Soyuz-T
The Soyuz-T (Russian: Союз-T, Union-T) spacecraft was the third generation Soyuz spacecraft, in service for seven years from 1979 to 1986. The T stood for transport (транспортный, Transportny). The revised spacecraft incorporated lessons learned from the Apollo Soyuz Test Project, Soyuz 7K-TM and Military Soyuz.
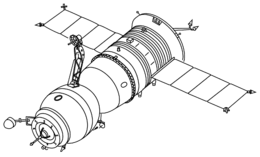 Soyuz-T spacecraft | |
| Manufacturer | Korolev |
|---|---|
| Country of origin | USSR |
| Operator | Soviet space program |
| Applications | Carry three cosmonauts to Salyut and Mir space stations and back |
| Specifications | |
| Regime | Low Earth orbit |
| Production | |
| Status | Out of service |
| Launched | 16 |
| Maiden launch | Soyuz T-1, 1979 |
| Last launch | Soyuz T-15, 1986 |
| Related spacecraft | |
| Derived from | Soyuz 7K-TM (Soyuz 7K-T) |
| Derivatives | Soyuz-TM |
The Soyuz-T was a major upgrade over previous Soyuz spacecraft, sporting solid-state electronics for the first time and a much more advanced onboard computer to help overcome the chronic docking problems that affected cosmonauts during space station missions. In addition, solar panels returned, allowing the Soyuz-T to fly up to 11 days independently as well as a redesigned propulsion system, the KTDU-426. Finally, it could at last carry three cosmonauts with pressure suits.
Missions
- Soyuz T-1 (uncrewed test, launched 1979)
- Soyuz T-2
- Soyuz T-3
- Soyuz T-4
- Soyuz T-5
- Soyuz T-6
- Soyuz T-7
- Soyuz T-8
- Soyuz T-9
- Soyuz T-10-1
- Soyuz T-10
- Soyuz T-11
- Soyuz T-12
- Soyuz T-13
- Soyuz T-14
- Soyuz T-15 (launched 1986)
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Soyuz spacecraft. |
- Russia New Russian spaceship will be able to fly to Moon - space corp
- RSC Energia: Concept Of Russian Manned Space Navigation Development
- Mir Hardware Heritage
- David S.F. Portree, Mir Hardware Heritage, NASA RP-1357, 1995
- Mir Hardware Heritage (wikisource)
- Information on Soyuz spacecraft
- OMWorld's ASTP Docking Trainer Page
- NASA - Russian Soyuz TMA Spacecraft Details
- Space Adventures circum-lunar mission - details
