Thracian language
The Thracian language (/ˈθreɪʃən/) is an extinct and poorly attested language, spoken in ancient times in Southeast Europe by the Thracians. The linguistic affinities of the Thracian language are poorly understood, but it is generally agreed that it was an Indo-European language with satem features.
| Thracian | |
|---|---|
| Region | Albania, Bulgaria, European Turkey, Southern Serbia parts of the region of Macedonia (including Paeonia), parts of Northern Greece, parts of Bithynia in Anatolia. Probably also spoken in parts of Dardania |
| Extinct | 6th century[1] |
Indo-European
| |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | txh |
txh | |
| Glottolog | thra1250[2] |
| Part of a series on |
| Indo-European topics |
|---|
 |
|
|
Philology
|
|
Origins |
|
Archaeology Pontic Steppe
Caucasus East Asia Eastern Europe Northern Europe Pontic Steppe Northern/Eastern Steppe Europe
South Asia Steppe Europe Caucasus India |
|
Peoples and societies Indo-Aryans Iranians
East Asia Europe East Asia Europe
Indo-Aryan Iranian
|
|
Religion and mythology
Indo-Aryan Iranian Others Europe
|
|
A contemporary, neighboring language, Dacian is usually regarded as closely related to Thracian. However, there is insufficient evidence with respect to either language to ascertain the nature of this relationship.
The point at which Thracian became extinct is a matter of dispute. However, it is generally accepted that Thracian was still in use in the 6th century AD: Antoninus of Piacenza wrote in 570 that there was a monastery in the Sinai, at which the monks spoke Greek, Latin, Syriac, Egyptian, and Bessian – a Thracian dialect.[3][4][5][6]
Other theories about Thracian remain controversial.
- Some linguists have suggested that the Albanian language and the ethnogenesis of the Albanians followed a migration by members of the Bessi westward into Albania.
- A classification put forward by some linguists, such as Harvey Mayer, suggests that Thracian (and Dacian) belonged to the Baltic branch of Indo-European.[7] However, this theory has not achieved the status of a general consensus among linguists.
These are among many competing hypotheses regarding the classification and fate of Thracian.[8]
Geographic distribution
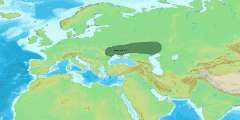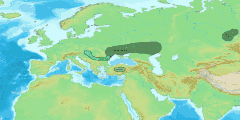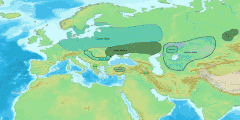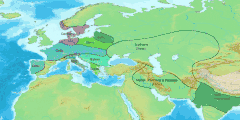
The Thracian language was spoken in what is now Bulgaria,[9][10] Romania, North Macedonia, Northern Greece, European Turkey and in parts of Bithynia (North-Western Asiatic Turkey).
Eastern Serbia is usually considered by paleolinguists to have been a Daco-Moesian language area. Moesian (after Vladimir Georgiev et al.) is grouped with Dacian.
Remnants of the Thracian language
Little is known for certain about the Thracian language, since no phrase beyond a few words in length has been satisfactorily deciphered, and the sounder decipherments given for the shorter phrases may not be completely accurate. Some of the longer inscriptions may indeed be Thracian in origin but they may not reflect actual Thracian language sentences, but rather jumbles of names or magical formulas.[11]
Enough Thracian lexical items have survived to show that Thracian was a member of the Indo-European language family and that it was a satemized language by the time it is attested. Besides the aforementioned inscriptions, Thracian is attested through personal names, toponyms, hydronyms, phytonyms, divine names, etc. and by a small number of words cited in Ancient Greek texts as being specifically Thracian.[12]
Other ancient Greek lexical items were not specifically identified as Thracian by the ancient Greeks but are hypothesized by paleolinguists as being or probably being of Thracian origin. Other lexical items are hypothesized on the basis of local anthroponyms, toponyms, hydronyms, oronyms, etc. mentioned in primary sources (see also List of ancient cities in Thrace and Dacia, List of Dacian plant names) .
Below is a table showing both words cited as being Thracian in classical sources, and lexical elements that have been extracted by paleolinguists from Thracian anthroponyms, toponyms, etc. In this table the closest cognates are shown, with an emphasis on cognates in Bulgarian, Albanian, Baltic, Slavic, Greek, and substratum and/or old-layer words in the Eastern Romance languages: Romanian, Aromanian, et cetera. See also the List of reconstructed Dacian words.
Significant cognates from any Indo-European language are listed. However, not all lexical items in Thracian are assumed to be from the Proto-Indo-European language, some non-IE lexical items in Thracian are to be expected.
