 251862814.
External links
- Practical Orthography of African Languages
- FileFormat.info – Fonts that support LATIN CAPITAL LETTER ENG (U+014A) and LATIN SMALL LETTER ENG (U+014B)