There are 23 words mentioned by ancient sources considered explicitly of Thracian origin and known meaning[13]
| Word | Meaning | Attested by | Cognates |
|---|---|---|---|
| asa | colt’s foot (Bessi) | Dioskurides | Lit. dial. asỹs ‘horse-tail, Equisetum’, Latv. aši, ašas ‘horse-tail, sedge, rush’ |
| βόλινθος (bólinthos) | aurochs, European bison | Aristotle | Proto-Slavic *volъ ("ox"). Pre-Greek, according to Beekes 2010: 225. |
| βρία (bría) | unfortified village | Hesychius, compare the Toponyms Πολτυμβρία, Σηλυ(μ)μβρία, and Βρέα in Thrace. | Compared to Greek ῥίον (ríon; "peak, foothills") and Tocharian A ri, B riye ("town") as if < *urih₁-. Alternatively, compare Proto-Celtic *brix- ("hill"). |
| βρίζα (bríza) | rye | Galen | Perhaps of Eastern origin, compare Greek ὄρυζα, Sanskrit vrīhí- ("rice"). |
| βρυνχός (brynkhós) | guitar | Compared with Slavic *bręčati "to ring". | |
| βρῦτος (brŷtos) | beer of barley | many | Germanic *bruþa- ("broth"), Old Irish bruth ("glow"), Latin dēfrŭtum ("must boiled down"). |
| dinupula, si/nupyla | wild melon | Pseudoapuleus | Lithuanian šùnobuolas, lit. ("dog’s apple"), or with Slavic *dynja ("melon"). |
| γέντον (génton) | meat | Herodian., Suid., Hesych | Taken from IE *gʷʰn-tó-, cf. Sanskrit hatá- ‘hit, killed’ |
| καλαμίνδαρ (kalamíndar) | plane-tree (Edoni) | Hesych. | |
| κη̃μος (kêmos) | a kind of fruit with follicle | Phot. Lex. | |
| κτίσται (ktístai) | Ctistae | Strabo | |
| midne | village | inscription from Rome | Latvian mītne ("a place of stay") |
| Πολτυμ(βρία) (poltym-bría) | board fence, a board tower | Old Norse spjald ("board"), Old English speld ("wood, log") | |
| ῥομφαία (rhomphaía) | broadsword | many | Compared with Latin rumpō ("to rupture"), Slavic: Russian разрубать, Polish rąbać ("to hack", "to chop", "to slash"), Polish rębajło ("eager swordsman") |
| σκάλμη (skálmē) | knife, sword | Soph. y Pollux, Marcus Anton., Hesych., Phot. L | Albanian shkallmë ("sword"), Old Norse skolm ("short sword, knife") |
| σκάρκη (skárkē) | a silver coin | Hesych., Phot. Lex. | |
| σπίνος (spínos) | a kind of stone (?) | Arist. | |
| τορέλλη (toréllē) | a refrain of lament mourn song | Hesych. | |
| ζαλμός (zalmós) | animal hide | Porphyr. | |
| ζειρά (zeira) | long robe worn by Arabs and Thracians | Hdt., Xen., Hesych. | |
| ζελᾶ (zelâ), also ζῆλα (zêla), ζηλᾱς (zelās) | wine | many | Compared with Greek χάλις (khális; "unblended wine") and Macedonian κάλιθος (kálithos; "wine") |
| ζετραία (zetraía) | pot | Pollux | |
| zibythides | the noble, most holy one | Hesych. | Lith. žibùtė ("shining") |
An additional 180 Thracian words have been reconstructed.[13]
The proposed Thracian words in the Ancient Greek lexicon are not numerous. They include the parth- element in Parthenon; balios ("dappled"; < PIE *bhel-, "to shine", Bul. bel/bial (бял) "white" or bljaskav 'bright, shiny'; Pokorny also cites Illyrian as a possible source, the non-Greek origin is argued on phonological grounds), bounos, "hill, mound".[14]
The Thracian horseman hero was an important figure in Thracian religion, mythology, and culture. Depictions of the Thracian Horseman are found in numerous archaeological remains and artifacts from Thracian regions. From the Duvanli ring and from cognates in numerous Indo-European languages, mezēna is seen to be a Thracian word for "horse", deriving from PIE *mend-. Another Thracian word for "horse" is hypothesized, but it looks certain, there is no disagreement among Thracologists: aspios, esvas, asb- (and some other variants; < PIE *ekwo , the Thracian showing a satem form similar to Sanskrit áśva-, "horse", Avestan aspa, "horse", Ossetic jäfs, Prussian aswinan ‘mare milk’, Lithuanian ašvíenis ‘stallion’, ašvà, dial. ešvà ‘mare’[15]), from Outaspios, Utaspios, an inscription associated with the Thracian horseman. Ut- based on the PIE root word ud- (meaning "up") and based on several Thracic items, would have meant "upon", "up", and Utaspios is theorized to have meant "On horse(back)", parallel to ancient Greek ephippos (epi-hippos).[16]
The early Indo-European languages had more than one word for horse; for example Latin had equus from PIE *ekwo- and mannus ("a pony") from another IE root, later receiving cabalus as a loanword.
In many cases in current Thracology, there is more than one etymology for a Thracian lexical item. For example, Thracian Diana Germetitha (Diana is from Latin while the epithet Germetitha is from Thracian) has two different proposed etymologies, "Diana of the warm bosom" (Olteanu; et al.?) or "Diana of the warm radiance" (Georgiev; et al.?). In other cases, etymologies for the Thracian lexical items may be sound, but some of the proposed cognates are not actually cognates, thus confusing the affinity of Thracian.
Inscriptions
Ezerovo inscription
Only four Thracian inscriptions of any length have been found. The first is a gold ring found in 1912 in the village of Ezerovo, Bulgaria; the ring was dated to the 5th century BC. On the ring an inscription is found written in a Greek script and consisting of 8 lines, the eighth of which is located on the edge, the rim, of the rotating disk; it reads: ΡΟΛΙΣΤΕΝΕΑΣΝ / ΕΡΕΝΕΑΤΙΛ / ΤΕΑΝΗΣΚΟΑ / ΡΑΖΕΑΔΟΜ / ΕΑΝΤΙΛΕΖΥ / ΠΤΑΜΙΗΕ / ΡΑΖ // ΗΛΤΑ
Dimitar Dechev (Germanised as D. Detschew) separates the words thus[17][18] ΡΟΛΙΣΤΕΝΕΑΣ ΝΕΡΕΝΕΑ ΤΙΛΤΕΑΝ ΗΣΚΟ ΑΡΑΖΕΑ ΔΟΜΕΑΝ ΤΙΛΕΖΥΠΤΑ ΜΙΗ ΕΡΑ ΖΗΛΤΑ i.e. Rolisteneas Nerenea tiltean ēsko Arazea domean Tilezypta miē era zēlta proposing the following translation
- I am Rolisteneas, a descendant of Nereneas; Tilezypta, an Arazian woman, delivered me to the ground.
Kyolmen inscription
A second inscription, hitherto undeciphered, was found in 1965 near the village of Kyolmen, Varbitsa Municipality, dating to the sixth century BC. Written in a Greek alphabet variant, it is possibly a tomb stele inscription similar to the Phrygian ones; Peter A. Dimitrov's transcription thereof is:[19]
i.e.
- ilasnletednlednenidakatroso
- eba·rozesasnēnetesaigekoa
- nblabaēgn
Duvanli inscription
A third inscription is again on a ring, found in Duvanli, Kaloyanovo Municipality, next to the left hand of a skeleton. It dates to the 5th century BC. The ring has the image of a horseman with the inscription surrounding the image. It is only partly legible (16 out of the initial 21)
- ΗΥΖΙΗ.....ΔΕΛΕ / ΜΕΖΗΝΑΙ
i.e.
- ēuziē.....dele / mezēnai
The meaning of the inscription is 'Horseman Eusie protect!'
These are the longest inscriptions preserved. The remaining ones are mostly single words or names on vessels and other artifacts.
Classification
The Thracian language in linguistic textbooks is usually treated either as its own branch of Indo-European, or is grouped with Dacian, together forming a Daco-Thracian branch of IE. Older textbooks often grouped it also with Illyrian or Phrygian. The belief that Thracian was close to Phrygian is no longer popular and has mostly been discarded.[22] The Thraco-Illyrian grouping has also been called into question. Daco-Thracian or Thraco-Dacian is the main hypothesis.
No definite evidence has yet been found that demonstrates that Thracian or Daco-Thracian belonged on the same branch as Albanian or Baltic or Balto-Slavic or Greco-Macedonian or Phrygian or any other IE branch. For this reason textbooks still treat Thracian as its own branch of Indo-European, or as a Daco-Thracian/Thraco-Dacian branch.
The generally accepted clades branched from the Proto-Indo-European language are, in alphabetical order, the Proto-Albanian language, Proto-Anatolian language, Proto-Armenian language, Proto-Balto-Slavic language, Proto-Celtic language, Proto-Germanic language, Proto-Greek language, Proto-Indo-Iranian language, Proto-Italic language, and the Proto-Tocharian language. Thracian, Dacian, Phrygian, Illyrian, Venetic, and Paeonian are fragmentarily attested and cannot be reliably categorized.
| Change | o > a | r > ir, ur (or) l > il, ul (ol) |
m > im, um (om) n > in, un (on) |
kʷ, gʷ, gʷʰ > k, g (k), g |
ḱ, ǵ, ǵʰ > s (p), z (d) |
p, t, k > pʰ, tʰ, kʰ |
b, d, g > p, t, k |
bʰ, dʰ, gʰ > b, d, g |
sr > str | tt, dt > st |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thracian | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| Dacian | + | + | + | + | + | - | - | + | + | - |
| Balto-Slavic | + | + | + | + | + | - | - | + | -/+ | + |
| Pelasgian | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ? | ? |
| Albanian | + | + | - | +/- | +/- | - | - | + | - | - |
| Germanic | + | + | + | - | - | - | + | + | + | - |
| Indo-Iranian | + | - | - | +/- | + | - | - | +/- | - | +/- |
| Greek | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | + |
| Phrygian | - | - | - | - | + | + | + | + | - | ? |
| Armenian | - | - | - | - | + | + | + | - | - | ? |
| Italic | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Celtic | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - |
| Hittite | + | - | - | - | - | - | + | + | ? | ? |
| Tocharian | +/- | - | - | - | - | - | + | + | - | ? |
| Proto-Indo-European | Dacian | Thracian | Phrygian |
|---|---|---|---|
| *o | a | a | o |
| *e | ie | e | e |
| *ew | e | eu | eu |
| *aw | a | au | |
| *r̥, *l̥ | ri | ur (or), ur (ol) | al |
| *n̥, *m̥ | a | un | an |
| *M | M | T | T |
| *T | T | TA (aspirated) | TA |
| *s | s | s | ∅ |
| *sw | s | s | w |
| *sr | str | str | br |
Note: Asterisk indicates reconstructed IE sound. M is a cover symbol for the row of voiced stops (mediae), T for unvoiced stops (tenues) and TA for aspirated stops (tenues aspiratae). ∅ indicates zero, a sound that has been lost.
| Indo-European | Dacian | Thracian |
|---|---|---|
| *b, *d, *g | b, d, g | p, t, k |
| *p, *t, *k | p, t, k | ph, th, kh |
| *ē | ä (a) | ē |
| *e (after consonant) | ie | e |
| *ai | a | ai |
| *ei | e | ei |
| *dt (*tt) | s | st |
Thraco-Dacian has been hypothesized as forming a branch of Indo-European along with Baltic.[25]
For a large proportion of the 300 Thracian geographic names there are cognates within the Baltic toponymy, most similarities between Thracian and Balto-Slavic personal and geographic names were found, especially Baltic. According to Duridinov the "most important impression make the geographic cognates of Baltic and Thracian" "the similarity of these parallels stretching frequently on the main element and the suffix simultaneously, which makes a strong impression". According to him there are occasional similarities between Slavic and Thracian because Slavic is related to Baltic, while almost no lexical similarities within Thracian and Phrygian were found.[26] This significant relatedness show close affinity and kinship of Thracian with Baltic.
The following table shows the cognates Thracian and Baltic place names:[13]
| Thracian place | Lithuanian place | Latvian place | Old Prussian place | cognates |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alaaiabria | Alajà | Lith. aléti ‘to be flooded’ | ||
| Altos | Altis | |||
| Antisara | Sarija | Sarape | ||
| Armonia | Armona, Armenà | Lith. armuõ, -eñs ‘a swamp, bog’, arma ‘the same’ | ||
| Armula | Armuliškis | lit. arma ‘mud’ | ||
| Arpessas | Varpe, Varputỹs, Várpapievis | Warpen, Warpunen | Latv. vārpats ‘whirlpool’, the Lith. varpýti (-pa, -pia) ‘to dig’ | |
| Arsela | Arsen | Arsio, Arse | ||
| Aspynthos | Latv. apse, the Old-Pruss. abse, the Lith. apušẽ | |||
| Atlas | Adula | |||
| Asamus | aśman- ‘stone’, Lit. ašmuo, ašmenys, | |||
| Vairos | Vaira | Lit. vairus ‘diverse’ | ||
| Baktunion | Batkunu kaimas | |||
| Beres | Bẽrė, Bėrẽ, Bėr-upis, Bėrupė | Bēr-upe, Berēka | Lit. bėras, Latv. bęrs ‘brown, swarthy’ | |
| Bersamae | Lith. béržas, the Latv. bẽrzs, Old-Pruss. berse | |||
| Veleka | Velėkas | Lit. velėklės ‘place in the water’ | ||
| Bolba bria | Balvi, Bàlvis, Bolva | Lith. Bálvis 'a lake', the Old-Pruss. Balweniken | ||
| Brenipara | Messapian brendon, Latv. briedis ‘deer’ | |||
| Calsus | Kalsi, Kalsiņš, Kals-Strauts ‘dry stream’ | Latv. kalst, kaltēt ‘dry’ | ||
| Chalastra | Lith. sravà ‘a stream’, the Latv. strava ‘stream, torrent’ | |||
| Daphabae | Lith. dãpas ‘a flood’ , Old-Pruss. ape ‘river’ | |||
| Dingion | Dingas, Dindze, Dingupite | Dinge | Latv. dinga ‘a plant’ and ‘fertile place’ | |
| Dimae | Dūmė | Dūmis | Dumen | Lit. dūmas ‘dark (for beef)’, Latv. dūms ‘dark-brown’ |
| Egerica | Vegerė | Vedzere | ||
| Ereta | Veretà | |||
| Gesia | Gesavà | Dzêsiens | Gesaw | Latv. dzēse ‘heron’ |
| Ginula | Ginuļi | Ginulle | Latv. g'inis, g'inst ‘to spoil’ | |
| Armonia | Armona | Lit. armuo, -ens ‘quagmire’ | ||
| Iuras | Jūra Jūrė, Jūrupis | Lit. and Latv. jūra ‘sea’ | ||
| Kabyle | Kabile | Cabula | ||
| Kallindia | Galindo, Galinden, Galynde | Galindai, Lit. galas ‘end’ | ||
| Kapisturia | Kaplava | Kapas-gals | Kappegalin |
Latv. kãpa, kãpe ‘long mountainous strip, dune, slope’, the Lith. kopà ‘sandy hill’ |
| Kurpisos | Kurpų kámas, Kurpulaukis | Kazūkurpe, Kurpesgrāvis, Kurpkalns | Lit. kurpti ‘to dig' | |
| Kersula | Keršuliškių kaimas | Lit. keršulis ‘pigeon’ | ||
| Knishava | Knisà | Knīsi, Knīši, Knīsukalns | Lith. knìsti ‘to dig, to rummage’ | |
| Kypsela | Kupšeliai | Kupšeļi | ||
| Kourpissos | Kurpų kaimas | Kazu-kurpe | ||
| Lingos | Lingė, Lingenai | Lingas, Lingi, Lingasdikis | Lingwar | Lit. lengė 'valley’ |
| Markellai | Markẽlis, Markelỹne | Marken | Lit. marka ‘pit’, merkti ‘dunk’ | |
| Meldia | Meldė, Meldínis | Meldine, Meldini | Mildio, Mildie | Zhemait. Melьdəikvirshe, Melьdəinəi, Lith. meldà, méldas ‘marsh reed’ , the Latv. meldi ‘reed’ |
| Mygdonia | Mūkė | Mukas | Zhemait. river Muka, Mukja | |
| Ostophos | Uõstas, Ũstas | Uostupe, Ũostup | Lit. pušynas ‘spurs forest’ | |
| Paisula | Paišeliai | Paissyn | Lit. paišai ‘soot’ | |
| Palae | Palà | Lit. palios ‘swamp' | ||
| Palnma | Palminỹs, Palmajos káimas | Paļmuota | Lit. palios ‘swamp' | |
| Panion | Old-Pruss. pannean ‘swamp, quagmire’ | |||
| Pannas | Panyen | Old Pruss. pannean ‘quagmire’, Gothic fani | ||
| Pautalia | Paũtupis | Pauteļi, Pautupīte, Pautustrauts | Pauta, Pauten | Lith. putà, pl. pùtos ‘foam, froth’, putóti ‘to foam’, the Latv. putas ‘foam’ |
| Pizos | Pisa ęzęrs | Pissa, Pissen, Pisse, Pysekaym, Piselauk | Latv. pīsa ‘swamp’ | |
| Praizes Limne | Praustuvė | Lith. praũsti (prausiù, -siaũ) ‘to wash’, prausỹnės ‘washing’, the Latv. prauslât ‘to spray, to sprinkle’ | ||
| Purdae | Purdyakasnis | Porden, Purde | ||
| Pusinon | Pusyne, Pušinė, Pušyno káimasPušinė | Lit. pušynas ‘spurs forest’, Zhemait. Pushina 'a stream', Pushine 'meadows' | ||
| Pupensis vicus(village) | Pupių káimas, Pupinė | Pupa | Pupkaym, Paupayn | Latinized vicus for ‘village', Lit. and Latv. pupa 'beans', kaimas 'village'(cf. Bobov Dol) |
| Purdae | Porden, Purde | Zhemait. Purdjaknisə Popelьki | ||
| Raimula | Raimoche | Lith. ráimas ‘motley, particoloured’ | ||
| Rhakule | Rãkija, Rakavos káimas | Roklawken, Rocke | Lith. ràkti, rankù, rakiaũ ‘to dig out, unearth’, Latv. rakt, rùoku ‘to dig’, rakņât ‘to dig’ | |
| Rhamae | Rãmis, Ramùne | Rāmava | Ramio, Rammenflys | Lit. ramus ‘quiet’ |
| Rhodope Mountains | Rudupe | Zhemait. Rudupja, Rudupə, Rudupi, Lith. rùdas ‘reddish, ruddy, dark yellow’, Lith. ùpė ‘river’ | ||
| Rhusion | Russe, Russien, Rusemoter | Lith. rūsỹs (and rúsas) ‘a pit for potatoes; cellar, basement’, the Latv. rūsa ‘a pit’ | ||
| Rumbodona | Rum̃ba, Rum̃ba, Rum̃b, Rum̃bas, Rumbai | Latv. rum̃ba ‘waterfall, river rapids’, Lith. rum̃bas, rùmbas, rumbà ‘periphery’ | ||
| Sarte | Sar̃tė, Sartà | Sār̃te, Sārtupe | Zhemait. Sarta, Sarti, Lit. sartas ‘red (horse)’, Latv. sarts ‘ruddy’ | |
| Scretisca | Skretiškė | Lit. skretė ‘circle’ | ||
| Seietovia | Sietuvà, Siẽtuvas | Zhemait. Setuva, Lit. sietuva ‘whirlpool’ | ||
| Sekina | Šėkinė | Lith. šėkas ‘recently mowed down grass, hay’, Latv. sêks ‘the same’ | ||
| Serme | Sermas | |||
| Silta | Šiltupis | Siltie, Siltums, Siltine | Lit. šiltas ‘warm, nice’ , Latv. sìlts ‘warm’ | |
| Skaptopara, Skalpenos, Skaplizo | Skalbupis, Skalbýnupis, Skalbstas, Skaptotai, Skaptùtis | Lith. skãplis ‘a type of axe’, Lith. skaptúoti ‘to cut, to carve' | ||
| Skarsa | Skarsin, Skarsaw | Lith. sker̃sas ‘transverse, oblique, slanting’, Sker̃sė, Sker̃s-upỹs, Sker̃sravi | ||
| Scombros | Lith. kumbrỹs, kum̃bris ‘hill, top of a mountain; small mountain’, Latv. kum̃bris ‘hump, hunch’ | |||
| Spindea | Spindžių káimas, Spindžiùs | Spindags | Lit. spindžius, spindis, 'clearing', Latv. spindis ‘spark’ | |
| Stambai | Strũobas, Struõbas | Lit. stramblys ‘cob’, Old-Pruss. strambo ‘stubble-field’ | ||
| Strauneilon | Strūnelė, Strūnà | Lit. sr(i)ūti ‘flow’ | ||
| Strymon | Lit. sraumuo ‘stream’ | |||
| Strauos | Latv. strava, Lit. srava ‘course’ | |||
| Suitula | Svite | Lit. švitulys ‘light’ | ||
| Souras | Sūris, Sūrupė, Sūupis | Sure | Lit. sūras ‘salty’ | |
| Succi | Šukis | Sukas, Sucis | ||
| Tarpodizos | Tárpija | Târpi, Tārpu pļava | Lith. tárpas ‘an interstice’ and ‘a gap, a crack’, Zhemait. Tarpu kalьne, Tarpdovdəi | |
| Tarporon | Lith. tárpas ‘an interstice’ | |||
| Tarpyllos | Terpìnė, Tárpija | |||
| Tirsai | Tirza | Tirskaymen | Lith. tir̃štis ‘density, thickness’ and ‘thicket, brush-wood’ | |
| Tranoupara | Tranỹs | Trani, Tranava | Lit. tranas ‘hornet’ | |
| Trauos | Traũšupis | Lith. traũšti ‘to break, to crumble’, traušus ‘brittle’, Latv. traušs, trausls ‘brittle, fragile’ | ||
| Tynta | Tunti, Tunte | Thuntlawken | Lit. tumtas, tuntas ‘flock' | |
| Urda, Urdaus | Ùrdupis, Urdenà | Urdava | Zhemait. Urdishki, Lit. urdulys ‘mount stream’, virti ‘spring’ | |
| Veleka | Velėkas | Lith. velėkles ‘a place, used for washing’ | ||
| Verzela | Vérža, Véržas | Lith. váržas ‘a basket for fish’, Latv. varza ‘dam’ | ||
| Vevocasenus | Vàive | Woywe, Wewa, Waywe | Latin vicus | |
| Zburulus | Žiburių káimas | Lit. žiburỹs ‘a fire, a light, something burning; a torch’ | ||
| Zilmissus | Žilmà, Žilmas | Latv. zelme ‘green grass or wheat’ | ||
| Zyakozeron | Žvakùtė | Zvakūž | Lith. žvãkė ‘a light, a candle’ |
Fate of the Thracians and their language
According to Skordelis, when Thracians were subjected by Alexander the Great they finally assimilated to Greek culture and became as Greek as Spartans and Athenians, although he considered the Thracian language as a form of Greek.[27] According to Crampton (1997) most Thracians were eventually Hellenized or Romanized, with the last remnants surviving in remote areas until the 5th century.[28] According to Marinov the Thracians were likely completely Romanized and Hellenized after the last contemporary references to them of the 6th century.[29] This theory holds the Christianization of the Roman Empire as the main factor of immediate assimilation.
A quick extinction would intensely contrast the avoidance of Hellenization at least by Albanian till the present, possibly with the help of isolated mountainous areas.
Another author considers that the interior of Thrace have never been Romanized or Hellenized (Trever, 1939).[30] This was followed also by Slavonization. According to Weithmann (1978) when the Slavs migrated, they encountered only a very superficially Romanized Thracian and Dacian population, which had not strongly identified itself with Imperial Rome, while Greek and Roman populations (mostly soldiers, officials, merchants) abandoned the land or were killed.[31] Because Pulpudeva survived as Plovdiv in Slavic languages, not under Philippopolis, some authors suggest that Thracian was not completely obliterated in the 7th century.[32]
See also
References
- Thracian at MultiTree on the Linguist List
- Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin, eds. (2017). "Thracian". Glottolog 3.0. Jena, Germany: Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History.
- Arnold Joseph Toynbee, Some problems of Greek history, Oxford University Press, 1969, p. 56: In the late sixth century there were still Bessian-speaking monks in the monastery at the foot of Mount Sinai (see P. Geyer Itinera Hierosolymitana, Vienna 1898, Templaky, pp. 184; 213.)
- Oliver Nicholson as ed., The Oxford Dictionary of Late Antiquity; Oxford University Press, 2018; ISBN 0192562460, p. 234:...The "Piacenza Pilgrim (56) mentioned Bessian-speaking monks on the Sinai Peninsula. ABA J. J. Wilkes, The Illyrians (1992)...
- J. P. Mallory, Douglas Q. Adams as ed., Encyclopedia of Indo-European Culture; Taylor & Francis, 1997; ISBN 1884964982, p. 576: The most recently attested Thracian personal names are found in two monasteries in the Near East (the Bessi of Mt Sinai) dating to the sixth century AD.
- Bessian is the language of the Bessi, one of the most prominent Thracian tribes. The origin of the monasteries is explained in a mediaeval hagiography written by Symeon the Metaphrast in Vita Sancti Theodosii Coenobiarchae in which he wrote that Saint Theodosius founded on the shore of the Dead Sea a monastery with four churches, in each being spoken a different language, among which Bessian was found. The place at which the monasteries were founded was called "Cutila", which may be a Thracian name.
- Harvey E. Mayer. DACIAN AND THRACIAN AS SOUTHERN BALTOIDIC LITUANUS. LITHUANIAN QUARTERLY JOURNAL OF ARTS AND SCIENCES. Volume 38, No.2 – Summer 1992. Editor of this issue: Antanas Klimas, University of Rochester . ISSN 0024-5089. 1992 LITUANUS Foundation, Inc.
- 1994 Gottfried Schramm: A New Approach to Albanian History
- Encyclopedia of European peoples, Carl Waldman, Catherine Mason, Infobase Publishing, 2006, ISBN 0-8160-4964-5, p. 205.
- Archaeology and language: the puzzle of Indo-European origins, Colin Renfrew, CUP Archive, 1990, ISBN 0-521-38675-6, p. 71.
- Olteanu et al.
- Duridanov, Ivan. "The Language of the Thracians". Retrieved 2007-01-14.
- Duridanov, I. (1976). The Language of the Thracians (An abridged translation of Ezikyt na trakite, Ivan Duridanov, Nauka i izkustvo, Sofia, 1976. (c) Ivan Duridanov).CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Olteanu hypothesizes that the Thracian toponym Basibounon may contain bouno(n), a Greek word for "hill" that may also be a Thracian word
- In Old Church Slavonic is found ehu, which may be a loan from Germanic ; otherwise the Slavic word for horse from ekwo- was lost, due perhaps to the lack of equestrianism among the early Slavs
- Georgiev, Olteanu et al.
- Duridanov, Ivan (1985). Die Sprache der Thraker. Bulgarische Sammlung (in German). 5. Hieronymus Verlag. ISBN 3-88893-031-6.
Ich bin Rolisteneas, Sprößling des Nereneas; Tilezypta, Arazerin nach ihrer Heimat, hat mich der Erde übergeben (d.h. begraben).
- Russu, Ion I. (1969). Die Sprache der Thrako-Daker (in German). Ed. Ştiinţificā.
- Dimitrov, Peter A. (2009). "The Kyolmen Stone Inscription". Thracian Language and Greek and Thracian Epigraphy. Cambridge Scholars Publishing. p. 5. ISBN 978-1-4438-1325-9.
- Written from right to left.
- Written from left to right.
- See C. Brixhe – Ancient languages of Asia Minor, Cambridge University Press, 2008
We will dismiss, at least temporarily, the idea of a Thraco-Phrygian unity. Thraco-Dacian (or Thracian and Daco-Mysian) seems to belong to the eastern (satem) group of Indo-European languages and its (their) phonetic system is far less conservative than that of Phrygian (see Brixhe and Panayotou 1994, §§ 3ff.) - Georgiev 1977, p. 63, 128, 282.
- Duridanov, 1985 & ch. VIII.
- Holst (2009):66.
- (Duridanov 1978: с. 128)
- Daskalov, Roumen; Vezenkov, Alexander. Entangled Histories of the Balkans – Volume Three: Shared Pasts, Disputed Legacies. BRILL. p. 51. ISBN 9789004290365.
- R.J. Crampton (1997). A Concise History of Bulgaria. Cambridge University Press. p. 4. ISBN 0-521-56719-X.
- Daskalov, Roumen; Vezenkov, Alexander. Entangled Histories of the Balkans – Volume Three: Shared Pasts, Disputed Legacies. BRILL. p. 10. ISBN 9789004290365.
- Trever, Albert Augustus. History of Ancient Civilization. Harcourt, Brace. p. 571
- Michael W. Weithmann, Die slawische Bevolkerung auf der griechischen Halbinsel (Munich 1978)
- Mallory, J. P.; Adams, Douglas Q. Encyclopedia of Indo-European Culture. Taylor & Francis. p. 576. ISBN 978-1-884964-98-5.
Further reading
- V.I. Georgiev, Introduction to the History of the Indo-European Languages, Sofia (1981).
- V.I. Georgiev, The Genesis of the Balkan Peoples, in: The Slavonic and East European Review, Vol. 44, No. 103 (Jul., 1966)
- I.I. Russu, Limba Traco-Dacilor / Die Sprache der Thrako-Daker, Bucharest (1967, 1969).
- Paul Kretschmer, "Glotta", in: Zeitschrift für griechische und lateinische Sprache 7 (1915).
- J.H. Holst, "Armenische Studien", Wiesbaden (2009).
- Alexianu Marius-Tiberius. Une catégorie d'esclaves thraces : les halônetoi. In: La fin du statut servile ? Affranchissement, libération, abolition. Volume II. Besançon 15-17 décembre 2005. Besançon : Presses Universitaires de Franche-Comté, 2008. pp. 487-492. (Actes des colloques du Groupe de recherche sur l'esclavage dans l'antiquité, 30-2) [www.persee.fr/doc/girea_0000-0000_2008_act_30_2_1057]
- Witczak, Krzysztof Tomasz. "Studies in Thracian vocabulary (I-VII)". In: Studia Indogermanica Lodziensia VII (2012). pp. 153-168.
- Vladimir E. Orel. "The Inscription from Kjolmen." Mediterranean Language Review 9 (1997): 77-82. www.jstor.org/stable/10.13173/medilangrevi.9.1997.0077.
External links
- The Language of the Thracians, an English translation of Ivan Duridanov's 1975 essay Ezikyt na trakite
- Sorin Olteanu's Thraco-Daco-Moesian Languages Project (SoLTDM) (sources, thesaurus, textual criticism, phonetics and morphology, substratum, historical geography a.o.)
- Thracian glossary
- Palaeolexicon – Word study tool of ancient languages (including Thracian dictionary)